The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately 1,144,000 km2 (442,000 sq mi) and a 2016 census population of 41,790, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of 2023 is 45,668. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and only city in the territory; its population was 19,569 as of the 2016 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission.
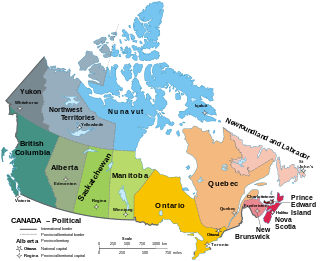
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.
National referendums are seldom used in Canada. The first two referendums in 1898 and 1942 saw voters in Quebec and the remainder of Canada take dramatically-opposing stands, and the third in 1992 saw most of the voters take a stand dramatically opposed to that of the politicians in power.

Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories have the power to make legislation relevant to the area, thus granting them a higher level of autonomy.

Paul Okalik is a Canadian politician. He is the first Inuk to have been called to the Nunavut Bar. He was also the first premier of Nunavut.
Canada holds elections for legislatures or governments in several jurisdictions: for the federal (national) government, provincial and territorial governments, and municipal governments. Elections are also held for self-governing First Nations and for many other public and private organizations including corporations and trade unions. Municipal elections can also be held for both upper-tier and lower-tier governments.
In Australia, referendums are public votes held on important issues where the electorate may approve or reject a certain proposal. In contemporary usage, polls conducted on non-constitutional issues are known as plebiscites, with the term referendum being reserved solely for votes on constitutional changes, which is legally required to make a change to the Constitution of Australia.

The 1948 Alberta general election was held on August 17, 1948, to elect members of the Legislative Assembly of Alberta.

The history of Northwest Territories capital cities begins with the purchase of the Territories by Canada from the Hudson's Bay Company in 1869, and includes a varied and often difficult evolution. Northwest Territories is unique amongst the other provinces and territories of Canada in that it has had seven capital cities in its history. The territory has changed the seat of government for numerous reasons, including civil conflict, development of infrastructure, and a history of significant revisions to its territorial boundaries.

The history of Canada (1982–present) refers to the period immediately following the Canada Act until the present.
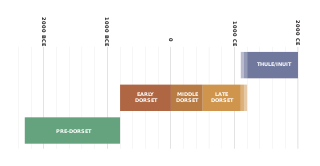
The history of Nunavut covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Eskimo thousands of years ago to present day. Prior to the colonization of the continent by Europeans, the lands encompassing present-day Nunavut were inhabited by several historical cultural groups, including the Pre-Dorset, the Dorsets, the Thule and their descendants, the Inuit.

Nunavut is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for independent government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.
The Nunavut Land Claim Agreement was signed on May 25, 1993, in Iqaluit, by representatives of the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut, the Government of Canada and the Government of the Northwest Territories. This agreement gave the Inuit of the central and eastern Northwest Territories a separate territory called Nunavut. It is the largest Aboriginal land claim settlement in Canadian history.

Nunavut Day is a public holiday in the Canadian territory of Nunavut.

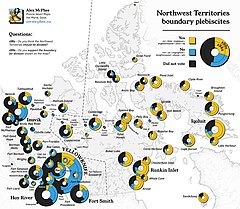
A plebiscite on the boundary between Northwest Territories and the new territory of Nunavut was held in the Northwest Territories on 4 May 1992. The proposed border was approved by 54% of voters. A second referendum later in the year gave the final approval to the creation of the new territory.
A referendum on the creation of the territory of Nunavut was held between 3 and 5 November 1992 in the territory set to become the new territory. It was approved by 69% of voters. On 25 May 1993 the Mulroney government and the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut signed the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement. On 10 June 1993 the parliament of Canada passed two laws dividing the Northwest Territories and providing for the formation of Nunavut on 1 April 1999.
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This article summarises referendum laws and practice in various countries.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held in Puerto Rico on June 11, 2017. The referendum had three options: becoming a state of the United States, independence/free association, or maintaining the current territorial status. Those who voted overwhelmingly chose statehood by 97%. This figure is attributed to a boycott led by the pro-status quo PPD party, which resulted in a 22.93% turnout.