
Ulysses was a robotic space probe whose primary mission was to orbit the Sun and study it at all latitudes. It was launched in 1990 and made three "fast latitude scans" of the Sun in 1994/1995, 2000/2001, and 2007/2008. In addition, the probe studied several comets. Ulysses was a joint venture of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), under leadership of ESA with participation from Canada's National Research Council. The last day for mission operations on Ulysses was 30 June 2009.

The Pioneer Venus project was part of the Pioneer program consisting of two spacecraft, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and the Pioneer Venus Multiprobe, launched to Venus in 1978. The program was managed by NASA's Ames Research Center.
High Energy Transient Explorer 1 (HETE-1) was a NASA astronomical satellite with international participation.

Guion Stewart Bluford Jr. is an American aerospace engineer, retired United States Air Force (USAF) officer and fighter pilot, and former NASA astronaut, in which capacity he became the first African American to go to space. While assigned to NASA, he remained a USAF officer rising to the rank of colonel. He participated in four Space Shuttle flights between 1983 and 1992. In 1983, as a member of the crew of the Orbiter Challenger on the mission STS-8, he became the first African American in space as well as the second person of African descent in space, after Cuban cosmonaut Arnaldo Tamayo Méndez.

STS-39 was the twelfth mission of the NASA Space Shuttle Discovery, and the 40th orbital shuttle mission overall. The primary purpose of the mission was to conduct a variety of payload experiments for the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD).

STS-56 was a NASA Space Shuttle Discovery mission to perform special experiments. The mission was launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on April 8, 1993.

STS-66 was a Space Shuttle program mission that was flown by the Space Shuttle Atlantis. STS-66 launched on 3 November 1994 at 11:59:43.060 am EDT from Launch Pad 39-B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Atlantis landed at Edwards Air Force Base on 14 November 1994 at 10:33:45 am EST.

The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) was a space observatory detecting photons with energies from 20 keV to 30 GeV, in Earth orbit from 1991 to 2000. The observatory featured four main telescopes in one spacecraft, covering X-rays and gamma rays, including various specialized sub-instruments and detectors. Following 14 years of effort, the observatory was launched from Space Shuttle Atlantis during STS-37 on April 5, 1991, and operated until its deorbit on June 4, 2000. It was deployed in low Earth orbit at 450 km (280 mi) to avoid the Van Allen radiation belt. It was the heaviest astrophysical payload ever flown at that time at 17,000 kilograms (37,000 lb).

The Venera 12 was an uncrewed Soviet space mission designed to explore the planet Venus. Venera 12 was launched on 14 September 1978 at 02:25:13 UTC.
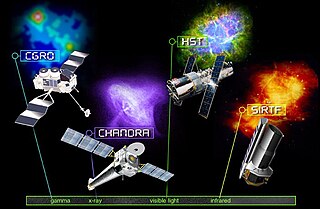
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: gamma rays, X-rays, visible and ultraviolet light, and infrared light.

A gamma-ray spectrometer (GRS) is an instrument for measuring the distribution of the intensity of gamma radiation versus the energy of each photon. The study and analysis of gamma-ray spectra for scientific and technical use is called gamma spectroscopy, and gamma-ray spectrometers are the instruments which observe and collect such data. Because the energy of each photon of EM radiation is proportional to its frequency, gamma rays have sufficient energy that they are typically observed by counting individual photons.

Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager was a NASA solar flare observatory. It was the sixth mission in the Small Explorer program (SMEX), selected in October 1997 and launched on 5 February 2002, at 20:58:12 UTC. Its primary mission was to explore the physics of particle acceleration and energy release in solar flares.

Space Dynamics Laboratory (SDL) is a nonprofit government contractor owned by Utah State University. SDL was formed in 1982 from the merger of Utah State University's Electro Dynamics Laboratories and the University of Utah's Upper Air Research Laboratory. The corporation has been responsible for the design, fabrication, and operation of sensors on over 430 payloads ranging from aircraft and rocket-borne experiments to space shuttle experiments and satellite-based sensor systems. SDL is the Missile Defense Agency's University Affiliated Research Center (UARC) and one of 14 UARCs in the nation. SDL provides sensor systems and supporting technologies to address challenges for the United States government. SDL designs and develops electro-optical sensors, builds small satellites, provides calibration services, and creates real-time data reconnaissance systems.
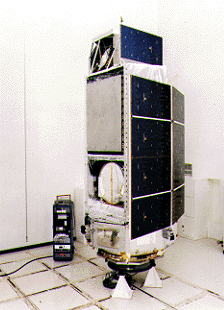
The last of NASA's three High Energy Astronomy Observatories, HEAO 3 was launched 20 September 1979 on an Atlas-Centaur launch vehicle, into a nearly circular, 43.6 degree inclination low Earth orbit with an initial perigeum of 486.4 km. The normal operating mode was a continuous celestial scan, spinning approximately once every 20 min about the spacecraft z-axis, which was nominally pointed at the Sun. Total mass of the observatory at launch was 2,660.0 kilograms (5,864.3 lb).

OSO 7 or Orbiting Solar Observatory 7, before launch known as OSO H is the seventh in the series of American Orbiting Solar Observatory satellites launched by NASA between 1962 and 1975. OSO 7 was launched from Cape Kennedy on 29 September 1971 by a Delta N rocket into a 33.1° inclination, low-Earth orbit, and re-entered the Earth's atmosphere on 9 July 1974. It was built by the Ball Brothers Research Corporation (BBRC), now known as Ball Aerospace, in Boulder Colorado.

Space research is scientific study carried out in outer space, and by studying outer space. From the use of space technology to the observable universe, space research is a wide research field. Earth science, materials science, biology, medicine, and physics all apply to the space research environment. The term includes scientific payloads at any altitude from deep space to low Earth orbit, extended to include sounding rocket research in the upper atmosphere, and high-altitude balloons.
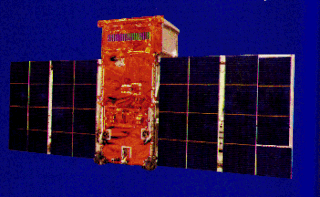
TD-1A, or Thor-Delta 1A, was a European astrophysical research satellite which was launched in 1972. Operated by the European Space Research Organisation, TD-1A made astronomical surveys primarily in the ultraviolet, but also using x-ray and gamma ray detectors.
Dr. Robert E. Huffman (1931–2008) was an American space scientist and author. He specialized in ultraviolet spectroscopy in the earth's upper atmosphere. Working for the United States Air Force, Dr. Huffman managed the Horizon Ultraviolet Program (HUP) experiments on two Space Shuttle flights: Columbia and Discovery.

Student Nitric Oxide Explorer, was a NASA small scientific satellite which studied the concentration of nitric oxide in the thermosphere. It was launched in 1998 as part of NASA's Explorer program. The satellite was the first of three missions developed within the Student Explorer Demonstration Initiative (STEDI) program funded by the NASA and managed by the Universities Space Research Association (USRA). STEDI was a pilot program to demonstrate that high-quality space science can be carried out with small, low-cost free-flying satellites on a time scale of two years from go-ahead to launch. The satellite was developed by the University of Colorado Boulder's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) and had met its goals by the time its mission ended with reentry in December 2003.


















