
Stealth technology, also termed low observable technology, is a sub-discipline of military tactics and passive and active electronic countermeasures, which covers a range of methods used to make personnel, aircraft, ships, submarines, missiles, satellites, and ground vehicles less visible to radar, infrared, sonar and other detection methods. It corresponds to military camouflage for these parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.

An air-to-air missile (AAM) is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying another aircraft. AAMs are typically powered by one or more rocket motors, usually solid fueled but sometimes liquid fueled. Ramjet engines, as used on the Meteor, are emerging as propulsion that will enable future medium- to long-range missiles to maintain higher average speed across their engagement envelope.

The Tor is an all-weather, low-to medium-altitude, short-range surface-to-air missile system designed for destroying airplanes, helicopters, cruise missiles, unmanned aerial vehicles and short-range ballistic threats (anti-munitions). Originally developed by the Soviet Union under the GRAU designation 9K330 Tor, the system is commonly known by its NATO reporting name, SA-15 "Gauntlet". A navalized variant was developed under the name 3K95 "Kinzhal", also known as the SA-N-9 "Gauntlet". Tor was designed to shoot down guided weapons like the AGM-86 ALCM and BGM-34 day and night, in bad weather and jamming situations. Tor can detect targets while on the move. The vehicle must stop intermittently when firing, although trials have been conducted with the aim of eliminating this restriction.

A counter-battery radar or weapon tracking radar is a radar system that detects artillery projectiles fired by one or more guns, howitzers, mortars or rocket launchers and, from their trajectories, locates the position on the ground of the weapon that fired it. Such radars are a subclass of the wider class of target acquisition radars.

The VERA passive radar is an electronic support measures (ESM) system that uses measurements of time difference of arrival (TDOA) of pulses at three or four sites to accurately detect and track airborne emitters. It is reportedly able to detect military "invisible aircraft". The manufacturer is ERA a.s., based in Pardubice.

The Northrop Grumman MQ-8 Fire Scout is an unmanned autonomous helicopter developed by Northrop Grumman for use by the United States Armed Forces. The Fire Scout is designed to provide reconnaissance, situational awareness, aerial fire support and precision targeting support for ground, air and sea forces. The initial RQ-8A version was based on the Schweizer 330, while the enhanced MQ-8B was derived from the Schweizer 333. The larger MQ-8C Fire Scout variant is based on the Bell 407.

The SCR-584 was an automatic-tracking microwave radar developed by the MIT Radiation Laboratory during World War II. It was one of the most advanced ground-based radars of its era, and became one of the primary gun laying radars used worldwide well into the 1950s. A trailer-mounted mobile version was the SCR-784.

The Pantsir missile system is a family of self-propelled, medium-range surface-to-air missile and anti-aircraft artillery systems. Three types of vehicles make up one system: a missile launcher, a radar truck and a command post. Starting with the Pantsir-S1 as the first version, it is produced by KBP Instrument Design Bureau of Tula, Russia, and is the successor to the Tunguska M1.

ARTHUR is a counter-battery radar system originally developed jointly for and in close co-operation with the Norwegian and Swedish armed forces by Ericsson Microwave Systems in both Sweden and Norway. It is also used by the British Army, under the names mobile artillery monitoring battlefield radar or mobile artillery monitoring battlefield asset (MAMBA).

Mersad is an Iranian low- to mid-range air defense system developed in 2010. It fires Shahin (Falcon) missiles which are reverse-engineered, domestically upgraded versions of the American MIM-23 Hawk surface-to-air missiles. It uses a series of domestically produced radars and electronic devices.

The Northrop Grumman Bat is a medium-altitude unmanned air vehicle originally developed for use by the United States Armed Forces. Designed primarily as an intelligence "ISR" gathering tool, the Bat features 30 lb (14 kg) payload capacity that is unmatched in a 10 ft (3.0 m) wing span.
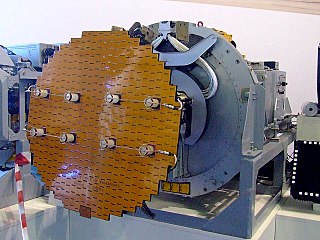
The Zhuk are a family of Russian all-weather multimode airborne radars developed by NIIR Phazotron for multi-role combat aircraft such as the MiG-29 and the Su-27. The PESA versions were also known as the Sokol.
JSC Vega Radio Engineering Corporation is a Russian company specializing in military radar and surveillance and C&C systems for ground-based, airborne and space systems like A-50, Almaz-1 and UAVs. Headquarters located in Moscow at 34, Kutuzovsky Prospekt.
The MAR-1 is an air-to-surface (ASM) and surface-to-surface (SSM) anti-radiation missile (ARM) with GPS/INS capability under development by Brazil's Mectron and the Aerospace Technology and Science Department of the Brazilian Air Force. It is designed to suppress enemy air defenses (SEAD) by targeting surveillance radars and fire-control radars.

The Falco is a tactical unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed and produced by Selex ES. The UAV is designed to be a medium-altitude, medium-endurance surveillance platform capable of carrying a range of payloads, including several types of high-resolution sensors. A larger variant, the Falco EVO, is capable of carrying larger payloads is also available. Neither system is designed to carry weapons, The launch customer, Pakistan, reportedly wanted the Falco armed, a request that Italy rejected.

EL/M-2106 ATAR is a solid state L band medium range tactical 3D radar with active electronically scanned array (AESA) in elevation.

The Ground Master 400 is a mobile long range radar system manufactured by Thales. GM400 is a fully digital active electronically scanned array long-range air defense 3D radar, offering detection from very high to very low altitudes. It tracks a wide range of targets from highly maneuverable tactical aircraft flying below several hundred feet to the unconventional small radar cross section devices, such as UAVs or cruise missiles.

TAI Şimşek is a turbojet-powered radio-controlled high-speed target drone designed, developed and built by Turkish Aerospace Industries (TAI) between 2009-2012 for the needs of the Turkish Armed Forces.















