
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a bushfire, desert fire, grass fire, hill fire, peat fire, prairie fire, vegetation fire, or veld fire. Some natural forest ecosystems depend on wildfire. Modern forest management often engages in prescribed burns to mitigate fire risk and promote natural forest cycles. However, controlled burns can turn into wildfires by mistake.

The 2008 wildfire season was one of California's most devastating in the 21st century. While 6,255 fires occurred, about two-thirds as many as in 2007, the total area burned— 1,593,690 acres —far exceeded that of previous years.

Air quality laws govern the emission of air pollutants into the atmosphere. A specialized subset of air quality laws regulate the quality of air inside buildings. Air quality laws are often designed specifically to protect human health by limiting or eliminating airborne pollutant concentrations. Other initiatives are designed to address broader ecological problems, such as limitations on chemicals that affect the ozone layer, and emissions trading programs to address acid rain or climate change. Regulatory efforts include identifying and categorising air pollutants, setting limits on acceptable emissions levels, and dictating necessary or appropriate mitigation technologies.

The 2010 Russian wildfires were several hundred wildfires that broke out across Russia, primarily in the west in summer 2010. They started burning in late July and lasted until early September 2010. The fires were associated with record-high temperatures, which were attributed to climate change—the summer had been the hottest recorded in Russian history—and drought.

From 12 to 16 April 2015, a series of wildfires spread across southern Siberia, Russia. In the Republic of Khakassia, 29 people were killed and 6,000 left homeless. Further east in Zabaykalsky Krai, four people died in wildfires near Chita. Damage was also reported in Inner Mongolia.

The 2015 wildfire season was the largest in Washington state history, with more than one million acres burning across the state from June to September. As many as 3,000 firefighters including 800 Washington National Guard members were deployed to fight the fires. The 17th Field Artillery Brigade of the United States Army also deployed 200 soldiers from Joint Base Lewis–McChord to help fight the fires.

On the morning of 1 July 2016, an Ilyushin Il-76 aircraft configured for aerial firefighting and belonging to the Russian Ministry of Emergency Situations crashed near Lake Baikal northeast of Irkutsk in Siberia, Russia. All ten crew members were killed.

The 2017 Washington wildfires were a series of wildfires that burned over the course of 2017, a year that set weather records for heat and aridity in both Western Washington and Eastern Washington.

The 2018 Washington wildfire season officially began June 1, 2018. A statewide state of emergency was declared by Governor Jay Inslee on July 31.

The 2019 Alberta wildfires have been described by NASA as part of an extreme fire season in the province. In 2019 there were a total of 803,393.32 hectares, which is over 3.5 times more land area burned than in the five-year average burned. The five year average is 747 fires destroying 146,360.08 hectares. There were 644 wildfires recorded in Alberta. By May 31, 10,000 people had been evacuated, 16 homes, and the Steen River CN railway bridge, had been destroyed.

The 2019 Siberian wildfires began in July 2019 in poorly accessible areas of northern Krasnoyarsk Krai, Sakha Republic and Zabaykalsky Krai, all in Siberia, Russia. By the end of the month the size of the fires reached 2,600,000 hectares. As of 30 July, there had been no reported deaths or injuries due to the fires.

The 2020 Washington wildfire season officially began in March 2020. The season was a part of the 2020 Western United States wildfires. By September, wildfires had burned over 713,000 acres, 181 homes had been lost, and one death occurred as a result. The 2020 fire season saw more individual fires than in any other recorded year.
The 2021 Washington wildfire season officially began in March 2021. By late April, all of Eastern Washington had been classified by the United States Drought Monitor as "abnormally dry" with moderate to severe drought conditions. The state had more than 630 wildfires by the first week of July, on par with the state's record 2015 wildfire season.

From June 2021, the taiga forests in Siberia and the Far East region of Russia were hit by unprecedented wildfires, following record-breaking heat and drought. For the first time in recorded history, wildfire smoke reached the North Pole.
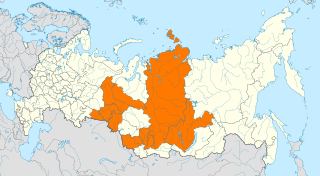
The 2022 Siberian wildfires were a series of wildfires in Russia that began in Siberia in early May 2022. Fires were concentrated in the Krasnoyarsk, Altai, Irkutsk, Kemerovo, Omsk, Kurgan regions, Khakassia and Sakha republics.

The 2022 Washington wildfire season officially began in March 2022. As of August 4, 2022, there have been four large wildfires that have burned 30,800 acres (12,500 ha) across the US state of Washington. This season started quieter than normal due to unusually colder weather that kept Eastern and Southeastern Washington burning index's largely below normal into July. As of October 2022, a total of 140,000 acres (57,000 ha) of land in the state was burned – the fewest number of acres burned since 2012.

Beginning in March 2023, and with increased intensity starting in June, Canada was affected by a record-setting series of wildfires. All 13 provinces and territories were affected, with large fires in Alberta, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, Nova Scotia, Ontario, and Quebec. The 2023 wildfire season had the most area burned in Canada's recorded history, surpassing the 1989, 1995, and 2014 fire seasons, as well as in recorded North American history, surpassing the 2020 Western US wildfire season.

The 2024 wildfires in Canada began as an extension of the record-setting 2023 wildfires. The country experienced an unusually long fire season in 2023 that lasted into the autumn; these fires smouldered through the winter and about 150 re-ignited as early as February 2024. By early May, large wildfires had broken out in Alberta, British Columbia, and Manitoba. Soon after, there were significant fires in Saskatchewan, the Northwest Territories, and Newfoundland and Labrador.

In 2024, far-reaching wildfires ignited and spread across large areas of Russian territory, primarily in Siberia and also in southern regions. The wildfires resulted in a burnt area of 8.8 million hectares by July 18, and carbon emissions of 6.8 megatons by July 1, equaling the combined June–July emissions of 2023 in just one month.

















