Related Research Articles

John Rackham, commonly known as Calico Jack, was an English pirate captain operating in the Bahamas and in Cuba during the early 18th century. His nickname was derived from the calico clothing that he wore, while Jack is a nickname for "John".
Robert Culliford was a pirate from Cornwall who is best remembered for repeatedly checking the designs of Captain William Kidd.

Edward England was an Irish pirate. The ships he sailed on included the Pearl and later the Fancy, for which England exchanged the Pearl in 1720. His flag was the classic Jolly Roger — almost exactly as the one "Black Sam" Bellamy used — with a human skull above two crossed bones on a black background. Like Bellamy, England was known for his kindness and compassion as a leader, unlike many other pirates of the time.

Henry Every, also known as Henry Avery, sometimes erroneously given as Jack Avery or John Avery, was an English pirate who operated in the Atlantic and Indian oceans in the mid-1690s. He probably used several aliases throughout his career, including Benjamin Bridgeman, and was known as Long Ben to his crewmen and associates.
Henry Jennings was an English privateer-turned-pirate. Jennings's first recorded act of piracy took place in early 1716 when, with three vessels and 150–300 men, Jennings's fleet ambushed the Spanish salvage camp from the 1715 Treasure Fleet. After the Florida raid, Jennings and his crew also linked up with Benjamin Hornigold's "three sets of pirates" from New Providence Island.
The Pirate Round was a sailing route followed by certain, mainly English, pirates, during the late 17th century and early 18th century. The course led from the western Atlantic, parallel to the Cape Route around the southern tip of Africa, stopping at Madagascar, then on to targets such as the coast of Yemen and India. The Pirate Round was briefly used again during the early 1720s. Pirates who followed the route are sometimes referred to as Roundsmen. The Pirate Round was largely co-extensive with the routes of the East India Company ships, of Britain and other nations.

John Bowen was a pirate of Créole origin active during the Golden Age of Piracy. He sailed with other famous contemporaries, including Nathaniel North and George Booth, who was his captain when he was a crewman aboard the Speaker. Over a four-year period, Bowen took about £170,000 in goods and coinage and retired to Bourbon for a brief period of time before his death in 1704.
See also 1703 in piracy, other events in 1704, 1705 in piracy, and Timeline of piracy.

John Quelch was an English pirate who had a lucrative but very brief career of about one year. His chief claim to historical significance is that he was the first person to be tried for piracy outside England under Admiralty Law and thus without a jury. These Admiralty courts had been instituted to tackle the rise of piracy in colonial ports where civil and criminal courts had proved ineffective.

Nathaniel North was a pirate during the Golden Age of Piracy, operating in the Indian Ocean under John Bowen and then as captain of the Defiant following Bowen's retirement in 1704. After losing the Defiant he ruled a pirate colony at Ambonaivo made up of his former crew before returning to sea. North reportedly retired with great wealth in 1709, settling in Madagascar and marrying a local woman, but was later murdered by her family.

Thomas Howard was a pirate primarily active in the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea during the Golden Age of Piracy. He served under other pirates of the time, including George Booth and John Bowen. He also commanded the 36-gun Prosperous. He later retired to Rajapur, in India, where he married a local woman. He was later murdered by her relatives.
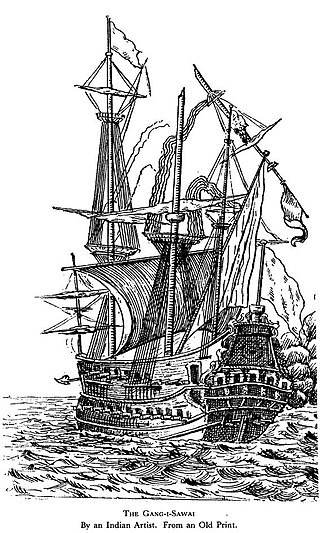
The Ganj-i-Sawai was an armed Ghanjah dhow belonging to the Mughals. During Aurangzeb's reign, it was captured on 7 September 1695 by the English pirate Henry Avery en route from present-day Mocha, Yemen to Surat, India. It was built on the order of Empress Mariam-uz-Zamani, great grandmother of Aurengzeb, after the capture of her ship named Rahimi.

The Atlantic World refers to the period between European colonization of the Americas (1492-) and the early nineteenth century. Piracy became prevalent in this era because of the difficulty of policing this vast area, the limited state control over many parts of the coast, and the competition between different European powers. The best known pirates of this era are the Golden Age Pirates who roamed the seas off the coasts of North America, Africa, and the Caribbean.
Robert Colley was an English pirate and privateer active near Newfoundland and the Indian Ocean.
George Raynor (1665–1743) was a pirate and privateer active in the Red Sea. As a pirate he captained the Batchelor’s Delight .
Thomas White was an English pirate active in the Caribbean and the Indian Ocean. He was only briefly a captain on his own, but served under several more prominent captains such as George Booth, John Bowen, Thomas Howard, John Halsey, and Nathaniel North.
Thomas Larimore was a privateer and pirate active in the Caribbean and off the eastern seaboard of the American colonies. After helping suppress Bacon’s Rebellion and serving as a militia leader he turned to piracy, his activities intertwined with those of fellow pirate John Quelch.
John Cole was a pirate active off the American eastern seaboard. His brief career is associated with Richard Worley and William Moody. He is known more for the unusual cargo of his pirate ship than for his piracy.
Paulsgrave Williams, first name occasionally Paul, Palsgrave, or Palgrave, was a pirate who was active 1716–1723 and sailed in the Caribbean, American eastern seaboard, and off West Africa. He is best known for sailing alongside Samuel Bellamy.
John Pro was a Dutch pirate best known for leading a pirate trading post near Madagascar.
References
- ↑ Hearn, Daniel Allen (13 August 2015). Legal Executions in New England A Comprehensive Reference, 1623-1960. McFarland Incorporated, Publishers. pp. 107–108. ISBN 9781476608532.