
The National Assembly was the authoritative legislative body of the Republic of China, from 1947 to 2005. Along with the Control Yuan and the Legislative Yuan, the National Assembly formed the tricameral parliament of the Republic of China.
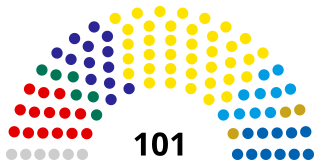
The Riigikogu is the unicameral parliament of Estonia. In addition to approving legislation, the Parliament appoints high officials, including the prime minister and chief justice of the Supreme Court, and elects the president. Among its other tasks, the Riigikogu also ratifies significant foreign treaties that impose military and proprietary obligations and bring about changes in law, as well as approves the budget presented by the government as law, and monitors the executive power.

The Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, often called Verkhovna Rada or simply Rada, is the unicameral parliament of Ukraine. The Verkhovna Rada has over 450 deputies, who are presided over by a speaker. The Verkhovna Rada meets in the Verkhovna Rada building in Ukraine's capital Kyiv. The deputies elected on 21 July 2019 Ukrainian parliamentary election were inaugurated on 29 August 2019.

The Supreme Council is the unicameral parliament of the Kyrgyz Republic. It was known as the Supreme Soviet of the Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic until 1991.

The Declaration "On the Restoration of Independence of the Republic of Latvia" was adopted on 4 May 1990 by the Supreme Soviet of the Latvian SSR in which Latvia declared independence from the Soviet Union. The Declaration stated that, although Latvia had de facto lost its independence in 1940, when it was annexed by the Soviet Union, the country had de jure remained a sovereign country as the annexation had been unconstitutional and against the will of the Latvian people.

The Supreme Soviet of the Lithuanian SSR was the supreme soviet of the Lithuanian SSR, one of the republics constituting the Soviet Union. The Supreme Soviet was established in August 1940 when the People's Seimas declared itself the provisional Supreme Soviet. According to the constitution it was very similar to modern democratic parliaments: it was elected every four years and had the power to create, amend and ratify the constitution, laws, and treaties and appoint officials in the Council of Ministers. However, in reality the elections were staged, the Soviet had very little actual power and carried out orders given by the Communist Party of Lithuania (CPL). The situation changed in 1988, when the Lithuanians began seeking independence from the Soviet Union. The political power shifted from CPL to the Soviet, which adopted a number of important constitutional amendments and laws, paving the way for the independence. The first free elections were held in February 1990 and were won by pro-independence Sąjūdis. During its first session the Supreme Soviet adopted the Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania and renamed itself the Supreme Council of the Republic of Lithuania.

The electoral system of the Soviet Union was varying over time, being based upon Chapter XIII of the provisional Fundamental Law of 1922, articles 9 and 10 of the 1924 Constitution and Chapter XI of the 1936 Constitution, with the electoral laws enacted in conformity with those. The Constitution and laws applied to elections in all Soviets, from the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union, the Union republics and autonomous republics, through to regions, districts and towns. Voting was claimed to be secret and direct with universal suffrage. However, in practice, between 1936 and 1989, voters could vote against candidates preselected by the Communist Party only by spoiling their ballots, or by voting against the only candidate, whereas votes for the party candidates could be cast simply by submitting a blank ballot. A person would be given a ballot by a clerk, and could immediately walk to the ballot box, and while there were booths in which one could strike the candidates they voted against off the ballot, this was easy to record and was not commonly done by voters.

The Supreme Soviet of the Russian SFSR, later Supreme Soviet of the Russian Federation, was the supreme government institution of the Russian SFSR in 1938–1990; in 1990–1993 it was a permanent legislature (parliament), elected by the Congress of People's Deputies of the Russian Federation.

The Government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) was the executive and administrative organ of the highest body of state authority, the All-Union Supreme Soviet. It was formed on 30 December 1922 and abolished on 26 December 1991. The government was headed by a chairman, most commonly referred to as the premier of the Soviet Union, and several deputy chairmen throughout its existence. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU), as "The leading and guiding force of Soviet society and the nucleus of its political system" per Article 6 of the state constitution, controlled the government by holding a two-thirds majority in the All-Union Supreme Soviet. The government underwent several name changes throughout its history, and was known as the Council of People's Commissars from 1922 to 1946, the Council of Ministers from 1946 to 1991, the Cabinet of Ministers from January to August 1991 and the Committee on the Operational Management of the National Economy from August to December 1991.
Elections to the Supreme Soviet were held in the Soviet Union on 12 December 1937. It was the first election held under the 1936 Soviet Constitution, which had formed the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union to replace the old legislature, the Congress of Soviets of the Soviet Union.
Elections to the Supreme Soviet were held in the Soviet Union on 10 February 1946. According to Soviet law, 325,000 out of an eligible adult population of 101,718,000 were disenfranchised for various reasons. This election was the first in which a 1945 decree allowed members of the Red Army stationed outside the Soviet Union to vote for both chambers of the Supreme Soviet in special 100,000-member districts, a practice which would continue for decades with the Red Army presence in the Eastern bloc.

The Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR was the supreme soviet of the Byelorussian SSR from 1938 to 1991. The Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR was preceded by the All-Byelorussian Central Executive Committee (1920-1938) and the All-Byelorussian Congress of Soviets (1919-1937). The Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR was briefly disbanded in 1941 due to the Great Patriotic War and was re-established in 1947. The Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR was briefly succeeded by the Supreme Soviet of Belarus from 1991 to 1996. The Supreme Soviet of Belarus was succeeded by the National Assembly of Belarus in 1996.

The Congress of People's Deputies of the Soviet Union was the highest body of state authority of the Soviet Union from 1989 to 1991.
Elections to the Supreme Soviet were held in the Soviet Union on 16 June 1974.
Elections to the Supreme Soviet were held in the Soviet Union on 4 March 1979. They were the first elections held under the 1977 Soviet constitution, which slightly reformed the composition of the Supreme Soviet.
Parliamentary elections were held in Estonia on 14 and 15 July 1940 alongside simultaneous elections in Latvia and Lithuania. The elections followed the Soviet occupation of the three countries. As was the case in Latvia and Lithuania, the elections in Estonia were blatantly rigged. They were also unconstitutional, since only seats for the lower chamber of the Riigikogu, the Chamber of Deputies, were contested; the upper chamber, the National Council, had been dissolved and was never reconvened. According to August Rei, one of independent Estonia's last envoys to Moscow, under the Estonian constitution, the Chamber of Deputies had "no legislative power" apart from the National Council.
Elections to the Supreme Soviet of the Estonian SSR were held on 16 February 1947. They were the first elections since the Estonian SSR was declared on 21 July 1940 and the first after World War II.
Supreme Soviet elections were held in the Ukrainian SSR on 26 June 1938 to elect deputies to the Supreme Soviet. They were held alongside elections to oblast councils and followed the national elections to the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union on 12 December 1937.

The Supreme Soviet of the Estonian SSR was the formal rubber stamp legislative body of the Estonian SSR without any substantive meaning, which was formally elected in general elections, but whose members were essentially appointed by the leadership of the Communist Party. Before 1988, the Supreme Soviet had no meaningful political role. After its first democratic elections on 18 March 1990, the institution was renamed the Supreme Council of the Republic of Estonia on 8 May 1990.

The Supreme Soviet of the Ukrainian SSR was the supreme soviet of the Ukrainian SSR, one of the union republics of the Soviet Union. The Supreme Soviet of the Ukrainian SSR was established in 1937 replacing the All-Ukrainian Congress of Soviets.











