
Jean-Louis Lebris de Kérouac, known as Jack Kerouac, was an American novelist and poet who, alongside William S. Burroughs and Allen Ginsberg, was a pioneer of the Beat Generation.
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Typically data is collected in text corpora, using either rule-based, statistical or neural-based approaches in machine learning and deep learning.

The Beat Generation was a literary subculture movement started by a group of authors whose work explored and influenced American culture and politics in the post-World War II era. The bulk of their work was published and popularized by Silent Generationers in the 1950s, better known as Beatniks. The central elements of Beat culture are the rejection of standard narrative values, making a spiritual quest, the exploration of American and Eastern religions, the rejection of economic materialism, explicit portrayals of the human condition, experimentation with psychedelic drugs, and sexual liberation and exploration.

Neal Leon Cassady was a major figure of the Beat Generation of the 1950s and the psychedelic and counterculture movements of the 1960s.

On the Road is a 1957 novel by American writer Jack Kerouac, based on the travels of Kerouac and his friends across the United States. It is considered a defining work of the postwar Beat and Counterculture generations, with its protagonists living life against a backdrop of jazz, poetry, and drug use. The novel is a roman à clef, with many key figures of the Beat movement, such as William S. Burroughs, Allen Ginsberg, and Neal Cassady represented by characters in the book, including Kerouac, himself, as the narrator, Sal Paradise.

The Town and the City is a novel by Jack Kerouac, published by Harcourt Brace in 1950. This was the first major work published by Kerouac, who later became famous for his second novel On the Road (1957). Like all of Jack Kerouac's major works, The Town and the City is essentially an autobiographical novel, though less directly so than most of his other works. The Town and the City was written in a conventional manner over a period of years, and much more novelistic license was taken with this work than after Kerouac's adoption of quickly written "spontaneous prose". The Town and the City was written before Kerouac had developed his own style, and it is heavily influenced by Thomas Wolfe.

Desolation Angels is a semi-autobiographical novel written by Beat Generation author Jack Kerouac, which makes up part of his Duluoz Legend. It was published in 1965, but was written years earlier, around the time On the Road was in the process of publication. The events described in the novel take place from 1956-1957. Much of the psychological struggle which the novel's protagonist, Jack Duluoz, undergoes in the novel reflects Kerouac's own increasing disenchantment with the Buddhist philosophy. Throughout the novel, Kerouac discusses his disenchantment with fame, and complicated feelings towards the Beat Generation. He also discusses his relationship with his mother and his friends such as Allen Ginsberg, Neal Cassady, Lucienn Carr and William S. Burroughs. The novel is also notable for being a relatively positive portrayal of homosexuality and homosexual characters, despite its use of words that were at the time considered homophobic slurs.

Computational creativity is a multidisciplinary endeavour that is located at the intersection of the fields of artificial intelligence, cognitive psychology, philosophy, and the arts.
Driver drowsiness detection is a car safety technology which helps prevent accidents caused by the driver getting drowsy. Various studies have suggested that around 20% of all road accidents are fatigue-related, up to 50% on certain roads.
Navlab is a series of autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles developed by teams from The Robotics Institute at the School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University. Later models were produced under a new department created specifically for the research called "The Carnegie Mellon University Navigation Laboratory". Navlab 5 notably steered itself almost all the way from Pittsburgh to San Diego.

In machine learning, feature learning or representation learning is a set of techniques that allows a system to automatically discover the representations needed for feature detection or classification from raw data. This replaces manual feature engineering and allows a machine to both learn the features and use them to perform a specific task.
WaveNet is a deep neural network for generating raw audio. It was created by researchers at London-based AI firm DeepMind. The technique, outlined in a paper in September 2016, is able to generate relatively realistic-sounding human-like voices by directly modelling waveforms using a neural network method trained with recordings of real speech. Tests with US English and Mandarin reportedly showed that the system outperforms Google's best existing text-to-speech (TTS) systems, although as of 2016 its text-to-speech synthesis still was less convincing than actual human speech. WaveNet's ability to generate raw waveforms means that it can model any kind of audio, including music.
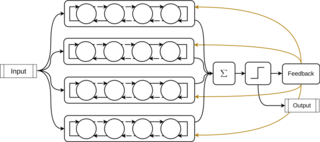
A Tsetlin machine is an artificial intelligence algorithm based on propositional logic.
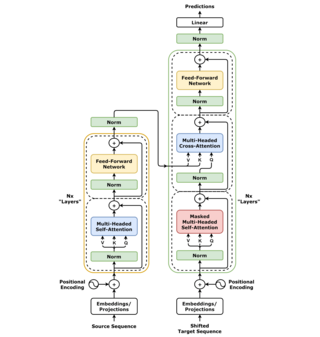
A transformer is a deep learning architecture developed by researchers at Google and based on the multi-head attention mechanism, proposed in the 2017 paper "Attention Is All You Need". Text is converted to numerical representations called tokens, and each token is converted into a vector via lookup from a word embedding table. At each layer, each token is then contextualized within the scope of the context window with other (unmasked) tokens via a parallel multi-head attention mechanism, allowing the signal for key tokens to be amplified and less important tokens to be diminished.
Bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) is a language model introduced in October 2018 by researchers at Google. It learns to represent text as a sequence of vectors using self-supervised learning. It uses the encoder-only transformer architecture. It is notable for its dramatic improvement over previous state-of-the-art models, and as an early example of a large language model. As of 2020, BERT is a ubiquitous baseline in natural language processing (NLP) experiments.

Seq2seq is a family of machine learning approaches used for natural language processing. Applications include language translation, image captioning, conversational models, and text summarization. Seq2seq uses sequence transformation: it turns one sequence into another sequence.
Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNN) are a family of machine learning models for computer vision, and specifically object detection and localization. The original goal of R-CNN was to take an input image and produce a set of bounding boxes as output, where each bounding box contains an object and also the category of the object. In general, R-CNN architectures perform selective search over feature maps outputted by a CNN.

Generative Pre-trained Transformer 2 (GPT-2) is a large language model by OpenAI and the second in their foundational series of GPT models. GPT-2 was pre-trained on a dataset of 8 million web pages. It was partially released in February 2019, followed by full release of the 1.5-billion-parameter model on November 5, 2019.
Prompt engineering is the process of structuring an instruction that can be interpreted and understood by a generative artificial intelligence (AI) model. A prompt is natural language text describing the task that an AI should perform: a prompt for a text-to-text language model can be a query such as "what is Fermat's little theorem?", a command such as "write a poem in the style of Edgar Allan Poe about leaves falling", or a longer statement including context, instructions, and conversation history.
ReRites is a literary work of "Human + A.I. poetry" by David Jhave Johnston that used neural network models trained to generate poetry which the author then edited. ReRites won the Robert Coover Award for a Work of Electronic Literature in 2022.












