Related Research Articles

Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada, variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 0.5 per cent of Canada's population.

Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories have the power to make legislation relevant to the area, thus granting them a higher level of autonomy.

Pond Inlet is a small, predominantly Inuit community in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada, located on northern Baffin Island. To the Inuit the name of the place "is and always has been Mittimatalik." The Scottish explorer Sir John Ross had named an arm of the sea that separates Bylot Island from Baffin Island as Pond's Bay, and the hamlet now shares that name. On 29 August 1921, the Hudson's Bay Company opened its trading post near the Inuit camp and named it Pond Inlet, marking the expansion of its trading empire into the High Arctic.
The minister of Crown–Indigenous relations is a minister of the Crown in the Canadian Cabinet, one of two ministers who administer Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada (CIRNAC), the department of the Government of Canada which is responsible for administering the Indian Act and other legislation dealing with "Indians and lands reserved for the Indians" under subsection 91(24) of the Constitution Act, 1867. The minister is also more broadly responsible for overall relations between the federal government and First Nations, Métis, and Inuit.

Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada is the department of the Government of Canada responsible for Canada's northern lands and territories, and one of two departments with responsibility for policies relating to Indigenous peoples in Canada.

Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, previously known as the Inuit Tapirisat of Canada, is a nonprofit organization in Canada that represents over 65,000 Inuit across Inuit Nunangat and the rest of Canada. Their mission is to "serve as a national voice protecting and advancing the rights and interests of Inuit in Canada."
The Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut was the organization officially recognized from 1982 to 1993 as representing the Inuit of what is now Nunavut, but was then part of the Northwest Territories, for the purpose of negotiating treaties and land claims settlements. In this role, it replaced the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, which represents Inuit across Canada, and has been superseded by Nunavut Tunngavik Incorporated.
Nunavut Tunngavik Incorporated is the legal representative of the Inuit of Nunavut for the purposes of native treaty rights and treaty negotiation. The presidents of NTI, Makivik Corporation, Nunatsiavut, and the Inuvialuit Regional Corporation, the four regional land claims organizations, govern the national body, the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (ITK) as its board of directors. NTI continues to play a central role in Nunavut, even after the creation of the Government of Nunavut. As the successor of the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut, which was a signatory of the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement on behalf of Inuit, NTI is responsible for ensuring that the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement is implemented fully by the Government of Canada and the Government of Nunavut and that all parties fulfill their obligations.
Tagak Curley is an Inuit leader, politician and businessman from Nunavut. As a prominent figure in the negotiations that led to the creation of Nunavut, Tagak is considered a living father of confederation in Canada. He was born in a hunting camp at Coral Harbour, Northwest Territories.
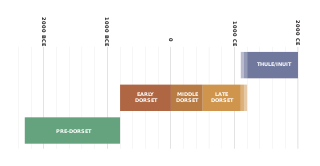
The history of Nunavut covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Eskimo thousands of years ago to present day. Prior to the colonization of the continent by Europeans, the lands encompassing present-day Nunavut were inhabited by several historical cultural groups, including the Pre-Dorset, the Dorsets, the Thule and their descendants, the Inuit.

Nunavut is the largest, easternmost, and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for self-government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.

Parker's Notch, named after former Commissioner of the Northwest Territories, John Havelock Parker, is a protrusion of the Northwest Territories southwards into Nunavut on Victoria Island. In the Northwest Territories the protrusion is part of the Inuvik Region and the Kitikmeot Region in Nunavut.

Polar Bear Pass National Wildlife Area is a National Wildlife Area on Bathurst Island within Qikiqtaaluk, Nunavut, Canada. It is on federal Crown land, and is administered by the Canadian Wildlife Service, a division of Environment Canada, with respect to the Canada Wildlife Act's National Wildlife Area Regulations. Land use is also subject to the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement. To the north and west is Qausuittuq National Park.

Inuit are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of North America, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, Yukon (traditionally), Alaska, and Chukotsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut.

The Inuvialuit Settlement Region, abbreviated as ISR, located in Canada's western Arctic, was designated in 1984 in the Inuvialuit Final Agreement by the Government of Canada for the Inuvialuit people. It spans 90,650 km2 (35,000 sq mi) of land, mostly above the tree line, and includes several subregions: the Beaufort Sea, the Mackenzie River delta, the northern portion of Yukon, and the northwest portion of the Northwest Territories. The ISR includes both Crown Lands and Inuvialuit Private Lands. Most of the ISR is represented by Nunakput, the territorial electoral district, meaning "our land" in Inuvialuktun.

Nirjutiqavvik National Wildlife Area is a National Wildlife Area on Coburg Island within the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in Baffin Bay's Lady Ann Strait between Ellesmere Island, to the north, and Devon Island to the south. The NWA includes Coburg Island and its surrounding marine area.

Canada welcomed its most recent territory, Nunavut, on April 1, 1999, after it separated from the Northwest Territories. With Nunavut's separation from the Northwest Territories came a need for new regulations regarding cultural history. Nunavut has the unique experience of having a large Aboriginal community that creates strong cultural ties within the legislation.
A referendum on the creation of the territory of Nunavut was held between 3 and 5 November 1992 in the territory set to become the new territory. It was approved by 69% of voters. On 25 May 1993 the Mulroney government and the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut signed the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement. On 10 June 1993 the parliament of Canada passed two laws dividing the Northwest Territories and providing for the formation of Nunavut on 1 April 1999.
Paul Aarulaaq Quassa is a Canadian politician who served as the fourth premier of Nunavut from November 2017 to June 2018. He served as a Member of the Legislative Assembly of Nunavut, representing Aggu from 2013 until 2021.
John Amagoalik is an Inuit politician from Nunavik (Québec). He campaigned for Inuit rights and made a significant contribution to the founding of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. He was Chairman of the Nunavut Implementation Commission and is widely regarded as the "Father of Nunavut".
References
- ↑ "Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Signed". Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami. Archived from the original on September 18, 2011. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- 1 2 Nunavut and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement — An Unresolved Relationship, 10th Anniversary Nunavut Archived 2016-08-13 at the Wayback Machine , Barry Dewar. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Minister of Public Works and Government Services Canada (1997). "Chapter 2 - Implementation Panel Report". 1996-1997 Annual Report on the Implementation of the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement. ISBN 0-662-63298-2 . Retrieved April 29, 2015.
- ↑ Shelagh D. Grant, Polar Imperative (D&M Publisher Inc, 2011), p. 384.
- ↑ Land Claims Archived 2015-01-06 at the Wayback Machine , Kitikmeot Inuit Association. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- ↑ Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada, Amendments to the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement. Retrieved April 30, 2015.