Electoral systems of the Australian states and territories are broadly similar to the electoral system used in federal elections in Australia.
This is a list of the members of the Australian House of Representatives in the First Australian Parliament, which was elected on 29 and 30 March 1901. There were 75 members, as required by the Constitution, as near as possible to twice the number of Senators which was then 36. South Australia and Tasmania had not been divided into electoral divisions in 1901 which resulted in the particular state voting as a single electorate. There were seven members for South Australia, and five members for Tasmania elected.
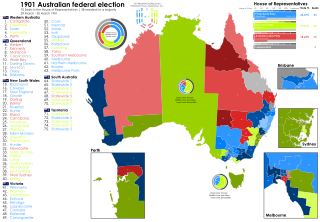
The 1901 Australian federal election for the inaugural Parliament of Australia was held in Australia on Friday 29 March and Saturday 30 March 1901. The elections followed Federation and the establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia on 1 January 1901. All 75 seats in the Australian House of Representatives, six of which were uncontested, as well as all 36 seats in the Australian Senate, were up for election.

The Court of Disputed Returns in Australia is a special jurisdiction of the High Court of Australia. The High Court, sitting as the Court of Disputed Returns, hears challenges regarding the validity of federal elections. The jurisdiction is twofold: (1) on a petition to the Court by an individual with a relevant interest or by the Australian Electoral Commission, or (2) on a reference by either house of the Commonwealth Parliament. This jurisdiction was initially established by Part XVI of the Commonwealth Electoral Act 1902 and is now contained in Part XXII of the Commonwealth Electoral Act 1918. Challenges regarding the validity of State elections are heard by the Supreme Court of that State as the State's Court of Disputed Returns.

George Mason Burns was an Australian politician. He was an Australian Labor Party member of the Australian House of Representatives from 1913 to 1917, representing the electorate of Illawarra. He had previously been a member of the Tasmanian House of Assembly from 1903 to 1906.

William Hartnoll was an Australian politician. Born in Longford, Van Diemen's Land, he was educated at Launceston Grammar School before becoming a shopkeeper, auctioneer and landowner. In 1884 he was elected to the Tasmanian House of Assembly as the member for South Launceston, transferring to Launceston in 1897. He was Minister for Lands and Works from 1892 to 1894. In 1901, Hartnoll contested the first federal election as a Free Trade candidate for the five-member Division of Tasmania, but was unsuccessful. However, in 1902, he was elected to the Australian House of Representatives in a by-election for Tasmania resulting from the death of sitting Free Trade MP Frederick Piesse. Hartnoll was successful, although there was a legal challenge to his election because he had nominated for candidacy via telegram and not by submitting a signed nomination form. In 1903, following the division of Tasmania into individual electorates, he contested the seat of Bass, but was defeated by the Protectionist candidate David Storrer. He died in 1932.

David Storrer was an Australian politician.
This article provides information on candidates who stood for the 1903 Australian federal election. The election was held on 16 December 1903.

Herbert James Mockford Payne was an Australian politician. He served as a Senator for Tasmania from 1920 to 1938 and as a member of the Tasmanian House of Assembly from 1903 to 1920.
This is a list of members of the Tasmanian House of Assembly between the 1900 election and the 1903 election.

The 2010 Tasmanian state election was held on 20 March 2010 to elect members to the Tasmanian House of Assembly. The 12-year incumbent Labor government, led by Premier of Tasmania David Bartlett, won a fourth consecutive term against the Liberal opposition, led by Will Hodgman, after Labor formed a minority government with the support of the Greens.
A by-election was held for the Australian House of Representatives seat of Wilmot in Tasmania on 26 February 1904. This was triggered by the death of former Premier of Tasmania and federal Free Trade Party MP Sir Edward Braddon on 2 February 1904.
James Joseph Gaffney was an Australian politician. He was a member of the Tasmanian House of Assembly from 1899 to 1903, representing the electorate of Lyell.

The 2018 Tasmanian state election was held on 3 March 2018 to elect all 25 members of the Tasmanian House of Assembly.

The Jacqui Lambie Network (JLN) is a political party in Australia, formed in May 2015. Bearing the name of its founder, Tasmanian senator Jacqui Lambie, it has served as the political vehicle for the former independent.

Blundell v Vardon, was the first of three decisions of the High Court of Australia concerning the 1906 election for senators for South Australia. Sitting as the Court of Disputed Returns, Barton J held that the election of Anti-Socialist Party candidate Joseph Vardon as the third senator for South Australia was void due to irregularities in the way the returning officers marked some votes. The Parliament of South Australia appointed James O'Loghlin. Vardon sought to have the High Court compel the governor of South Australia to hold a supplementary election, however the High Court held in R v Governor of South Australia; Ex parte Vardon that it had no power to do so. Vardon then petitioned the Senate seeking to remove O'Loghlin and rather than decide the issue, the Senate referred the matter to the High Court. The High Court held in Vardon v O'Loghlin that O'Loghlin had been invalidly appointed and ordered a supplementary election. Vardon and O'Loghlin both contested the supplementary election, with Vardon winning with 54% of the vote.

Chanter v Blackwood and the related case of Maloney v McEacharn were a series of decisions of the High Court of Australia, sitting as the Court of Disputed Returns arising from the 1903 federal election for the seats of Riverina and Melbourne in the House of Representatives. Chanter v Blackwood , and Maloney v McEacharn , determined questions of law as to the validity of certain votes. In Chanter v Blackwood Griffith CJ held that 91 votes were invalid and because this exceeded the majority, the election was void, while Chanter v Blackwood dealt with questions of costs. In Maloney v McEacharn more than 300 votes were found to be invalid and the parties agreed it was appropriate for the election to be declared void.
William Aikenhead was an Australian politician, who was a member of the Tasmanian House of Assembly from 1898 until his death in office in 1902.

The Tasmanian Nationals are a political party in the Australian state of Tasmania, aligned with the National Party of Australia. The party is not currently registered with the Tasmanian Electoral Commission, and is not separately registered with the Australian Electoral Commission, unlike the other state branches of the Nationals.
The Tasmanian Labor Party, officially known as the Australian Labor Party (Tasmanian Branch) and commonly referred to simply as Tasmanian Labor, is the Tasmanian branch of the Australian Labor Party. It has been one of the most successful state Labor parties in Australia in terms of electoral success.









