
Irrigation is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been developed by many cultures around the world. Irrigation helps to grow crops, maintain landscapes, and revegetate disturbed soils in dry areas and during times of below-average rainfall. In addition to these uses, irrigation is also employed to protect crops from frost, suppress weed growth in grain fields, and prevent soil consolidation. It is also used to cool livestock, reduce dust, dispose of sewage, and support mining operations. Drainage, which involves the removal of surface and sub-surface water from a given location, is often studied in conjunction with irrigation.

The Central Valley is a broad, elongated, flat valley that dominates the interior of California, United States. It is 40–60 mi (60–100 km) wide and runs approximately 450 mi (720 km) from north-northwest to south-southeast, inland from and parallel to the Pacific coast of the state. It covers approximately 18,000 sq mi (47,000 km2), about 11% of California's land area. The valley is bounded by the Coast Ranges to the west and the Sierra Nevada to the east.

West Sussex is a ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Surrey to the north, East Sussex to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Hampshire to the west. The largest settlement is Crawley, and the county town is the city of Chichester.

A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern.

An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to semiarid climates, but are also found in more humid environments subject to intense rainfall and in areas of modern glaciation. They range in area from less than 1 square kilometer (0.4 sq mi) to almost 20,000 square kilometers (7,700 sq mi).

The San Joaquin River is the longest river of Central California. The 366-mile (589 km) long river starts in the high Sierra Nevada and flows through the rich agricultural region of the northern San Joaquin Valley before reaching Suisun Bay, San Francisco Bay, and the Pacific Ocean. An important source of irrigation water as well as a wildlife corridor, the San Joaquin is among the most heavily dammed and diverted of California's rivers.

Chichester is a cathedral city and civil parish in the Chichester district of West Sussex, England. It is the only city in West Sussex and is its county town. It was a Roman and Anglo-Saxon settlement and a major market town from those times through Norman and medieval times to the present day. It is the seat of the Church of England Diocese of Chichester and is home to a 12th-century cathedral.
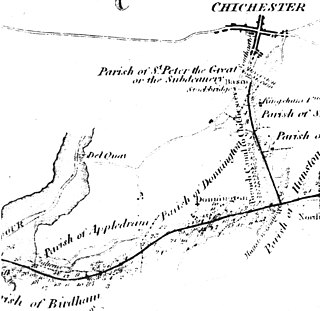
The Chichester Canal is a ship canal in England. Partly navigable, its course is essentially intact and runs 3.8 miles (6.1 km) from the sea at Birdham on Chichester Harbour to Chichester through two locks. The canal was opened in 1822 and took three years to build. The canal could take ships of up to 100 long tons (100 t). Dimensions were limited to 85 feet long, 18 feet (5.5 m) wide and a draft of up to 7 feet (2.1 m). As denoted by the suffix -chester, Chichester is a Roman settlement, and 300 Denarii were unearthed when Chichester Basin was formed in the 1820s.
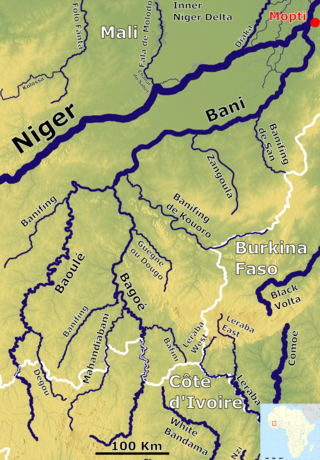
The Bani River is the principal tributary of the Niger River in Mali. The river is formed from the confluence of the Baoulé and Bagoé rivers some 160 km (99 mi) east of Bamako and it merges with the Niger near Mopti. Its length is about 1,100 km (680 mi).

The Awash River is a major river of Ethiopia. Its course is entirely contained within the boundaries of Ethiopia and empties into a chain of interconnected lakes that begin with Lake Gargori and end with Lake Abbe on the border with Djibouti, some 100 kilometres from the head of the Gulf of Tadjoura. The Awash River is the principal stream of an endorheic drainage basin covering parts of the Amhara, Oromia and Somali Regions, as well as the southern half of the Afar Region. The Awash River basin, spanning 23 administrative zones, covers 10% of Ethiopia's area.

The Indian rivers interlinking project is a proposed large-scale civil engineering project that aims to effectively manage water resources in India by linking rivers using a network of reservoirs and canals to enhance irrigation and groundwater recharge and reduce persistent floods in some parts and water shortages in other parts of the country. India accounts for 18% of global population and about 4% of the world's water resources. One of the solutions to solve the country's water woes is to link its rivers and lakes.

Singleton is a village, Anglican parish and civil parish in the Chichester district of West Sussex, England. It lies in the Lavant valley, 5 miles (8 km) miles north of Chichester on the A286 road to Midhurst.

Lavant is a civil parish in the Chichester district of West Sussex, England, 2.2 miles (3.5 km) north of Chichester. It includes three villages: Mid Lavant and East Lavant, which are separate Anglican parishes, and the much smaller West Lavant. It takes its name from the River Lavant which flows from East Dean to Chichester.

The River Lavant is a winterbourne that rises at East Dean and flows west to Singleton, then south past West Dean and Lavant to Chichester. From east of Chichester its natural course was south to the sea at Pagham, but the Romans diverted it to flow around the southern walls of Chichester and then west into Chichester Harbour.

The aim of water security is to make the most of water's benefits for humans and ecosystems. The second aim is to limit the risks of destructive impacts of water to an acceptable level. These risks include for example too much water (flood), too little water or poor quality (polluted) water. People who live with a high level of water security always have access to "an acceptable quantity and quality of water for health, livelihoods and production". For example, access to water, sanitation and hygiene services is one part of water security. Some organizations use the term water security more narrowly for water supply aspects only.

Greater Mexico City, a metropolitan area with more than 19 million inhabitants including Mexico's capital with about 9 million inhabitants, faces tremendous water challenges. These include groundwater overexploitation, land subsidence, the risk of major flooding, the impacts of increasing urbanization, poor water quality, inefficient water use, a low share of wastewater treatment, health concerns about the reuse of wastewater in agriculture, and limited cost recovery. Overcoming these challenges is complicated by fragmented responsibilities for water management in Greater Mexico City:

The environmental impact of irrigation relates to the changes in quantity and quality of soil and water as a result of irrigation and the subsequent effects on natural and social conditions in river basins and downstream of an irrigation scheme. The effects stem from the altered hydrological conditions caused by the installation and operation of the irrigation scheme.

The Shule River is the second largest inland river in Gansu Province, China, and one of the three major inland river systems in the Hexi Corridor.

The Autumn of 2000 was the wettest recorded in the United Kingdom since records began in 1766. Several regions of Atlantic Europe from France to Norway received double their average rainfall and there were severe floods and landslides in the southern Alps. In October and November 2000 a successive series of extratropical cyclones caused severe flooding across the UK.

The Albuquerque Basin is a structural basin and ecoregion within the Rio Grande rift in central New Mexico. It contains the city of Albuquerque.




















