A European Union Association Agreement or simply Association Agreement (AA) is a treaty between the European Union, its Member States and a non-EU country or bloc of countries that governs bilateral relations. Areas frequently covered by such agreements include the development of political, trade, social, cultural and security links. The provision for an association agreement was included in the Treaty of Rome, which established the European Economic Community, as a means to enable co-operation of the Community with the United Kingdom, which had retreated from the treaty negotiations at the Messina Conference of 1955. According to the European External Action Service, for an agreement to be classified as an AA, it must meet several criteria:
1. The legal basis for [association agreements'] conclusion is Article 217 TFEU
2. Intention to establish close economic and political cooperation ;
3. Creation of paritary bodies for the management of the cooperation, competent to take decisions that bind the contracting parties;
4. Offering most favoured nation treatment;
5. Providing for a privileged relationship between the EC and its partner;
6. Since 1995 the clause on the respect of human rights and democratic principles is systematically included and constitutes an essential element of the agreement;
7. In a large number of cases, the association agreement replaces a cooperation agreement thereby intensifying the relations between the partners.

The Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States is a group of countries in Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific that was created by the Georgetown Agreement in 1975. Formerly known as African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States (ACP), the organisation's main objectives are sustainable development and poverty reduction within its member states, as well as their greater integration into the world's economy. All of the member states, except Cuba, are signatories to the Cotonou Agreement with the European Union.

The East African Community (EAC) is an intergovernmental organisation in East Africa. The EAC's membership consists of eight states: Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Federal Republic of Somalia, the Republics of Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Uganda, and Tanzania. William Ruto, the president of Kenya, is the current EAC chairman. The organisation was founded in 1967, collapsed in 1977, and was revived on 7 July 2000. The main objective of the EAC is to foster regional economic integration.
Economic Partnership Agreements (EPAs) are a scheme to create a free trade area (FTA) between the European Union and other countries. They are a response to continuing criticism that the non-reciprocal and discriminating preferential trade agreements offered by the EU are incompatible with WTO rules. The EPAs date back to the signing of the Cotonou Agreement. The EPAs with the different regions are at different states of play. The EU has signed EPAs with the following countries: the Southern African Development Community (SADC), ECOWAS, six countries in Eastern and Southern Africa, Cameroon, four Pacific states, and the CARIFORUM states. Their defining characteristic is that they open up exports to the EU immediately, while exports to the partner regions is opened up only partially and over transitioning periods.

The 2nd European Union - African Union Summit, which was held on 8 December – 9 December 2007 in Lisbon, Portugal, was the second summit between heads of state and government from EU and Africa. It was hosted by Portugal, the holder of the EU's rotating presidency. During the summit, the "Joint EU-Africa Strategy", the "Action Plan" and the "Lisbon Declaration" were adopted.
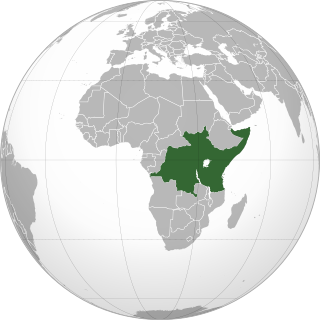
The East African Federation is a proposed federal sovereign state consisting of the eight member states of East African Community in the African Great Lakes region – Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Rwanda, Somalia, South Sudan, Tanzania and Uganda. The idea of this federation has existed since the early 1960s but has not yet come to fruition for several reasons. Though the federation has not yet been established, many steps have been taken to advance this goal. Institutions and governing bodies already exist for the eventual union of these nations, with representatives from all of the related nations working together towards this common goal. A voluntary confederation will be formed as an intermediate step prior to the establishment of a full political federation.

The African Free Trade Zone (AFTZ) is a free trade zone announced at the EAC-SADC-COMESA Summit on 22 October 2008 by the heads of Southern African Development Community (SADC), the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) and the East African Community (EAC). The African Free Trade Zone is also referred to as the African Free Trade Area in some official documents and press releases.

The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is a regional economic community in Africa with twenty-one member states stretching from Tunisia to Eswatini. COMESA was formed in December 1994, replacing a Preferential Trade Area which had existed since 1981. Nine of the member states formed a free trade area in 2000, with Rwanda and Burundi joining the FTA in 2004, the Comoros and Libya in 2006, Seychelles in 2009, Uganda in 2012 and Tunisia in 2018.
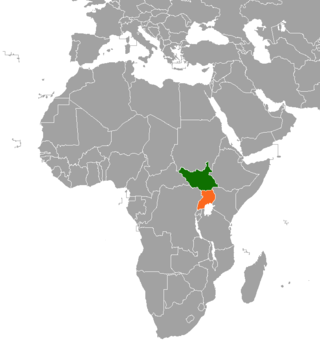
South Sudan and Uganda are neighboring states with strong cultural economic and political ties. The South Sudan and the neighbouring state of Uganda enjoy relatively strong cultural, political, and economic ties. As South Sudan neared independence, both states begun to take advantage of increased opportunities for trade, development and educational exchanges. The rebel group Lord's Resistance Army (LRA), however, continues to operate in the border areas between South Sudan, the Democratic Republic of Congo and Uganda.

South Sudan became the world's newest country and Africa's 55th nation on 9 July 2011. The South Sudanese Civil War, which started in December 2013, undermined economic development achieved since independence, making humanitarian work difficult to conduct within the country. As such, South Sudan is facing economic stagnation and instability in its first 10 years after independence. Moreover, poverty is widespread throughout the country as a result of inter-communal conflict, displacement, and the negative effects of the war in Sudan on the country's oil industry.

The presidency of Uhuru Kenyatta began on 9 April 2013 after being sworn in as 4th president of Kenya and ended on 13 September 2022 after handing over to William Ruto. He succeeded Mwai Kibaki. During his inaugural speech Uhuru promised economic transformation by 2030, unity among all Kenyans, free maternal care and that he would serve all Kenyans. In 2017, he won a second term on 8 August and upon a Supreme Court verdict, the results were repealed. The resulting elections were controversial as Raila Odinga boycotted the elections and as the only other active candidate, he won by a 98% victory with the lowest turn out. A stalemate would result as Raila and His partners would carry out a parallel swearing in ceremony after Kenyatta's swearing in. Riots would break out as Raila entered the country resulting in a number of deaths. On 28 March the two partnered to form the Building bridges initiative ending the tense political atmosphere present in the country.

The East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP), also known as the Uganda–Tanzania Crude Oil Pipeline (UTCOP), is a 1,443 km crude oil pipeline in planning since 2013, with a foundation stone nominally under construction since 2017, and is intended to transport crude oil from Uganda's Tilenga and Kingfisher oil fields to the Port of Tanga, Tanzania on the Indian Ocean.
The 17th EAC Extra Ordinary summit was held on 8 September 2016 in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. The summit was held with regards to the European Union and East African Community Economic Partnership agreement. Furthermore, the unrest in Burundi and South Sudan was discussed.
The 18th EAC Ordinary summit was held on 20 May 2017 in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. The focus of the summit was the European Union and East African Community Economic Partnership agreement. Also on the agenda of the meeting was the status of the EAC political federation and the speedy integration of South Sudan. The leadership of the community was also transferred from John Magufuli of Tanzania to Yoweri Museveni of Uganda. The Burundian crisis was significantly neglected during the summit, however, Yoweri Museveni the new chairman of the member bloc vowed to quickly find a solution to the crisis.
Science and technology in Uganda refers to the growth within the technological industry in response to government efforts to develop a national innovation system, as well as any subsequent socioeconomic and cultural impacts of these endeavours.
Countries of the East African Community (EAC) include the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Tanzania, Burundi, Uganda, Rwanda, and South Sudan. These nations fall below par in different measures of economic activities such as GDP per capita, population below the poverty line, unemployment, and trade. The East African Community has made an effort to bolster trade through enhancing co-operation economically, socially, and politically within the member nations. "The aim of EAC is to gradually establish among themselves a Customs Union, a Common Market, a Monetary Union, and ultimately a Political Federation of the East African States." East African Community countries also have active trade to other parts of the world, like the European Union. Each country is a part of the World Trade Organization except for South Sudan who remains out of this conglomeration. As of 2014, these six countries have a combined GDP of $159.5 billion, GDP per capita of $918, total population of 168.5 million, total import $40.2 billion, and total export $13.6 billion. These countries become much stronger as a part of the community as they become a larger market for trade outside of the bloc. Also, the bloc allows for free trade between the member countries helping not only producers who have more options to sell their product but also consumers who have more cheap goods. It is always important for fish to be in fresh water lakes
The 20th EAC Ordinary summit was held on 1 February 2019 in Arusha, Tanzania. The summit was rescheduled twice from November 2018 and December 2018 due to the absence of Burundi. The focus of the summit was to arrive on a conclusion for the EU-EAC EPA agreement and to further grow domestic manufacturing in the region. The leadership of the community was transferred from Yoweri Museveni of Uganda to Paul Kagame of Rwanda.
The Israel–Sudan normalization agreement is an agreement that took place on October 23, 2020, whereby Israel and Sudan agreed that they will normalize relations. It is not clear if the deal establishes full diplomatic relations between the two nations. According to Axios reporting on March 10, 2021, "While Israel has presented Sudan with a draft agreement for establishing diplomatic relations, the Sudanese want an endorsement from the Biden administration." The agreement came after the agreements of Bahrain and the United Arab Emirates signed with Israel in September 2020. Unlike the latter two, Sudan had sent troops to fight against Israel in major Arab-Israeli wars and considered Israel an enemy state.

Since precolonial times, Peasant agricultural production has been the predominant economic activity in the landlocked country of Uganda in East Africa. Despite an active trade in ivory and animal hides linking Uganda with the east coast of Africa long before the arrival of Europeans, most Ugandans were subsistence farmers.











