
Valuyki is a town in Belgorod Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Valuy and Oskol Rivers, 150 kilometers (93 mi) east of Belgorod and 15 km north of the Russia–Ukraine border. Population: 33,032 (2021 Census); 35,322 (2010 Census); 35,790 (2002 Census); 34,863 (1989 Soviet census).

The Supreme Council of the Republic of Khakassia is the regional parliament of Khakassia, a federal subject of Russia. A total of 50 deputies are elected for five-year terms.

Parliamentary elections were held in Transnistria on 12 December 2010. All 43 seats of the Supreme Council of Transnistria were up for election. Transnistria uses first past the post with 43 single seat constituencies.

The regional parliaments of Russia are the regional legislatures in the federal subjects of Russia, which have different names but are often collectively referred to as regional parliaments.

Parliamentary elections were held in Transnistria on 29 November 2015, alongside municipal elections.

The Supreme Council of the Republic of Belarus of the 13th convocation was the Belarusian parliament elected in 1995. Parliament began work on January 9, 1996. The powers of the Supreme Council of the 13th convocation were discontinued on November 27, 1996, after the President of Belarus Alexander Lukashenko signed the Law "On termination of powers of the Republic of Belarus of the 13th convocation of the Supreme Council".

Valentin Olegovich Konovalov is a Russian politician who has served as the Head of Khakassia since 2018. He was a local politician before assuming the office.

Parliamentary elections were held in Transnistria on 29 November 2020, alongside municipal elections.

28th Convocation Republic of Belarus deputies to Local Councils of Deputies elections are elections to Belarus Local Councils to Deputies elections conducted on 18 February 2018. Electoral campaign started in November 2017. Citizens of the respective administrative subdivision elect the council for a term of four years under procedure set within the Electoral Code of Republic of Belarus.

Maya Ivanovna Ettyryntyna was a Soviet and Russian politician and former Member of the Federation Council from Chukotka Autonomous Okrug (1994–1996).
The 1996 Russian elections were held from 25 February to 29 December. President Boris Yeltsin won re-election on 3 July, defeating Gennady Zyuganov.
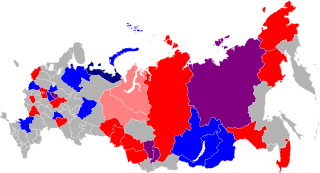
The 2023 Russian elections took place in Russia on Sunday, 10 September 2023, with several regions allowing voting on 8 and 9 September. There were three by-elections to the 8th State Duma, 22 gubernatorial elections, 16 regional parliamentary elections, and many elections on the municipal and local level.
The 2023 People's Khural of Kalmykia election took place on 8–10 September 2023, on common election day. All 27 seats in the People's Khural were up for reelection.
The 2023 Supreme Council of the Republic of Khakassia election took place on 8–10 September 2023, on common election day, coinciding with 2023 Khakassia head election. All 50 seats in the Supreme Council were up for reelection.

The 2024 Russian elections were held in large part, on Sunday, 8 September 2024, with several regions allowing voting on 6 and 7 September. There were three by-elections to the 8th State Duma, 19 gubernatorial elections, 13 regional parliamentary elections, and many elections on the municipal level.
The 2024 Parliament of the Kabardino-Balkarian Republic election took place on 8 September 2024, on common election day. All 70 seats in the Parliament were up for reelection.
The 2024 People's Assembly of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic election took place on 6–8 September 2024, on common election day. All 50 seats in the People's Assembly were up for reelection.
The 2024 State Assembly of the Mari El Republic election took place on 6–8 September 2024, on common election day. All 52 seats in the State Assembly were up for reelection.
The 2024 State Council of the Republic of Tatarstan election took place on 8 September 2024, on common election day. All 100 seats in the State Council were up for reelection.
The 2024 Great Khural of the Republic of Tuva election took place on 8 September 2024, on common election day. All 32 seats in the Great Khural were up for reelection.















