
The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of Canada's population. Together with Canada's easternmost province, Newfoundland and Labrador, the Maritime provinces make up the region of Atlantic Canada.

Nova Scotia is a province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime provinces.
Telefilm Canada is a Canadian Crown corporation that supports Canada's audiovisual industry. Headquartered in Montreal, Telefilm Canada provides services to the Canadian audiovisual industry with four regional offices in Vancouver, British Columbia; Toronto, Ontario; Montreal, Quebec; and Halifax, Nova Scotia. The primary mandate of the corporation is to finance and promote Canadian productions through its various funds and programs.
In Canada, the Regional Development Agencies (RDA) are the seven federal government agencies responsible for addressing key economic challenges and furthering economic development, diversification, and job creation specific to their respective regions.
New Brunswick Community College (NBCC) is a public college located throughout various locations in New Brunswick, Canada, including Moncton, Miramichi, Fredericton, Saint John, St. Andrews, and Woodstock.

Maritime Union is a proposed political union of the three Maritime provinces of Canada – New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island – to form a single new province.
Local government in Canada can be defined as all elected local authorities which are legally empowered to make decisions on behalf of its electors, excluding the federal government, provincial and territorial governments, and First Nations, Métis and Inuit governments. This can include municipalities, school boards, health authorities, and so on.

CANARIE is the not-for-profit organisation which operates the national backbone network of Canada's national research and education network (NREN). The organisation receives the majority of its funding from the Government of Canada. It supports the development of research software tools; provides cloud resources for startups and small businesses; provides access and identity management services; and supports the development of policies, infrastructure and tools for research data management.
Expenditures by federal and provincial organizations on scientific research and development accounted for about 10% of all such spending in Canada in 2006. These organizations are active in natural and social science research, engineering research, industrial research and medical research.
Crown corporations are government organizations in Canada with a mixture of commercial and public-policy objectives. They are directly and wholly owned by the Crown.

Newfoundland and Labrador has had the same growing pains as other provinces in developing its own form of education and now boasts a very strong, although relatively small, system. The direction of Newfoundland and Labrador's policy has evolved rapidly since the late 1990s, with increased funding, participation rates, accessibility and transferability. Many of the directives the government has been acting upon in the past 10 years have been a result of recommendations that stemmed from a 2005 white paper: Foundation for Success: White Paper on Public Post-Secondary Education. It set the course for furthering the strategic directives of the provincial post-secondary education sector. Some of its recommendations aimed to:

Higher education in Prince Edward Island refers to education provided by higher education institutions in the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island. In Canada, education is the responsibility of the provinces and there is no Canadian federal ministry governing education. Prince Edward Island has two post-secondary institutions authorized to grant degrees: one university, the University of Prince Edward Island, and one college, Maritime Christian College. There are also two community colleges: Holland College, which operates centres across the province, and Collège de l'Île, which offers post secondary education in French. The governing body for higher education in Prince Edward Island is the Department of Innovation and Advanced Learning, headed by the Minister of Innovation and Advanced Learning, the Honourable Allen Roach.

Higher education in New Brunswick refers to education provided by higher education institutions in the Canadian province of New Brunswick. Higher education has a rich history in New Brunswick. The first English-language university in Canada was the University of New Brunswick. Mount Allison University was the first in the British Empire to award a baccalaureate to a woman, Grace Annie Lockhart, B.Sc. in 1875. Education is the responsibility of the provinces in Canada and there is no federal ministry governing it.

Higher education in Nova Scotia refers to education provided by higher education institutions. In Canada, education is the responsibility of the provinces and there is no Canadian federal ministry governing education. Nova Scotia has a population of one million people, but is home to ten public universities and the Nova Scotia Community College, which offers programs at 13 locations.
The Atlantic Canada Organization of Research Networks - Nova Scotia (ACORN-NS) operates an advanced research and education network in Nova Scotia, Canada.

Bernadette Jordan is a Canadian politician who served as Minister of Fisheries, Oceans, and the Canadian Coast Guard from 2019 to 2021. A member of the Liberal Party of Canada, she was elected to represent the riding of South Shore—St. Margarets in the House of Commons in the 2015 election and was defeated by Rick Perkins in 2021.

Cybera is a not-for-profit corporation responsible for the operation of Alberta's Optical Regional Advanced Network. This network, known as CyberaNet, connects Alberta's research universities, colleges, K-12 schools, not-for-profits, and business incubators to one another and to the global grid of research and education networks using optical fibre. Cybera is funded by grants and its membership. The head office is located in the University of Calgary Research Park, with an additional office in downtown Edmonton.

The Digital Repository of Ireland (DRI) is a digital repository for Ireland's humanities, social science and cultural heritage data. It was designed as an open access infrastructure that allows for interactive use and sustained growth. Three institutions, Royal Irish Academy (RIA), Trinity College Dublin (TCD), and Maynooth, currently manage the repository and implement its policies, guidelines and training. The Department of Education and Skills has primarily funded DRI since 2016 through the Higher Education Authority and the Irish Research Council. As of 2018, DRI is home to over 28,000 items.
Donald A. Young was a Canadian scientist whose research greatly impacted potato production in North America, and the international French-fry industry. He is best known for developing the Shepody potato. Released in 1980, Shepody was the first potato developed specifically for the North American French fry market and quickly became popular with farmers. Young received many honours throughout his career, including the prestigious Order of Canada.
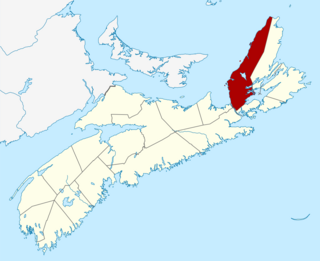
The Municipality of the County of Inverness is a county municipality on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada. It provides local government to about 17,000 residents of the historical county of the same name, except for the incorporated town of Port Hawkesbury and the Whycocomagh 2 Miꞌkmaq reserve, both of which are enclaves. Public services are provided in the areas of recreation, tourism, administration, finance, and public works.










