Related Research Articles

The House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Australia, the upper house being the Senate. Its composition and powers are set down in Chapter I of the Constitution of Australia.
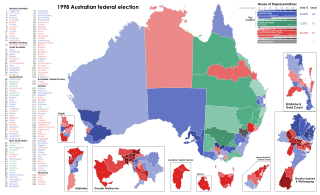
The 1998 Australian federal election was held to determine the members of the 39th Parliament of Australia. It was held on 3 October 1998. All 148 seats of the House of Representatives and 40 seats of the 76 seat Senate were up for election. The incumbent centre-right Liberal/National Coalition government led by Prime Minister John Howard of the Liberal Party and coalition partner Tim Fischer of the National Party defeated the centre-left Australian Labor Party opposition led by Opposition Leader Kim Beazley, despite losing the nationwide popular and two-party preferred vote. However, the Australian Labor Party gained seats compared to the previous election.

The 2004 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 9 October 2004. All 150 seats in the House of Representatives and 40 seats in the 76-member Senate were up for election. The incumbent Liberal Party of Australia led by Prime Minister of Australia John Howard and coalition partner the National Party of Australia led by John Anderson defeated the opposition Australian Labor Party led by Mark Latham.

The 1996 Australian federal election was held to determine the members of the 38th Parliament of Australia. It was held on 2 March 1996. All 148 seats of the House of Representatives and 40 seats of the 76-seat Senate were up for election. The Liberal/National Coalition led by Opposition Leader John Howard of the Liberal Party and coalition partner Tim Fischer of the National Party defeated the incumbent Australian Labor Party government led by Prime Minister Paul Keating in a landslide victory. The Coalition won 94 seats in the House of Representatives, which is the largest number of seats held by a federal government to date, and only the second time a party had won over 90 seats at a federal election.

Brendan Michael Smyth is an Australian former politician, who was a member of the Australian Capital Territory Legislative Assembly representing the electorate of Brindabella for the Liberal Party from 1998 until 2016. From 2002 to 2006 Smyth was the ACT Leader of the Opposition and served briefly as the Deputy Chief Minister during 2000 and 2001. He has held the ACT portfolios Urban Services, Business, Tourism and the Arts, and Police and Emergency Services.

The 1987 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 11 July 1987, following the granting of a double dissolution on 5 June by the Governor-General Sir Ninian Stephen. Consequently, all 148 seats in the House of Representatives as well as all 76 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Australian Labor Party, led by Prime Minister Bob Hawke, defeated the opposition Liberal Party of Australia, led by John Howard and the National Party of Australia led by Ian Sinclair. This was the first, and to date only, time the Labor Party won a third consecutive election.
The term swing refers to the extent of change in voter support, typically from one election or opinion poll to another, expressed as a positive or negative percentage point. For the Australian House of Representatives and the lower or unicameral houses of the parliaments of all the states and territories except Tasmania and the ACT, as well as Tasmania's upper house, Australia employs preferential voting in single-member constituencies. Under the full-preference instant-runoff voting system, in each seat the candidate with the lowest vote is eliminated and their preferences are distributed, which is repeated until only two candidates remain. While every seat has a two-candidate preferred (TCP) result, seats where the major parties have come first and second are commonly referred to as having a two-party-preferred (TPP) result. The concept of "swing" in Australian elections is not simply a function of the difference between the votes of the two leading candidates, as it is in Britain. To know the majority of any seat, and therefore the swing necessary for it to change hands, it is necessary to know the preferences of all the voters, regardless of their first preference votes. It is not uncommon in Australia for candidates who have comfortable leads on the first count to fail to win the seat, because "preference flows" go against them.

The 1906 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 12 December 1906. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives, and 18 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Protectionist Party minority government led by Prime Minister Alfred Deakin retained government, despite winning the fewest House of Representatives votes and seats of the three parties. Parliamentary support was provided by the Labour Party led by Chris Watson, while the Anti-Socialist Party, led by George Reid, remained in opposition.

In Australian politics, the two-party-preferred vote, commonly referred to as simply preferences, is the result of an election or opinion poll after preferences have been distributed to the two candidates with the highest number of votes who, in some cases, can be independents. For the purposes of TPP, the Liberal/National Coalition is usually considered a single party, with Labor being the other major party. Typically the TPP is expressed as the percentages of votes attracted by each of the two major parties, e.g. "Coalition 50%, Labor 50%", where the values include both primary votes and preferences. The TPP is an indicator of how much swing has been attained/is required to change the result, taking into consideration preferences, which may have a significant effect on the result.

The 1977 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 10 December 1977. All 124 seats in the House of Representatives and 34 of the 64 seats in the Senate were up for election.

The 1975 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 13 December 1975. All 127 seats in the House of Representatives and all 64 seats in the Senate were up for election, due to a double dissolution.

The 1949 Australian federal election was held on Saturday, 10 December, 1949. All 121 seats in the House of Representatives and 42 of the 60 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Labor Party, led by Prime Minister Ben Chifley, was defeated by the opposition Liberal–Country coalition under Robert Menzies in a landslide. Menzies became prime minister for a second time, his first period having ended in 1941. This election marked the end of the 8-year Curtin-Chifley Labor government that had been in power since 1941 and started the 23-year Liberal/Country Coalition government. This was the first time the Liberal party won government at the federal level.

The 1943 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 21 August 1943. All 74 seats in the House of Representatives and 19 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Labor Party, led by Prime Minister John Curtin, defeated the opposition Country–UAP coalition led by Arthur Fadden in a landslide. The Labor party TPP result of 58.2% is its highest, in its history.
The 1918 Swan by-election was a by-election for the Division of Swan in the Australian House of Representatives, following the death of the sitting member Sir John Forrest. Held on 26 October 1918, the by-election led to the election of the youngest person to be elected until 2010 to the Parliament of Australia, Edwin Corboy. It saw the conservative vote split between the Country Party and the Nationalist Party, which directly prompted the introduction of preferential voting in Australia.
Environmentalists for Nuclear Energy Australia, formerly called Conservatives for Climate and Environment, was a political party registered in Australia from 2007 to 2010. EFN-Australia referred to itself as a not-for-profit environmental association, registered as a political party. It was the Australian affiliate of Environmentalists for Nuclear, and the party campaigned unsuccessfully to gain nuclear power in Australia.

The 2010 Australian federal election was held on Saturday, 21 August 2010 to elect members of the 43rd Parliament of Australia. The incumbent centre-left Australian Labor Party led by Prime Minister Julia Gillard won a second term against the opposition centre-right Liberal Party of Australia led by Opposition Leader Tony Abbott and Coalition partner the National Party of Australia, led by Warren Truss, after Labor formed a minority government with the support of three independent MPs and one Australian Greens MP.
The Centre Party, previously the Country Party, was a minor Australian political party in the state of Tasmania. Initially formed in 1962 as a new Tasmanian branch of the Country Party of Australia after decades of inactivity in the state, it at first enjoyed no electoral success. In the run up to the 1969 election the party was joined by Kevin Lyons, a former Liberal turned independent member of the Assembly for Braddon, who renamed it the Centre Party and retained his seat at the election, securing the balance of power and serving as Deputy Premier in a coalition government until 1972. Upon the coalition's collapse the Centre Party faded away before being dissolved in 1975.

The 1901 New South Wales state election was held on 3 July 1901 for all of the 125 seats in the 19th New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in single-member constituencies with a first past the post voting system. The Parliamentary Electorates Act of 1893 had conferred the right to vote on every male British subject over 21 years of age who was resident in New South Wales for a year or more. The 19th parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 11 June 1901 by the Governor, Lord Beauchamp, on the advice of the Premier, John See.

The 2022 Australian federal election was held on Saturday 21 May 2022 to elect members of the 47th Parliament of Australia. The incumbent Liberal/National Coalition government, led by Prime Minister Scott Morrison, sought to win a fourth consecutive term in office but was defeated by the opposition Labor Party, led by Anthony Albanese. Up for election were all 151 seats in the lower house, the House of Representatives, as well as 40 of the 76 seats in the upper house, the Senate.

The 2025 Australian federal election will be held on or before 17 May 2025 to elect members of the 48th Parliament of Australia. 150 seats in the House of Representatives and likely 40 of the 76 seats in the Senate will be contested. It is expected that at this election, the Labor government of Prime Minister Anthony Albanese will be seeking re-election to a second term in office, opposed by the Liberal/National Coalition under Leader of the Opposition Peter Dutton, minor parties such as the Greens, and independents.
References
- ↑ "ALP in by-election".
- ↑ House of Representatives Practice, 6th Edition, Ch. 3. Elections and the electoral system. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ↑ "By-Elections 1972-1974". Psephos. Archived from the original on 16 March 2011. Retrieved 4 July 2010.