The Free Democratic Party is a liberal political party in Germany.
The German Democratic Party was a liberal political party in the Weimar Republic, considered centrist or centre-left. Along with the right-liberal German People's Party, it represented political liberalism in Germany between 1918 and 1933. It was formed in 1918 from the Progressive People's Party and the liberal wing of the National Liberal Party, both of which had been active in the German Empire.

The Centre Party, officially the German Centre Party and also known in English as the Catholic Centre Party, is a Christian democratic political party in Germany. It was most Influential in the German Empire and Weimar Republic. Formed in 1870, it successfully battled the Kulturkampf waged by Chancellor Otto von Bismarck against the Catholic Church. It soon won a quarter of the seats in the Reichstag, and its middle position on most issues allowed it to play a decisive role in the formation of majorities. The party name Zentrum (Centre) originally came from the fact that Catholic representatives would take up the middle section of seats in parliament between the social democrats and the conservatives.

Otto Braun was a politician of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) during the Weimar Republic. From 1920 to 1932, with only two brief interruptions, Braun was Minister President of the Free State of Prussia. The continuity of personnel in high office resulted in a largely stable government in Prussia, in contrast to the sometimes turbulent politics of the Reich. During his term of office, Prussia's public administration was reorganized along democratic lines. He replaced many monarchist officials with supporters of the Weimar Republic, strengthened and democratized the Prussian police, and made attempts to fight the rise of the Nazi Party.

Prussia was a German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. The Knights had to relocate their headquarters to Mergentheim, but managed to keep land in Livonia until 1561.

The Weimar Coalition is the name given to the coalition government formed by the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), the German Democratic Party (DDP) and the Catholic Centre Party (Z), who together had a large majority of the delegates to the Constituent Assembly that met at Weimar in 1919, and were the principal groups that designed the constitution of the Weimar Republic. These three parties were seen as the most committed to Germany's new democratic system, and together governed Germany until the elections of 1920, when the first elections under the new constitution were held, and both the SPD and especially the DDP lost a considerable share of their votes. Although the Coalition was revived in the ministry of Joseph Wirth from 1921 to 1922, the pro-democratic elements never truly had a majority in the Reichstag from this point on, and the situation gradually grew worse for them with the continued weakening of the DDP. This meant that any pro-republican group that hoped to attain a majority would need to form a "Grand Coalition" with the conservative-liberal German People's Party (DVP), which only gradually moved from monarchism to republicanism over the course of the Weimar Republic and was virtually wiped out politically after the death of their most prominent figure, Foreign Minister Gustav Stresemann in 1929.

Presidential elections were held in Germany on 29 March 1925, with a runoff on 26 April. They were the first direct elections to the office of President of the Reich, Germany's head of state during the 1919–33 Weimar Republic. The first President, Friedrich Ebert, who had died on 28 February 1925, had been elected indirectly, by the National Assembly, but the Weimar Constitution required that his successor be elected by the "whole German people". Paul von Hindenburg was elected as the second president of Germany in the second round of voting.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 5 March 1933, after the Nazi seizure of power on 30 January and just six days after the Reichstag fire. The election saw Nazi stormtroopers unleash a widespread campaign of violence against the Communist Party (KPD), left-wingers, trade unionists, the Social Democratic Party and the Centre Party. They were the last multi-party elections in a united Germany until 1990.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 31 July 1932, following the premature dissolution of the Reichstag. The Nazi Party made significant gains and became the largest party in the Reichstag for the first time, although they failed to win a majority. The Communist Party increased their vote share as well. All other parties combined held less than half the seats in the Reichstag, meaning no majority coalition government could be formed without including at least one of these two parties.
Federal elections were held in Germany on 6 June 1920 to elect the first Reichstag of the Weimar Republic. It succeeded the Weimar National Assembly elected in January 1919, which had drafted and ratified the republican constitution. The election was delayed in three electoral districts – Schleswig-Holstein and East Prussia until 20 February 1921, and Upper Silesia (Oppeln) until 19 November 1922 – due to territorial plebiscites.

The Free State of Prussia was one of the constituent states of Germany from 1918 to 1947. The successor to the Kingdom of Prussia after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I, it continued to be the dominant state in Germany during the Weimar Republic, as it had been during the empire, even though most of Germany's post-war territorial losses in Europe had come from its lands. It was home to the federal capital Berlin and had 62% of Germany's territory and 61% of its population. Prussia changed from the authoritarian state it had been in the past and became a parliamentary democracy under its 1920 constitution. During the Weimar period it was governed almost entirely by pro-democratic parties and proved more politically stable than the Republic itself. With only brief interruptions, the Social Democratic Party (SPD) provided the Minister President. Its Ministers of the Interior, also from the SPD, pushed republican reform of the administration and police, with the result that Prussia was considered a bulwark of democracy within the Weimar Republic.

The Reichstag of the German Empire was Germany's lower House of Parliament from 1871 to 1918. Within the governmental structure of the Reich, it represented the national and democratic element alongside the federalism of the Bundesrat and the monarchic and bureaucratic element of the executive, embodied in the Reich chancellor. Together with the Bundesrat, the Reichstag had legislative power and shared in decision-making on the budget. It also had certain rights of control over the executive branch and could engage the public through its debates. The emperor had little political power, and over time the position of the Reichstag strengthened with respect to both the imperial government and the Bundesrat.

The Prussian Constitution of 1920 formed the legal framework for the Free State of Prussia, a constituent state of the Weimar Republic, from 1918 to 1947. It was based on democratic parliamentary principles and replaced the Constitution of 1848/50. During the National Socialist era, it was eroded to the point of irrelevance and following World War II lost legal force when the state of Prussia was abolished by the Allies in 1947.

The Fehrenbach cabinet, headed by Chancellor Constantin Fehrenbach of the Centre Party, was the fourth democratically elected government of the Weimar Republic. It took office on 25 June 1920 when it replaced the first cabinet of Hermann Müller, which had resigned due to the poor showing of the coalition parties in the June 1920 elections to the new Reichstag. The 1920 Reichstag replaced the Weimar National Assembly, which had served as Germany's interim parliament and written and approved the Weimar Constitution.

The 1931 Prussian Landtag referendum was an attempt to prematurely dissolve the sitting session of the Landtag (parliament) of the Weimar German state of Prussia. The referendum, which took place according to Article 6 of the 1920 Prussian Constitution, was triggered by a petition launched in the spring of 1931 by the anti-republican veterans' organization Der Stahlhelm. It was supported by several right-wing parties including the Nazis, as well as by the Communist Party of Germany (KPD). Even though 93.9% of those voting on 9 August 1931 opted to dissolve the Landtag, the referendum failed because the turnout of 39.2% did not meet the minimum 50% requirement.
State elections were held in the Free State of Prussia on 26 January 1919. The elections were held a week after the elections to the federal National Assembly, and were the first elections of Prussian institutions held using proportional representation and with women's suffrage. The election was also the first truly free and fair Prussian election, as it was the first election held after the abolition of the Prussian three-class franchise, which grouped voters by the amount of taxes paid and gave disproportionate weight to the wealthy.

State elections were held in the Free State of Prussia on 20 February 1921 to elect 406 of the 428 members of the Landtag of Prussia. The governing coalition of the Social Democratic Party, Centre Party, and German Democratic Party suffered major losses, losing one-third of its collective voteshare from 1919, but retained a narrow majority. The right-liberal German People's Party (DVP) and reactionary nationalist German National People's Party (DNVP) made the largest gains, with the DNVP becoming the second largest party by voteshare. The Communist Party of Germany contested its first Prussian election, winning 31 seats.
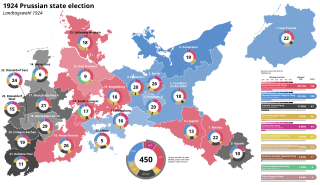
State elections were held in the Free State of Prussia on 7 December 1924 to elect all 450 members of the Landtag of Prussia. The governing coalition of the Social Democratic Party, Centre Party, and German Democratic Party made minimal gains or losses, with most change happening amongst the opposition. The German National People's Party made significant gains, nearly surpassing the SPD as the largest party, while the Independent Social Democratic Party collapsed. The German People's Party also lost a portion of the gains it had made in the previous election. The National Socialist Freedom Party, a branch of the Nazi Party formed after the Beer Hall Putsch, won 2.5% of the vote and 11 seats.

State elections were held in the Free State of Prussia on 24 April 1932 to elect all 423 members of the Landtag of Prussia. They were the last free election in Prussia, as the next election in 1933 took place under the Nazi regime, and Prussia was then abolished after World War II.

The 2023 Bremen state election was held on 14 May 2023 to elect the 21st Bürgerschaft of Bremen. Elections to the city councils of Bremen and Bremerhaven, the two municipal entities comprising the state of Bremen, were held simultaneously. The incumbent government was a coalition of the Social Democratic Party (SPD), Alliance 90/The Greens, and The Left led by Mayor Andreas Bovenschulte.