Related Research Articles

Boers are the descendants of the proto Afrikaans-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled Dutch Cape Colony, but the United Kingdom incorporated it into the British Empire in 1806. The name of the group is derived from Trekboer then later "boer", which means "farmer" in Dutch and Afrikaans.

The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of Canada's population. Together with Canada's easternmost province, Newfoundland and Labrador, the Maritime provinces make up the region of Atlantic Canada.
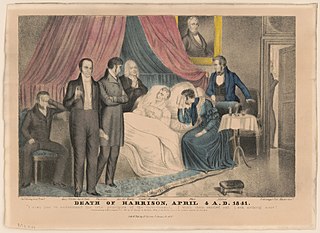
1841 (MDCCCXLI) was a common year starting on Friday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar, the 1841st year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 841st year of the 2nd millennium, the 41st year of the 19th century, and the 2nd year of the 1840s decade. As of the start of 1841, the Gregorian calendar was 12 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the start of the war, the French colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on their native allies.

The first modern humans are believed to have inhabited South Africa more than 100,000 years ago. In 1999, UNESCO designated the region the Cradle of Humankind World Heritage site. South Africa's first known inhabitants have been referred to as the Khoisan, the Khwe and the San. Starting in about 1,000 BCE, these groups were then joined by the Bantu tribes who migrated from Western and Central Africa during what is known as the Bantu expansion.

The first written records of the region come from Arab traders in the 9th and 10th centuries. In medieval times, the region was dominated by the Trans-Saharan trade and was ruled by the Mali Empire. In the 16th century, the region came to be ruled by the Songhai Empire. The first Europeans to visit the Gambia River were the Portuguese in the 15th century, in 1447, who attempted to settle on the river banks, but no settlement of significant size was established. Descendants of the Portuguese settlers remained until the 18th century. In the late 16th century, English merchants attempted to begin a trade with the Gambia, reporting that it was "a river of secret trade and riches concealed by the Portuguese."

Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In the United States, it is regarded as a standalone conflict under this name. Elsewhere it is usually viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession. It is also known as the Third Indian War. In France it was known as the Second Intercolonial War.
The history of Florida can be traced to when the first Paleo-Indians began to inhabit the peninsula as early as 14,000 years ago. They left behind artifacts and archeological evidence. Florida's written history begins with the arrival of Europeans; the Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León in 1513 made the first textual records. The state received its name from that conquistador, who called the peninsula La Pascua Florida in recognition of the verdant landscape and because it was the Easter season, which the Spaniards called Pascua Florida.
The following lists events that happened during the 1790s in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during the 1780s in South Africa.

Albany, South Africa was a district in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Grahamstown was traditionally the administrative capital, cultural centre and largest town of the Albany district.

The geography of North Africa has been reasonably well known among Europeans since classical antiquity in Greco-Roman geography. Northwest Africa was known as either Libya or Africa, while Egypt was considered part of Asia.

Pieter Mauritz Retief was a Voortrekker leader. Settling in 1814 in the frontier region of the Cape Colony, he later assumed command of punitive expeditions during the sixth Xhosa War. He became a spokesperson for the frontier farmers who voiced their discontent, and wrote the Voortrekkers' declaration at their departure from the colony.

The Xhosa Wars were a series of nine wars between the Xhosa Kingdom and the British Empire as well as Trekboers in what is now the Eastern Cape in South Africa. These events were the longest-running military resistance against European colonialism in Africa.
The history of Pensacola, Florida, begins long before the Spanish claimed founding of the modern city in 1698. The area around present-day Pensacola was inhabited by Native American peoples thousands of years before the historical era.
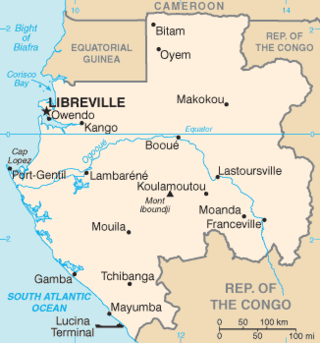
Cape Lopez is a headland on the coast of Gabon, west central Africa. The westernmost point of Gabon, it separates the Gulf of Guinea from the South Atlantic Ocean. Cape Lopez is the northernmost point of a low, wooded island between two mouths of the Ogooué River. There is an oil terminal at the southeast side of the cape, and the seaport of Port-Gentil lies about 10 km southeast of the cape. A lighthouse has existed on the Cape since 1897; the current tower was built in 1911, but has been inactive for many years and is in danger of collapsing from erosion.

Robert Jacob Gordon was a Dutch explorer, soldier, artist, naturalist and linguist of Scottish descent.

Cookhouse is a small village located in Eastern Cape province, South Africa, some 170 kilometres (110 mi) north of Port Elizabeth and 24 kilometres (15 mi) east of Somerset East, on the west bank of the Great Fish River.

The Dutch Cape Colony was a Dutch United East India Company (VOC) colony in Southern Africa, centered on the Cape of Good Hope, from where it derived its name. The original colony and the successive states that the colony was incorporated into occupied much of modern South Africa. Between 1652 and 1691, it was a Commandment, and between 1691 and 1795, a Governorate of the VOC. Jan van Riebeeck established the colony as a re-supply and layover port for vessels of the VOC trading with Asia. The Cape came under VOC rule from 1652 to 1795 and from 1803 to 1806 was ruled by the Batavian Republic. Much to the dismay of the shareholders of the VOC, who focused primarily on making profits from the Asian trade, the colony rapidly expanded into a settler colony in the years after its founding.

Nova Scotia is a Canadian province located in Canada's Maritimes. The region was initially occupied by Mi'kmaq. The colonial history of Nova Scotia includes the present-day Maritime Provinces and the northern part of Maine, all of which were at one time part of Nova Scotia. In 1763, Cape Breton Island and St. John's Island became part of Nova Scotia. In 1769, St. John's Island became a separate colony. Nova Scotia included present-day New Brunswick until that province was established in 1784. During the first 150 years of European settlement, the colony was primarily made up of Catholic Acadians, Maliseet, and Mi'kmaq. During the last 75 years of this time period, there were six colonial wars that took place in Nova Scotia. After agreeing to several peace treaties, the long period of warfare ended with the Halifax Treaties (1761) and two years later, when the British defeated the French in North America (1763). During those wars, the Acadians, Mi'kmaq and Maliseet from the region fought to protect the border of Acadia from New England. They fought the war on two fronts: the southern border of Acadia, which New France defined as the Kennebec River in southern Maine, and in Nova Scotia, which involved preventing New Englanders from taking the capital of Acadia, Port Royal and establishing themselves at Canso.
References
See Years in South Africa for list of References