
The two-round system, also called ballotage, top-two runoff, or two-round plurality, is a single winner voting method. It is sometimes called plurality-runoff, although this term can also be used for other, closely-related systems such as ranked-choice voting or the exhaustive ballot. It falls under the class of plurality-based voting rules, together with instant-runoff and first-past-the-post (FPP). In a two-round system, both rounds are held under choose-one voting, where the voter marks a single favorite candidate. The two candidates with the most votes in the first round proceed to a second round, where all other candidates are excluded.

The House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of the Netherlands, the States General, the other one being the Senate. It has 150 seats, which are filled through elections using party-list proportional representation. Generally, the house is located in the Binnenhof in The Hague, however, it has temporarily moved to the former building of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs at Bezuidenhoutseweg 67 in The Hague while the Binnenhof is being renovated.
Coombs' method is a ranked voting system. Like instant-runoff (IRV-RCV), Coombs' method is a sequential-loser method, where the last-place finisher according to one method is eliminated in each round. However, unlike in instant-runoff, each round has electors voting against their least-favorite candidate; the candidate ranked last by the most voters is eliminated.

The president of Albania, officially styled the President of the Republic of Albania, is the head of state, commander-in-chief of the military and the representative of the unity of the Albanian people.

The president of the Republic of Lithuania is the head of state of the Republic of Lithuania. The president directs and appoints the executive branch of the Government of Lithuania, represents the nation internationally and is the commander-in-chief of the Lithuanian Armed Forces. The president is directly elected by the citizens of Lithuania for a five-year term, with the office holder limited to serving two terms consecutively. The current president is Gitanas Nausėda who assumed office on July 12, 2019.

The National Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate. The National Assembly's legislators are known as députés, meaning "delegate" or "envoy" in English; etymologically, it is a cognate of the English word deputy, the standard term for legislators in many parliamentary systems.
Bucklin voting is a class of voting methods that can be used for single-member and multi-member districts. As in highest median rules like the majority judgment, the Bucklin winner will be one of the candidates with the highest median ranking or rating. It is named after its original promoter, the Georgist politician James W. Bucklin of Grand Junction, Colorado, and is also known as the Grand Junction system.

Legislative elections were held in France on 10 June and 17 June 2007 to elect the 13th National Assembly of the Fifth Republic, a few weeks after the presidential election run-off on 6 May. 7,639 candidates stood for 577 seats, including France's overseas possessions. Early first-round results projected a large majority for President Nicolas Sarkozy's Union for a Popular Movement (UMP) and its allies; however, second-round results showed a closer race and a stronger left. Nevertheless, the right retained its majority from 2002 despite losing some 40 seats to the Socialists.

The Senate is the upper house of the Parliament of the Czech Republic. The seat of the Senate is Wallenstein Palace in Prague.
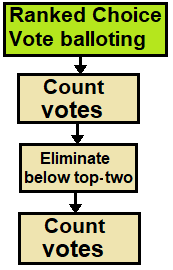
The contingent vote is an electoral system used to elect a single representative in which a candidate requires a majority of votes to win. It is a form of preferential voting. The voter ranks the candidates in order of preference, and when the votes are counted, the first preference votes only are counted. If no candidate has a majority of the votes cast, then all but the two leading candidates are eliminated and the votes received by the eliminated candidates are distributed among the two remaining candidates according to voters' preferences.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Republic of the Congo in 2002; the first round was held on 26 May and the second round on 20 June. The Congolese Labour Party (PCT) and its allies won a majority of seats in the National Assembly.
Block plurality voting is a winner-take-all method for multi-winner elections. Each voter may cast as many votes as the number of seats to be filled. The usual result when the candidates divide into parties is that the most popular party in the district sees its full slate of candidates elected.
Instant-runoff voting (IRV), also known as ranked-choice voting (RCV), preferential voting (PV), or the alternative vote (AV), is a multi-round elimination method where the loser of each round is determined by the first-past-the-post method. In academic contexts, the term instant-runoff voting is generally preferred as it does not run the risk of conflating the method with methods of ranked voting in general.
An electoral or voting system is a set of rules used to determine the results of an election. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices.

Territorial Council elections were held in the French overseas collectivity of Saint Barthélemy on 18 March 2012.

General elections were held in Monaco on 25 February and 3 March 1963. The elections were the first since the promulgation of a new constitution implemented after Prince Rainier III relinquished his absolute rule over the principality, and the first in which women were permitted to vote. The result was a victory for the National and Democratic Union, which won 17 of the 18 seats in the National Council.
The 2020 French municipal elections were held from 15 March to 28 June to renew the municipal councils of the approximately 35,000 French communes. The first round took place on 15 March and the second round was postponed to 28 June due to the COVID-19 pandemic.

The Assembly of French Guiana is the regional legislature of French Guiana. It was first elected in 2015, replacing the General Council of French Guiana and the Regional Council of French Guiana.












