C is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code, device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems.

In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database.
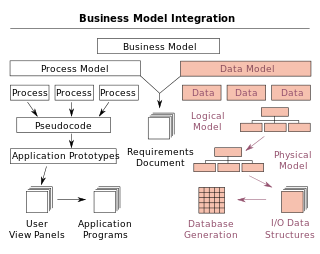
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.
A resource fork is a fork of a file on Apple's classic Mac OS operating system that is used to store structured data. It is one of the two forks of a file, along with the data fork, which stores data that the operating system treats as unstructured. Resource fork capability has been carried over to the modern macOS for compatibility.
Material Exchange Format (MXF) is a container format for professional digital video and audio media defined by a set of SMPTE standards. A typical example of its use is for delivering advertisements to TV stations and tapeless archiving of broadcast TV programs. It is also used as part of the Digital Cinema Package for delivering movies to commercial theaters.
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express data, information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure of a programming language.
External Data Representation (XDR) is a standard data serialization format, for uses such as computer network protocols. It allows data to be transferred between different kinds of computer systems. Converting from the local representation to XDR is called encoding. Converting from XDR to the local representation is called decoding. XDR is implemented as a software library of functions which is portable between different operating systems and is also independent of the transport layer.

A flat-file database is a database stored in a file called a flat file. Records follow a uniform format, and there are no structures for indexing or recognizing relationships between records. The file is simple. A flat file can be a plain text file, or a binary file. Relationships can be inferred from the data in the database, but the database format itself does not make those relationships explicit.
Structured systems analysis and design method (SSADM) is a systems approach to the analysis and design of information systems. SSADM was produced for the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency, a UK government office concerned with the use of technology in government, from 1980 onwards.

Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying certain formal techniques. It may be applied as part of broader Model-driven engineering (MDE) concept.
STEP-file is a widely used data exchange form of STEP. ISO 10303 can represent 3D objects in computer-aided design (CAD) and related information. Due to its ASCII structure, a STEP-file is easy to read, with typically one instance per line. The format of a STEP-file is defined in ISO 10303-21 Clear Text Encoding of the Exchange Structure.
Encoded Archival Description (EAD) is a standard for encoding descriptive information regarding archival records.

The shapefile format is a geospatial vector data format for geographic information system (GIS) software. It is developed and regulated by Esri as a mostly open specification for data interoperability among Esri and other GIS software products. The shapefile format can spatially describe vector features: points, lines, and polygons, representing, for example, water wells, rivers, and lakes. Each item usually has attributes that describe it, such as name or temperature.

CityGML is an open standardised data model and exchange format to store digital 3D models of cities and landscapes. It defines ways to describe most of the common 3D features and objects found in cities and the relationships between them. It also defines different standard levels of detail (LoDs) for the 3D objects, which allows the representation of objects for different applications and purposes, such as simulations, urban data mining, facility management, and thematic inquiries.

EXPRESS is a standard for generic data modeling language for product data. EXPRESS is formalized in the ISO Standard for the Exchange of Product model STEP, and standardized as ISO 10303-11.
PostScript fonts are font files encoded in outline font specifications developed by Adobe Systems for professional digital typesetting. This system uses PostScript file format to encode font information.
System Configuration description Language formerly known as Substation Configuration description Language (SCL) is the language and representation format specified by IEC 61850 for the configuration of electrical substation devices. This includes representation of modeled data and communication services specified by IEC 61850–7–X standard documents. The complete SCL representation and its details are specified in IEC 61850-6 standard document. It includes data representation for substation device entities; its associated functions represented as logical nodes, communication systems and capabilities. The complete representation of data as SCL enhances the different devices of a substation to exchange the SCL files and to have a complete interoperability.
SDTM defines a standard structure for human clinical trial (study) data tabulations and for nonclinical study data tabulations that are to be submitted as part of a product application to a regulatory authority such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The Submission Data Standards team of Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) defines SDTM.

Metadata is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
ISAD(G) (General International Standard Archival Description) defines the elements that should be included in an archival finding aid. It was approved by the International Council on Archives (ICA/CIA) as an international framework standard to register archival documents produced by corporations, persons and families.







