The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately 1,127,711.92 km2 (435,412.01 sq mi) and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of the second quarter of 2024 is 44,936. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and the only city in the territory; its population was 20,340 as of the 2021 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission.
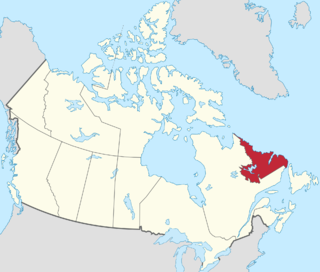
Labrador is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its population. It is separated from the island of Newfoundland by the Strait of Belle Isle. It is the largest and northernmost geographical region in the four Atlantic provinces.

Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada, variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 0.5 per cent of Canada's population.

Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories have the power to make legislation relevant to the area, thus granting them a higher level of autonomy.

Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, previously known as the Inuit Tapirisat of Canada, is a nonprofit organization in Canada that represents over 65,000 Inuit across Inuit Nunangat and the rest of Canada. Their mission is to "serve as a national voice protecting and advancing the rights and interests of Inuit in Canada."

The history of Northwest Territories capital cities begins with the purchase of the Territories by Canada from the Hudson's Bay Company in 1869, and includes a varied and often difficult evolution. Northwest Territories is unique amongst the other provinces and territories of Canada in that it has had seven capital cities in its history. The territory has changed the seat of government for numerous reasons, including civil conflict, development of infrastructure, and a history of significant revisions to its territorial boundaries.

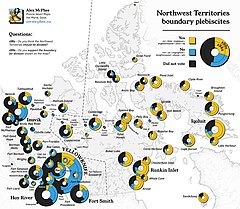
The Northwest Territories division plebiscite was a stand-alone, territory-wide plebiscite conducted on April 14, 1982. This was the first territory-wide plebiscite conducted in Northwest Territories history. The results of the plebiscite would eventually lead to the creation of Nunavut, and spawn three other plebiscites during the creation process of the new territory.
The Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut was the organization officially recognized from 1982 to 1993 as representing the Inuit of what is now Nunavut, but was then part of the Northwest Territories, for the purpose of negotiating treaties and land claims settlements. In this role, it replaced the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, which represents Inuit across Canada, and has been superseded by Nunavut Tunngavik Incorporated.
Nunavut Tunngavik Incorporated is the legal representative of the Inuit of Nunavut for the purposes of native treaty rights and treaty negotiation. The presidents of NTI, Makivik Corporation, Nunatsiavut, and the Inuvialuit Regional Corporation, the four regional land claims organizations, govern the national body, the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (ITK) as its board of directors. NTI continues to play a central role in Nunavut, even after the creation of the Government of Nunavut. As the successor of the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut, which was a signatory of the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement on behalf of Inuit, NTI is responsible for ensuring that the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement is implemented fully by the Government of Canada and the Government of Nunavut and that all parties fulfill their obligations.
Lancaster Sound is a body of water in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located between Devon Island and Baffin Island, forming the eastern entrance to the Parry Channel and the Northwest Passage. East of the sound lies Baffin Bay; to the west lies Viscount Melville Sound. Further west a traveller would enter the M'Clure Strait before heading into the Arctic Ocean.
Tagak Curley is an Inuk leader, politician and businessman from Nunavut. As a prominent figure in the negotiations that led to the creation of Nunavut, Tagak is considered a living Father of Confederation in Canada. He was born in a hunting camp at Coral Harbour, Northwest Territories.

The history of the Northwest Territories covers the period from thousands of years ago to the present day. Prior to European colonization, the lands that encompass present-day Northwest Territories were inhabited for millennia by several First Nations. European explorers and fur traders began to explore the region since the late-16th century. By the 17th century, the British laid claim to both the North-Western Territory and Rupert's Land; and granted the Hudson's Bay Company a commercial fur trade monopoly over the latter region.
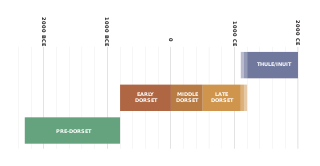
The history of Nunavut covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Eskimo thousands of years ago to present day. Prior to the colonization of the continent by Europeans, the lands encompassing present-day Nunavut were inhabited by several historical cultural groups, including the Pre-Dorset, the Dorsets, the Thule and their descendants, the Inuit.

Nunavut is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for self-government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.

The Northwest Territories is a territory in Northern Canada, specifically in Northwestern Canada between Yukon Territory and Nunavut including part of Victoria Island, Melville Island, and other islands on the western Arctic Archipelago. Originally a much wider territory enclosing most of central and northern Canada, the Northwest Territories was created in 1870 from the Hudson's Bay Company's holdings that were sold to Canada from 1869-1870. In addition, Alberta and Saskatchewan were formed from the territory in 1905. In 1999, it was divided again: the eastern portion became the new territory of Nunavut. Yellowknife stands as its largest city and capital. It has a population of 42,800 and has an area of 532,643 sq mi (1,379,540 km2). The current territory lies west of Nunavut, north of latitude 60° north, and east of Yukon.
The Nunavut Land Claims Agreement was signed on May 25, 1993, in Iqaluit, by representatives of the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut, the Government of Canada and the Government of the Northwest Territories. This agreement gave the Inuit of the central and eastern Northwest Territories a separate territory called Nunavut. It is the largest Aboriginal land claim settlement in Canadian history.

Inuit are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, Yukon (traditionally), Alaska, and Chukotsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut.
A referendum on the creation of the territory of Nunavut was held between 3 and 5 November 1992 in the territory set to become the new territory. It was approved by 69% of voters. On 25 May 1993 the Mulroney government and the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut signed the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement. On 10 June 1993 the parliament of Canada passed two laws dividing the Northwest Territories and providing for the formation of Nunavut on 1 April 1999.

Indigenous or Aboriginal self-government refers to proposals to give governments representing the Indigenous peoples in Canada greater powers of government. These proposals range from giving Aboriginal governments powers similar to that of local governments in Canada to demands that Indigenous governments be recognized as sovereign, and capable of "nation-to-nation" negotiations as legal equals to the Crown, as well as many other variations.