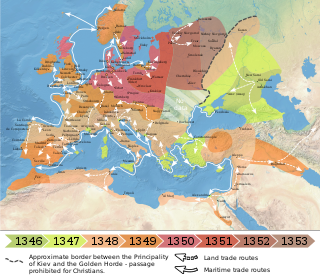
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as 50 million people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. The disease is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis and spread by fleas and through the air. One of the most significant events in European history, the Black Death had far-reaching population, economic, and cultural impacts. It was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. The plague created religious, social and economic upheavals, with profound effects on the course of European history.

Plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Symptoms include fever, weakness and headache. Usually this begins one to seven days after exposure. There are three forms of plague, each affecting a different part of the body and causing associated symptoms. Pneumonic plague infects the lungs, causing shortness of breath, coughing and chest pain; bubonic plague affects the lymph nodes, making them swell; and septicemic plague infects the blood and can cause tissues to turn black and die.

Henry Tifft Gage was an American lawyer, politician and diplomat. A Republican, Gage was elected to a single term as the 20th governor of California from 1899 to 1903. Gage was also the U.S. Minister to Portugal for several months in 1910.

Oswaldo Gonçalves Cruz, was a Brazilian physician, pioneer bacteriologist, epidemiologist and public health officer and the founder of the Oswaldo Cruz Institute.

The third plague pandemic was a major bubonic plague pandemic that began in Yunnan, China, in 1855. This episode of bubonic plague spread to all inhabited continents, and ultimately led to more than 12 million deaths in India and China, and at least 10 million Indians were killed in British Raj India alone, making it one of the deadliest pandemics in history. According to the World Health Organization, the pandemic was considered active until 1960, when worldwide casualties dropped to 200 per year. Plague deaths have continued at a lower level for every year since.

Adolfo Lutz was a Brazilian physician, father of tropical medicine and medical zoology in Brazil, and a pioneer epidemiologist and researcher in infectious diseases.

The Great Plague of Marseille, also known as the Plague of Provence, was the last major outbreak of bubonic plague in Western Europe. Arriving in Marseille, France, in 1720, the disease killed over 100,000 people: 50,000 in the city during the next two years and another 50,000 to the north in surrounding provinces and towns.

The Bombay plague epidemic was a bubonic plague epidemic that struck the city of Bombay in the late nineteenth century. The plague killed thousands, and many fled the city, leading to a drastic fall in the population of the city. In September 1896, Bombay's municipal administration declared the presence of bubonic plague in the city. The administration of ineffective protocols furthered the spread. By January 1897, half the population fled to the countryside.
John Ashburton Thompson was a British-Australian physician and an international authority on plague and leprosy.

Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well as swollen and painful lymph nodes occurring in the area closest to where the bacteria entered the skin. Acral necrosis, the dark discoloration of skin, is another symptom. Occasionally, swollen lymph nodes, known as "buboes", may break open.

The fifth cholera pandemic (1881–1896) was the fifth major international outbreak of cholera in the 19th century. The endemic origin of the pandemic, as had its predecessors, was in the Ganges Delta in West Bengal. While the Vibrio cholerae bacteria had not been able to spread to western Europe until the 19th century, faster and improved modes of modern transportation, such as steamships and railways, reduced the duration of the journey considerably and facilitated the transmission of cholera and other infectious diseases. During the fourth 1863–1875 cholera pandemic, the third International Sanitary Conference convened in 1866 in Constantinople had identified religious pilgrimages to be "the most powerful of all causes" of cholera and again Hindu and Muslim pilgrimages were an important factor in the spread of the disease.

Baron Kitasato Shibasaburō was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist. He is remembered as the co-discoverer of the infectious agent of bubonic plague in Hong Kong during an outbreak in 1894, almost simultaneously with Alexandre Yersin.
The 1994 plague in India was an outbreak of bubonic and pneumonic plague in south-central and western India from 26 August to 18 October 1994. 693 suspected cases and 56 deaths were reported from the five affected Indian states as well as the Union Territory of Delhi. These cases were from Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and New Delhi. There are no reports of cases being exported to other countries.

Joseph James Kinyoun was an American physician and the founder of the United States' Hygienic Laboratory, the predecessor of the National Institutes of Health.

The San Francisco plague of 1900–1904 was an epidemic of bubonic plague centered on San Francisco's Chinatown. It was the first plague epidemic in the continental United States. The epidemic was recognized by medical authorities in March 1900, but its existence was denied for more than two years by California's Republican governor Henry Gage. His denial was based on business reasons, to protect the reputations of San Francisco and California and to prevent the loss of revenue due to quarantine. The failure to act quickly may have allowed the disease to establish itself among local animal populations. Federal authorities worked to prove that there was a major health problem, and they isolated the affected area; this undermined Gage's credibility, and he lost the governorship in the 1902 elections. The new governor, George Pardee, implemented public-health measures and the epidemic was stopped in 1904. There were 121 cases identified, resulting in 119 deaths.

The 1924 Los Angeles pneumonic plague outbreak was an outbreak of the pneumonic plague in Los Angeles, California that began on September 28, 1924, and was declared fully contained on November 13, 1924. It represented the first time that the plague had emerged in Southern California since plague outbreaks had previously surfaced in San Francisco and Oakland. The suspected reason for this outbreak was a rat epizootic where squirrels that were found to be plague infected were secondarily infected by rats. Due to the evidence of infected squirrels near San Luis Obispo County as late as July 1924 and the migration habits of both squirrels and rats, it is thought that squirrels were the original source of the plague outbreak in Los Angeles.
Globally about 600 cases of plague are reported a year. In 2017 and November 2019 the countries with the most cases include the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Madagascar, and Peru.
The Directorate-General of Health is a division of the Portuguese public administration concerned with public health. Even though it is statutorily a service of the Ministry of Health, it is a public agency with administrative autonomy. It was created in 1899, after a plague outbreak in Porto, in order to coordinate efforts and planning against future disease outbreaks and epidemics.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Portugal was a part of the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. On 2 March 2020, the virus was confirmed to have reached the country when it was reported that two men, a 60-year-old doctor who travelled to the north of Italy on vacation and a 33-year-old man working in Spain, tested positive for COVID-19. On 16 March 2020, the first death from COVID-19 was reported in Portugal.














