
The House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Australia, the upper house being the Senate. Its composition and powers are set down in Chapter I of the Constitution of Australia.
The Protectionist Party, also known as the Protectionist Liberal Party or Liberal Protectionist Party, was an Australian political party, formally organised from 1887 until 1909, with policies centred on protectionism. The party advocated protective tariffs, arguing it would allow Australian industry to grow and provide employment. It had its greatest strength in Victoria and in the rural areas of New South Wales. Its most prominent leaders were Sir Edmund Barton and Alfred Deakin, who were the first and second prime ministers of Australia.
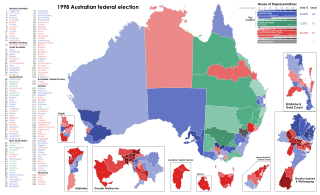
The 1998 Australian federal election was held to determine the members of the 39th Parliament of Australia. It was held on 3 October 1998. All 148 seats of the House of Representatives and 40 seats of the 76 seat Senate were up for election. The incumbent centre-right Liberal/National Coalition government led by Prime Minister John Howard of the Liberal Party and coalition partner Tim Fischer of the National Party defeated the centre-left Australian Labor Party opposition led by Opposition Leader Kim Beazley, despite losing the nationwide popular and two-party preferred vote. However, the Australian Labor Party gained seats compared to the previous election.
The Liberal Party was a parliamentary party in Australian federal politics between 1909 and 1917. The party was founded under Alfred Deakin's leadership as a merger of the Protectionist Party and Anti-Socialist Party, an event known as the Fusion.
Elections in Australia take place periodically to elect the legislature of the Commonwealth of Australia, as well as for each Australian state and territory and for local government councils. Elections in all jurisdictions follow similar principles, although there are minor variations between them. The elections for the Australian Parliament are held under the federal electoral system, which is uniform throughout the country, and the elections for state and territory Parliaments are held under the electoral system of each state and territory. An election day is always a Saturday, but early voting is allowed in the lead-up to it.
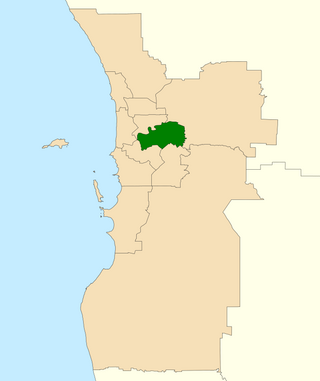
The Division of Swan is an Australian electoral division located in Western Australia.

John Verran was an Australian politician and trade unionist. He served as premier of South Australia from 1910 to 1912, the second member of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) to hold the position.

The 1943 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 21 August 1943. All 74 seats in the House of Representatives and 19 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Labor Party, led by Prime Minister John Curtin, defeated the opposition Country–UAP coalition led by Arthur Fadden in a landslide. The Labor party TPP result of 58.2% is its highest, in its history.

The 1934 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 15 September 1934. All 74 seats in the House of Representatives, and 18 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent United Australia Party led by Prime Minister of Australia Joseph Lyons formed a minority government, with 33 out of 74 seats in the House.

The 1919 Australian federal election was held on 13 December 1919 to elect members to the Parliament of Australia. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives and 19 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Nationalist Party government won re-election, with Prime Minister Billy Hughes continuing in office.

The 1917 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 5 May 1917. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives and 18 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Nationalist Party, led by Prime Minister Billy Hughes, defeated the opposition Labor Party led by Frank Tudor in a landslide.

The 1914 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 5 September 1914. The election had been called before the declaration of war in August 1914. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives and all 36 seats in the Senate were up for election, as a result of the first double dissolution being granted. The incumbent Liberal Party, led by Prime Minister Joseph Cook, was defeated by the opposition Labor Party under Andrew Fisher, who returned for a third term as prime minister.

The 1913 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 31 May 1913. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives, and 18 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Labor Party, led by Prime Minister Andrew Fisher, was defeated by the opposition Commonwealth Liberal Party under Joseph Cook, marking the second time an Australian Prime Minister was defeated at an election. The new government had a majority of just a single seat, and held a minority of seats in the Senate. It would last only 15 months, suffering defeat at the 1914 election.
The 1918 Swan by-election was a by-election for the Division of Swan in the Australian House of Representatives, following the death of the sitting member Sir John Forrest. Held on 26 October 1918, the by-election led to the election of the youngest person to be elected until 2010 to the Parliament of Australia, Edwin Corboy. It saw the conservative vote split between the Country Party and the Nationalist Party, which directly prompted the introduction of preferential voting in Australia.
This article provides information on candidates who stood for the 1914 Australian federal election. The election was held on 5 September 1914.
A by-election was held for the Australian House of Representatives seat of Wide Bay on 11 December 1915. This was triggered by the resignation of former Labor Party Prime Minister and MP Andrew Fisher.
The history of the Australian Labor Party has its origins in the Labour parties founded in the 1890s in the Australian colonies prior to federation. Labor tradition ascribes the founding of Queensland Labour to a meeting of striking pastoral workers under a ghost gum tree in Barcaldine, Queensland in 1891. The Balmain, New South Wales branch of the party claims to be the oldest in Australia. Labour as a parliamentary party dates from 1891 in New South Wales and South Australia, 1893 in Queensland, and later in the other colonies.
Section 13 of the Constitution of Australia provides for three aspects of the terms of members of the Australian Senate: the timing of elections, the commencement date of their terms and for the Senate to allocate long (six-year) and short (three-year) terms following a double dissolution of the Parliament of Australia. While members of the House of Representatives and territory senators have a maximum three-year term, state senators have a fixed six-year term, subject only to the parliament being dissolved by a double dissolution.
The 5 September 1914 election was a double dissolution election which meant all 36 seats in the Senate were up for election, with each Australian states electing six members, with half to serve a six-year term and the rest to serve a three year term. Terms were taken to have commenced on 1 July 1914. The Senate resolved that in each State the three senators who received the most votes would sit for a six-year term, finishing on 30 June 1920 while the other half would sit for a three-year term, finishing on 30 June 1917.











