
South Korea maintains diplomatic relations with 191 countries. The country has also been a member of the United Nations since 1991, when it became a member state at the same time as North Korea. South Korea has also hosted major international events such as the 1988 Summer Olympics and 2002 World Cup Football Tournament and the 2011 IAAF World Championships Daegu South Korea. Furthermore, South Korea had hosted the 2018 Winter Olympics which took place in Pyeongchang from 9 to 25 February.

Incheon International Airport — or simply Incheon Airport — is the main international airport serving Seoul, the capital of South Korea. It is also one of the largest and busiest airports in the world.

Renault Korea Co., Ltd. is a South Korean car manufacturer headquartered in Busan where its single assembly site is also located, with additional facilities at Seoul (administration), Giheung and Daegu.

Lotte Chilsung Beverage Co., Ltd. is a drink manufacturer in South Korea affiliated with Lotte Corporation. The company's name, Chilsung, signifies "Big Dipper" or seven stars, and its logo displays seven stars aligned in a row.

Daewon Media, formerly Daiwon C&A Holdings, is a South Korean company specializing in character and animation-related business. Founded in 1973, Daewon's subsidiaries include Daewon C.I., Haksan Publishing, and Daewon Broadcasting; it is involved in comic publishing, animation production, video gaming, character licensing, TV animation broadcasting, and animation importing/exporting. Its current chair and co-CEO is Jung Wook and its president and co-CEO is Ahn Hyeon-dong.

Uniqlo Co., Ltd. is a Japanese casual wear designer and retailer.
Boycotts of Japanese products have been conducted by numerous Korean, Chinese and American civilian and governmental organizations in response to real or disputed Japanese aggression and atrocities, whether military, political or economic.

The People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Republic of Korea formally established modern diplomatic relations in August 1992. South Korea was the last Asian country to establish relations with the People's Republic of China. In recent years, China and South Korea have endeavored to boost their strategic and cooperative partnership in numerous sectors, as well as promoting a high level relationship. Trade, tourism and multiculturalism, specifically, have been the most important factors of strengthening two neighbouring countries' cooperative partnership. Despite this, historical, political and cultural disputes have still played several roles on the relations between South Korea and China, especially with China being politically aligned with North Korea.

South Korea's Ministry of Foreign Affairs is in charge of the country's foreign relations, as well as handling matters related to overseas Korean nationals. It was established on 17 July 1948.
Anti-Korean sentiment in China refers to opposition, hostility, hatred, distrust, fear, and general dislike of Korean people or culture in China. This is sometimes referred to in China as the xianhan sentiment, which some have argued has been evoked by perceived Korean arrogance that has challenged the sense of superiority that the Chinese have traditionally associated with their 5,000-year-old civilization.

Legislative elections were held in South Korea on 11 April 2012. The election was won by the ruling Saenuri or New Frontier Party, which renewed its majority in the National Assembly, despite losing seats. The election was read as a bellwether for the presidential election to be held later in the year. The result confounded exit polls and media analysis, which had predicted a closer outcome.

Presidential elections were held in South Korea on 19 December 2012. They were the sixth presidential elections since democratization and the establishment of the Sixth Republic, and were held under a first-past-the-post system, in which there was a single round of voting and the candidate receiving the highest number of votes was elected. Under the South Korean constitution, a president is restricted to a single five-year term in office. The term of the then incumbent president Lee Myung-bak ended on 24 February 2013. According to the Korea Times, 30.7 million people voted with turnout at 75.8%. Park Geun-hye of the Saenuri party was elected the first female South Korean president with 51.6% of the vote opposed to 48.0% for her opponent Moon Jae-in. Park's share of the vote was the highest won by any candidate since the beginning of free and fair direct elections in 1987 and the first such election in which any candidate won a majority. Moreover, as of the 2022 election, this is the latest South Korean presidential election in which the winning candidate won an absolute majority of the vote.

Japan–South Korea relations refers to the diplomatic relations between Japan and the Republic of Korea. As the Sea of Japan and the Korea Strait geographically separate the two nations, political interactions date back from the 6th century when the kingdom of Baekje officially established relations with the Yamato Kingship of Japan. During the ancient era, the southern region of the Korean Peninsula served as the closest port for economic trade and cultural exchange between the Japanese archipelago and mainland Asia. Such relations would continue by the late 19th century when both Japan and Korea undergo modernization from Western powers up until 1910, when Korea became a colony of Japan.

"Do not buy Russian goods!" or "Boycott Russian goods!" is a nonviolent resistance campaign to boycott Russian commerce in Ukraine. The protest started on 14 August 2013 as a reaction to a Russian trade embargo against Ukrainian goods. It was organized by Vidsich on social media. The campaign expanded to mass distribution of leaflets, posters, and stickers in over 45 cities and towns. Having faded by the beginning of the Euromaidan demonstrations in November 2013, it was renewed on 2 March 2014, during the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation and the Russo-Ukrainian War.
There have been campaigns advocating for a boycott of products made in China. Commonly cited reasons for boycotting China include the alleged low quality of products, human rights issues, territorial conflicts involving China, support for separatist movements within China, and objection to more specific matters relating to China, including the government's mismanagement of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Events of 2019 in South Korea.

The Japan–South Korea trade dispute, also known as the Japan–South Korea economic war, was an economic conflict between Japan and South Korea.

Coupang, Inc. is a US-based technology company headquartered in Seattle, Washington and incorporated under the Delaware General Corporation Law. Founded in 2010 by Bom Kim, the company operates a retail business, food delivery service, and OTT streaming service, with offices in South Korea, Taiwan, the United States, India, and Singapore.

Yoon Suk Yeol is a South Korean politician and prosecutor who has served as the 13th president of South Korea since 2022. Following his impeachment, his powers are currently suspended.
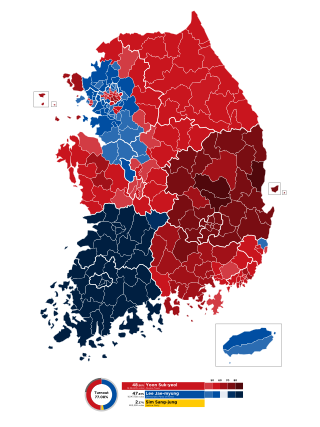
Presidential elections were held in South Korea on 9 March 2022. Under the South Korean constitution, presidents are restricted to a single five-year term, meaning that incumbent president Moon Jae-in was ineligible to run for a second term. Opposition candidate Yoon Suk Yeol of the People Power Party won the election, defeating candidate Lee Jae-myung of the incumbent Democratic Party.
















