
In computing, multitasking is the concurrent execution of multiple tasks over a certain period of time. New tasks can interrupt already started ones before they finish, instead of waiting for them to end. As a result, a computer executes segments of multiple tasks in an interleaved manner, while the tasks share common processing resources such as central processing units (CPUs) and main memory. Multitasking automatically interrupts the running program, saving its state and loading the saved state of another program and transferring control to it. This "context switch" may be initiated at fixed time intervals, or the running program may be coded to signal to the supervisory software when it can be interrupted.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system (OS) for real-time computing applications that processes data and events that have critically defined time constraints. An RTOS is distinct from a time-sharing operating system, such as Unix, which manages the sharing of system resources with a scheduler, data buffers, or fixed task prioritization in multitasking or multiprogramming environments. All operations must verifiably complete within given time and resource constraints or else fail safe. Real-time operating systems are event-driven and preemptive, meaning the OS can monitor the relevant priority of competing tasks, and make changes to the task priority. Event-driven systems switch between tasks based on their priorities, while time-sharing systems switch the task based on clock interrupts.
Collaborative software or groupware is application software designed to help people working on a common task to attain their goals. One of the earliest definitions of groupware is "intentional group processes plus software to support them."
AppleScript is a scripting language created by Apple Inc. that facilitates automated control of Mac applications. First introduced in System 7, it is currently included in macOS in a package of automation tools. The term AppleScript may refer to the scripting language, to a script written in the language, or to the macOS Open Scripting Architecture that underlies the language.
In computing, scheduling is the action of assigning resources to perform tasks. The resources may be processors, network links or expansion cards. The tasks may be threads, processes or data flows.

iWork is an office suite of applications created by Apple for its macOS, iPadOS, and iOS operating systems, and also available cross-platform through the iCloud website.
A collaborative real-time editor is a type of collaborative software or web application which enables real-time collaborative editing, simultaneous editing, or live editing of the same digital document, computer file or cloud-stored data – such as an online spreadsheet, word processing document, database or presentation – at the same time by different users on different computers or mobile devices, with automatic and nearly instantaneous merging of their edits.
Operational transformation (OT) is a technology for supporting a range of collaboration functionalities in advanced collaborative software systems. OT was originally invented for consistency maintenance and concurrency control in collaborative editing of plain text documents. Its capabilities have been extended and its applications expanded to include group undo, locking, conflict resolution, operation notification and compression, group-awareness, HTML/XML and tree-structured document editing, collaborative office productivity tools, application-sharing, and collaborative computer-aided media design tools. In 2009 OT was adopted as a core technique behind the collaboration features in Apache Wave and Google Docs.
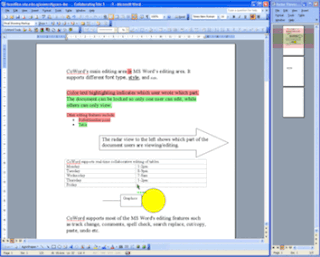
CoWord is a software add-on to Microsoft Word to enable multiple users to edit the same document over the Internet with MS Word. It is a part of the CoOffice suite of collaboration tools for Microsoft Office.

Open Cobalt is a free and open-source software platform for constructing, accessing, and sharing virtual worlds both on local area networks or across the Internet, with no need for centralized servers.
OS 2200 is the operating system for the Unisys ClearPath Dorado family of mainframe systems. The operating system kernel of OS 2200 is a lineal descendant of Exec 8 for the UNIVAC 1108 and was previously known as OS 1100. Documentation and other information on current and past Unisys systems can be found on the Unisys public support website.
ShowDocument is an online web application that allows multiple users to conduct web meetings, upload, share and review documents from remote locations. The service was developed by the HBR Labs company, established in 2007.
Sync.in was a web-based collaborative real-time editor, from Cynapse. It allowed multiple people to edit the same text document simultaneously. Participants could see others' changes in real-time, with each author's text in their own color. A chat box in the sidebar allowed participants to communicate.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Perl programming language:
Google Slides is a presentation program and part of the free, web-based Google Docs suite offered by Google. Google Slides is available as a web application, mobile app for: Android, iOS, and as a desktop application on Google's ChromeOS. The app is compatible with Microsoft PowerPoint file formats. The app allows users to create and edit files online while collaborating with other users in real-time. Edits are tracked by a user with a revision history presenting changes. An editor's position is highlighted with an editor-specific color and cursor and a permissions system regulates what users can do. Updates have introduced features using machine learning, including "Explore," offering and "tasks to other users."

Google Sheets is a spreadsheet application and part of the free, web-based Google Docs Editors suite offered by Google. Google Sheets is available as a web application; a mobile app for: Android, iOS, and as a desktop application on Google's ChromeOS. The app is compatible with Microsoft Excel file formats. The app allows users to create and edit files online while collaborating with other users in real-time. Edits are tracked by which user made them, along with a revision history. Where an editor is making changes is highlighted with an editor-specific color and cursor. A permissions system regulates what users can do. Updates have introduced features that use machine learning, including "Explore", which offers answers based on natural language questions in the spreadsheet. Sheets is one of the services provided by Google that also includes Google Docs, Google Slides, Google Drawings, Google Forms, Google Sites and Google Keep.
In distributed computing, a conflict-free replicated data type (CRDT) is a data structure that is replicated across multiple computers in a network, with the following features:
- The application can update any replica independently, concurrently and without coordinating with other replicas.
- An algorithm automatically resolves any inconsistencies that might occur.
- Although replicas may have different state at any particular point in time, they are guaranteed to eventually converge.

Google Docs is an online word processor and part of the free, web-based Google Docs Editors suite offered by Google. Google Docs is accessible via a web browser as a web-based application and is also available as a mobile app on Android and iOS and as a desktop application on Google's ChromeOS.

Collabora Online is an open source online office suite based on LibreOffice, enabling web-based collaborative real-time editing of word processing documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and vector graphics. Optional apps are available for desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and Chromebooks.










