| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 5 New Jersey seats to the United States House of Representatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Elections to the United States House of Representatives in New Jersey for the 6th Congress were held October 10, 1798.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 5 New Jersey seats to the United States House of Representatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Elections to the United States House of Representatives in New Jersey for the 6th Congress were held October 10, 1798.
All previous elections had been held on an at-large basis. Five Federalists had been elected in the previous election. For this election, New Jersey switched, for the first time, to using districts.
Three incumbents ran for re-election, of whom, two of whom lost to Democratic-Republicans. The incumbents Jonathan Dayton (F) and Thomas Sinnickson (F) did not run for re-election. In the districts with no incumbents, one was won by a Democratic-Republican and the other by a Federalist, for a net gain of 3 seats by the Democratic-Republicans
| District | Democratic-Republican | Federalist | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern [1] | John Condit | 3,378 | 52.5% | James Schureman (I) | 3,054 | 47.5% |
| Northern [2] | Aaron Kitchell | 3,399 | 72.5% | Mark Thomson (I) | 1,287 | 27.5% |
| Western [3] | James Linn | 1,613 | 51.3% | Samuel R. Stewart | 979 | 31.1% |
| Archibald Mercer | 554 | 17.6% | ||||
| Middle [4] | Thomas Henderson | 379 | 19.0% | James H. Imlay (I) | 1,614 | 81.0% |
| Southern [5] | Jonathan Elmer | 1,266 | 43.5% | Franklin Davenport | 1,644 | 56.5% |
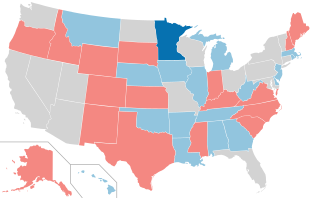
The 1990 United States Senate elections were held on Tuesday, November 6, 1990, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. The Democratic Party increased its majority with a net gain of one seat from the Republican Party. The election cycle took place in the middle of President George H. W. Bush's term, and as with most other midterm elections, the party not holding the presidency gained seats in Congress. This was the first time since 1980 that any party successfully defended all their own seats, and the first time Democrats did so since 1958.

The 1978 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, in the middle of Democratic President Jimmy Carter's term. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies.

The 1964 United States Senate elections were held on November 3. The 33 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. They coincided with the election of President Lyndon B. Johnson by an overwhelming majority, to a full term. His Democratic Party picked up a net two seats from the Republicans. As of 2023, this was the last time either party has had a two-thirds majority in the Senate, which allowed the Senate Democrats to override a veto, propose constitutional amendments, or convict and expel certain officials without any votes from Senate Republicans. However, internal divisions would have prevented the Democrats from having done so. The Senate election cycle coincided with Democratic gains in the House in the same year.

The 1998 United States House of Representatives elections were held on November 3, 1998, to elect U.S. Representatives to serve in the 106th United States Congress. They were part of the midterm elections held during President Bill Clinton's second term. They were a major disappointment for the Republicans, who were expecting to gain seats due to the embarrassment Clinton suffered during the Monica Lewinsky scandal and the "six-year itch" effect observed in most second-term midterm elections. However, the Republicans lost five seats to the Democrats, although they retained a narrow majority in the House. A wave of Republican discontent with Speaker Newt Gingrich prompted him to resign shortly after the election; he was replaced by Congressman Dennis Hastert of Illinois.

The 1932 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 73rd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 8, 1932, while Maine held theirs on September 12. They coincided with the landslide election of President Franklin D. Roosevelt.

The 1824–25 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 7, 1824, and August 30, 1825. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 19th United States Congress convened on December 5, 1825. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.

The 1812–13 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 3, 1812, and April 30, 1813. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 13th United States Congress convened on May 24, 1813. They coincided with James Madison being re-elected president.

The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1800, and August 1, 1801. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 7th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1801. They were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist. Elections were held for all 106 seats, representing 15 states.

The 1798–99 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1798 in New York and August 1, 1799 in Tennessee. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, with some after the official start of the 6th United States Congress on March 4, 1799, but before the start of the first session of this Congress in Philadelphia on December 2, 1799. These elections were held during President John Adams term. It was the last congressional session before the move to the new capital at Washington, D.C. Elections were held for all 106 seats, representing 16 states.
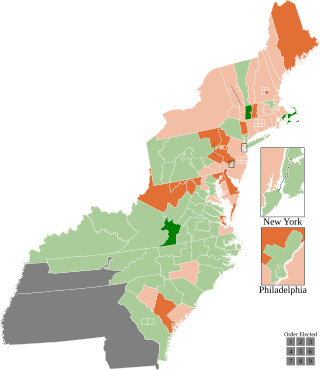
The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

The 1800 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 29 to May 1, 1800, to elect ten U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 7th United States Congress.

The 1806 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 29 to May 1, 1806, to elect 17 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 10th United States Congress.

The 1808 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 26 to 28, 1808, to elect 17 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 11th United States Congress. At the same time, a vacancy was filled in the 10th United States Congress.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives were held in Pennsylvania on October 14, 1806, for the 10th Congress.

Elections to the House of Representatives were held in Pennsylvania on October 14, 1794, for the Fourth Congress.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives were held in Pennsylvania on October 13, 1812, for the 13th Congress.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives were held in Pennsylvania on October 14, 1800, for the 7th Congress.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives were held in Pennsylvania on October 9, 1798, for the 6th Congress.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives were held in Pennsylvania on October 11, 1796, for the 5th Congress.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives were held in Pennsylvania on October 11, 1808, for the 11th Congress.