Related Research Articles

Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham was a medieval mathematician, astronomer, and physicist of the Islamic Golden Age from present-day Iraq. Referred to as "the father of modern optics", he made significant contributions to the principles of optics and visual perception in particular. His most influential work is titled Kitāb al-Manāẓir, written during 1011–1021, which survived in a Latin edition. The works of Alhazen were frequently cited during the scientific revolution by Isaac Newton, Johannes Kepler, Christiaan Huygens, and Galileo Galilei.

Islamic philosophy is philosophy that emerges from the Islamic tradition. Two terms traditionally used in the Islamic world are sometimes translated as philosophy—falsafa, which refers to philosophy as well as logic, mathematics, and physics; and Kalam, which refers to a rationalist form of Scholastic Islamic theology which includes the schools of Maturidiyah, Ashaira and Mu'tazila.
Early Islamic philosophy or classical Islamic philosophy is a period of intense philosophical development beginning in the 2nd century AH of the Islamic calendar and lasting until the 6th century AH. The period is known as the Islamic Golden Age, and the achievements of this period had a crucial influence in the development of modern philosophy and science. For Renaissance Europe, "Muslim maritime, agricultural, and technological innovations, as well as much East Asian technology via the Muslim world, made their way to western Europe in one of the largest technology transfers in world history." This period starts with al-Kindi in the 9th century and ends with Averroes at the end of 12th century. The death of Averroes effectively marks the end of a particular discipline of Islamic philosophy usually called the Peripatetic Arabic School, and philosophical activity declined significantly in Western Islamic countries, namely in Islamic Spain and North Africa, though it persisted for much longer in the Eastern countries, in particular Persia and India where several schools of philosophy continued to flourish: Avicennism, Illuminationist philosophy, Mystical philosophy, and Transcendent theosophy.

Science in the medieval Islamic world was the science developed and practised during the Islamic Golden Age under the Abbasid Caliphate of Baghdad, the Umayyads of Córdoba, the Abbadids of Seville, the Samanids, the Ziyarids and the Buyids in Persia and beyond, spanning the period roughly between 786 and 1258. Islamic scientific achievements encompassed a wide range of subject areas, especially astronomy, mathematics, and medicine. Other subjects of scientific inquiry included alchemy and chemistry, botany and agronomy, geography and cartography, ophthalmology, pharmacology, physics, and zoology.

Vitello was a Polish friar, theologian, natural philosopher and an important figure in the history of philosophy in Poland.

Kamal al-Din Hasan ibn Ali ibn Hasan al-Farisi or Abu Hasan Muhammad ibn Hasan ) was a Persian Muslim scientist. He made two major contributions to science, one on optics, the other on number theory. Farisi was a pupil of the astronomer and mathematician Qutb al-Din al-Shirazi, who in turn was a pupil of Nasir al-Din Tusi.
Abu-Abdullah Muhammad ibn Īsa Māhānī was a Persian mathematician and astronomer born in Mahan, and active in Baghdad, Abbasid Caliphate. His known mathematical works included his commentaries on Euclid's Elements, Archimedes' On the Sphere and Cylinder and Menelaus' Sphaerica, as well as two independent treatises. He unsuccessfully tried to solve a problem posed by Archimedes of cutting a sphere into two volumes of a given ratio, which was later solved by 10th century mathematician Abū Ja'far al-Khāzin. His only known surviving work on astronomy was on the calculation of azimuths. He was also known to make astronomical observations, and claimed his estimates of the start times of three consecutive lunar eclipses were accurate to within half an hour.
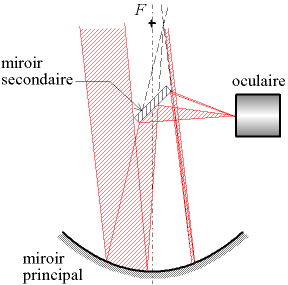
Catoptrics deals with the phenomena of reflected light and image-forming optical systems using mirrors. A catoptric system is also called a catopter (catoptre).
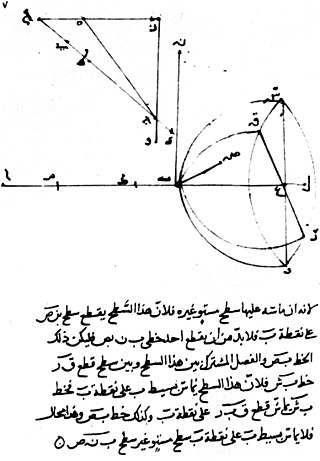
Ibn Sahl was a Persian mathematician and physicist of the Islamic Golden Age, associated with the Buyid court of Baghdad. Nothing in his name allows us to glimpse his country of origin.

The Newton disk, also known as the disappearing color disk, is a well-known physics experiment with a rotating disk with segments in different colors appearing as white when it's spun rapidly about its axis.

Optics began with the development of lenses by the ancient Egyptians and Mesopotamians, followed by theories on light and vision developed by ancient Greek philosophers, and the development of geometrical optics in the Greco-Roman world. The word optics is derived from the Greek term τα ὀπτικά meaning 'appearance, look'. Optics was significantly reformed by the developments in the medieval Islamic world, such as the beginnings of physical and physiological optics, and then significantly advanced in early modern Europe, where diffractive optics began. These earlier studies on optics are now known as "classical optics". The term "modern optics" refers to areas of optical research that largely developed in the 20th century, such as wave optics and quantum optics.

Latin translations of the 12th century were spurred by a major search by European scholars for new learning unavailable in western Europe at the time; their search led them to areas of southern Europe, particularly in central Spain and Sicily, which recently had come under Christian rule following their reconquest in the late 11th century. These areas had been under Muslim rule for a considerable time, and still had substantial Arabic-speaking populations to support their search. The combination of this accumulated knowledge and the substantial numbers of Arabic-speaking scholars there made these areas intellectually attractive, as well as culturally and politically accessible to Latin scholars. A typical story is that of Gerard of Cremona, who is said to have made his way to Toledo, well after its reconquest by Christians in 1085, because he:
arrived at a knowledge of each part of [philosophy] according to the study of the Latins, nevertheless, because of his love for the Almagest, which he did not find at all amongst the Latins, he made his way to Toledo, where seeing an abundance of books in Arabic on every subject, and pitying the poverty he had experienced among the Latins concerning these subjects, out of his desire to translate he thoroughly learnt the Arabic language.
Islamic cosmology is the cosmology of Islamic societies. Islamic cosmology is not a single unitary system, but is inclusive of a number of cosmological systems, including Quranic cosmology, the cosmology of the Hadith collections, as well as those of Islamic astronomy and astrology. Broadly, cosmological conceptions themselves can be divided into thought concerning the physical structure of the cosmos (cosmography) and the origins of the cosmos (cosmogony).

The Book of Optics is a seven-volume treatise on optics and other fields of study composed by the medieval Arab scholar Ibn al-Haytham, known in the West as Alhazen or Alhacen.

During the High Middle Ages, the Islamic world was an important contributor to the global cultural scene, innovating and supplying information and ideas to Europe, via Al-Andalus, Sicily and the Crusader kingdoms in the Levant. These included Latin translations of the Greek Classics and of Arabic texts in astronomy, mathematics, science, and medicine. Translation of Arabic philosophical texts into Latin "led to the transformation of almost all philosophical disciplines in the medieval Latin world", with a particularly strong influence of Muslim philosophers being felt in natural philosophy, psychology and metaphysics. Other contributions included technological and scientific innovations via the Silk Road, including Chinese inventions such as paper, compass and gunpowder.
The natural sciences saw various advancements during the Golden Age of Islam, adding a number of innovations to the Transmission of the Classics. During this period, Islamic theology was encouraging of thinkers to find knowledge. Thinkers from this period included Al-Farabi, Abu Bishr Matta, Ibn Sina, al-Hassan Ibn al-Haytham and Ibn Bajjah. These works and the important commentaries on them were the wellspring of science during the medieval period. They were translated into Arabic, the lingua franca of this period.

The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century.
Roshdi Rashed, born in Cairo in 1936, is a mathematician, philosopher and historian of science, whose work focuses largely on mathematics and physics of the medieval Arab world. His work explores and illuminates the unrecognized Arab scientific tradition, being one of the first historians to study in detail the ancient and medieval texts, their journey through the Eastern schools and courses, their immense contributions to Western science, particularly in regarding the development of algebra and the first formalization of physics.

Ptolemy's Optics is a 2nd-century book on geometrical optics, dealing with reflection, refraction, and colour. The book was most likely written late in Ptolemy's life, after the Almagest, during the 160s. The work is of great importance in the early history of optics. The Greek text has been lost completely. Fragments of the work survive only in the form of a Latin translation, prepared around 1154 by Eugene of Palermo, based on an Arabic translation which was presumably based on the Greek original. Both the Arabic and the Greek texts are lost entirely, and the Latin text is "badly mangled". The Latin text was edited by Albert Lejeune in 1956. The 1996 English translation by Mark Smith is based on Lejeune's Latin text.
References
- ↑ Sabra, A. I. (1989). The Optics of Ibn al-Haytham. Books I–II–III: On Direct Vision. London: The Warburg Institute, University of London. ISBN 0-85481-072-2.
- Sabra also produced an Arabic edition of books IV-V: The Optics of Ibn al-Haytham. IV-V: On Reflection and Images Seen by Reflection. Two volumes: I: Text, Introductions, Concordance Tables; II: Apparatus, Diagrams, Appendices, Analytical Index, Plates. 760pp. Kuwait: The National Council for Culture, Arts and Letters, 2002.
- ↑ History of Science 25, pp. 223–43
- ↑ "The Society: The George Sarton Medal". Archived from the original on September 22, 2010. Retrieved January 29, 2011.