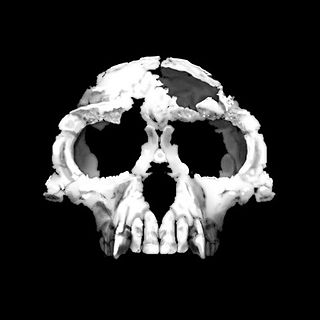
Ardipithecus is a genus of an extinct hominine that lived during the Late Miocene and Early Pliocene epochs in the Afar Depression, Ethiopia. Originally described as one of the earliest ancestors of humans after they diverged from the chimpanzees, the relation of this genus to human ancestors and whether it is a hominin is now a matter of debate. Two fossil species are described in the literature: A. ramidus, which lived about 4.4 million years ago during the early Pliocene, and A. kadabba, dated to approximately 5.6 million years ago. Initial behavioral analysis indicated that Ardipithecus could be very similar to chimpanzees; however, more recent analysis based on canine size and lack of canine sexual dimorphism indicates that Ardipithecus was characterised by reduced aggression, and that they more closely resemble bonobos.

Australopithecus (, OS-trə-lə-PITH-i-kəs, -loh-; or is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genera Homo, Paranthropus, and Kenyanthropus evolved from some Australopithecus species. Australopithecus is a member of the subtribe Australopithecina, which sometimes also includes Ardipithecus, though the term "australopithecine" is sometimes used to refer only to members of Australopithecus. Species include A. garhi, A. africanus, A. sediba, A. afarensis, A. anamensis, A. bahrelghazali, and A. deyiremeda. Debate exists as to whether some Australopithecus species should be reclassified into new genera, or if Paranthropus and Kenyanthropus are synonymous with Australopithecus, in part because of the taxonomic inconsistency.

Donald Carl Johanson is an American paleoanthropologist. He is best known for discovering the fossil of a female hominin australopithecine known as "Lucy" in the Afar Triangle region of Hadar, Ethiopia.

Australopithecus afarensis is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would not take place until the 1970s. From 1972 to 1977, the International Afar Research Expedition—led by anthropologists Maurice Taieb, Donald Johanson and Yves Coppens—unearthed several hundreds of hominin specimens in Hadar, Ethiopia, the most significant being the exceedingly well-preserved skeleton AL 288-1 ("Lucy") and the site AL 333. Beginning in 1974, Mary Leakey led an expedition into Laetoli, Tanzania, and notably recovered fossil trackways. In 1978, the species was first described, but this was followed by arguments for splitting the wealth of specimens into different species given the wide range of variation which had been attributed to sexual dimorphism. A. afarensis probably descended from A. anamensis and is hypothesised to have given rise to Homo, though the latter is debated.
Paleoanthropology or paleo-anthropology is a branch of paleontology and anthropology which seeks to understand the early development of anatomically modern humans, a process known as hominization, through the reconstruction of evolutionary kinship lines within the family Hominidae, working from biological evidence and cultural evidence.

Laetoli is a pre-historic site located in Enduleni ward of Ngorongoro District in Arusha Region, Tanzania. The site is dated to the Plio-Pleistocene and famous for its Hominina footprints, preserved in volcanic ash. The site of the Laetoli footprints is located 45 km south of Olduvai gorge. The location and tracks were discovered by archaeologist Mary Leakey and her team in 1976, and were excavated by 1978. Based on analysis of the footfall impressions "The Laetoli Footprints" provided convincing evidence for the theory of bipedalism in Pliocene Hominina and received significant recognition by scientists and the public. Since 1998, paleontological expeditions have continued under the leadership of Amandus Kwekason of the National Museum of Tanzania and Terry Harrison of New York University, leading to the recovery of more than a dozen new Hominina finds, as well as a comprehensive reconstruction of the paleoecology. The site is a registered National Historic Sites of Tanzania.
Hadar or Hadar Formation is a paleontological fossil site located in Mille district, Administrative Zone 1 of the Afar Region, Ethiopia, 15 km upstream (west) of the A1 road's bridge across the Awash River.

Australopithecus africanus is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived between about 3.3 and 2.1 million years ago in the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of South Africa. The species has been recovered from Taung, Sterkfontein, Makapansgat, and Gladysvale. The first specimen, the Taung child, was described by anatomist Raymond Dart in 1924, and was the first early hominin found. However, its closer relations to humans than to other apes would not become widely accepted until the middle of the century because most had believed humans evolved outside of Africa. It is unclear how A. africanus relates to other hominins, being variously placed as ancestral to Homo and Paranthropus, to just Paranthropus, or to just P. robustus. The specimen "Little Foot" is the most completely preserved early hominin, with 90% of the skeleton intact, and the oldest South African australopith. However, it is controversially suggested that it and similar specimens be split off into "A. prometheus".
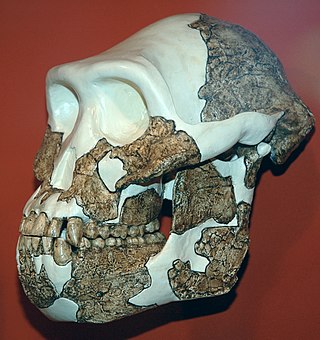
Australopithecus anamensis is a hominin species that lived approximately between 4.3 and 3.8 million years ago and is the oldest known Australopithecus species, living during the Plio-Pleistocene era.

Paranthropus aethiopicus is an extinct species of robust australopithecine from the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2.7–2.3 million years ago. However, it is much debated whether or not Paranthropus is an invalid grouping and is synonymous with Australopithecus, so the species is also often classified as Australopithecus aethiopicus. Whatever the case, it is considered to have been the ancestor of the much more robust P. boisei. It is debated if P. aethiopicus should be subsumed under P. boisei, and the terms P. boisei sensu lato and P. boisei sensu stricto can be used to respectively include and exclude P. aethiopicus from P. boisei.

Australopithecus garhi is a species of australopithecine from the Bouri Formation in the Afar Region of Ethiopia 2.6–2.5 million years ago (mya) during the Early Pleistocene. The first remains were described in 1999 based on several skeletal elements uncovered in the three years preceding. A. garhi was originally considered to have been a direct ancestor to Homo and the human line, but is now thought to have been an offshoot. Like other australopithecines, A. garhi had a brain volume of 450 cc (27 cu in); a jaw which jutted out (prognathism); relatively large molars and premolars; adaptations for both walking on two legs (bipedalism) and grasping while climbing (arboreality); and it is possible that, though unclear if, males were larger than females. One individual, presumed female based on size, may have been 140 cm tall.

The australopithecines, formally Australopithecina or Hominina, are generally any species in the related genera of Australopithecus and Paranthropus. It may also include members of Kenyanthropus, Ardipithecus, and Praeanthropus. The term comes from a former classification as members of a distinct subfamily, the Australopithecinae. They are classified within the Australopithecina subtribe of the Hominini tribe. These related species are sometimes collectively termed australopithecines, australopiths, or homininians. They are the extinct, close relatives of modern humans and, together with the extant genus Homo, comprise the human clade. Members of the human clade, i.e. the Hominini after the split from the chimpanzees, are called Hominina.

Australopithecus bahrelghazali is an extinct species of australopithecine discovered in 1995 at Koro Toro, Bahr el Gazel, Chad, existing around 3.5 million years ago in the Pliocene. It is the first and only australopithecine known from Central Africa, and demonstrates that this group was widely distributed across Africa as opposed to being restricted to East and southern Africa as previously thought. The validity of A. bahrelghazali has not been widely accepted, in favour of classifying the specimens as A. afarensis, a better known Pliocene australopithecine from East Africa, because of the anatomical similarity and the fact that A. bahrelghazali is known only from 3 partial jawbones and an isolated premolar. The specimens inhabited a lakeside grassland environment with sparse tree cover, possibly similar to the modern Okavango Delta, and similarly predominantly ate C4 savanna foods—such as grasses, sedges, storage organs, or rhizomes—and to a lesser degree also C3 forest foods—such as fruits, flowers, pods, or insects. However, the teeth seem ill-equipped to process C4 plants, so its true diet is unclear.

AL 129-1 is a fossilized knee joint of the species Australopithecus afarensis. It was discovered in Hadar, Ethiopia by Donald Johanson in November 1973.

AL 288-1, commonly known as Lucy or Dinkʼinesh, is a collection of several hundred pieces of fossilized bone comprising 40 percent of the skeleton of a female of the hominin species Australopithecus afarensis. It was discovered in 1974 in Ethiopia, at Hadar, a site in the Awash Valley of the Afar Triangle, by Donald Johanson, a paleoanthropologist of the Cleveland Museum of Natural History.

Selam (DIK-1/1) is the fossilized skull and other skeletal remains of a three-year-old Australopithecus afarensis female hominin, whose bones were first found in Dikika, Ethiopia in 2000 and recovered over the following years. Although she has often been nicknamed Lucy's baby, the specimen has been dated at 3.3 million years ago, approximately 100,000 years older than "Lucy".
AL 333, commonly referred to as the "First Family", is a collection of prehistoric hominid teeth and bones. Discovered in 1975 by Donald Johanson's team in Hadar, Ethiopia, the "First Family" is estimated to be about 3.2 million years old, and consists of the remains of at least thirteen individuals of different ages. They are generally thought to be members of the species Australopithecus afarensis. There are multiple theories about the hominids' cause of death and some debate over their species and sexual dimorphism.

LH 4 or Laetoli Hominid 4 is the catalogue number of a fossilized mandible which was discovered by Mary Leakey in 1974 from Laetoli, Tanzania.
Australopithecus deyiremeda is an extinct species of australopithecine from Woranso–Mille, Afar Region, Ethiopia, about 3.5 to 3.3 million years ago during the Pliocene. Because it is known only from three partial jawbones, it is unclear if these specimens indeed represent a unique species or belong to the much better-known A. afarensis. A. deyiremeda is distinguished by its forward-facing cheek bones and small cheek teeth compared to those of other early hominins. It is unclear if a partial foot specimen exhibiting a dextrous big toe can be assigned to A. deyiremeda. A. deyiremeda lived in a mosaic environment featuring both open grasslands and lake- or riverside forests, and anthropologist Fred Spoor suggests it may have been involved in the Kenyan Lomekwi stone-tool industry typically assigned to Kenyanthropus. A. deyiremeda coexisted with A. afarensis, and they may have exhibited niche partitioning to avoid competing with each other for the same resources, such as by relying on different fallback foods during leaner times.
The Middle Awash Project is an international research expedition conducted in the Afar Region of Ethiopia with the goal of determining the origins of humanity. The project has the approval of the Ethiopian Culture Ministry and a strong commitment to developing Ethiopian archaeology, paleontology and geology research infrastructure. This project has discovered over 260 fossil specimens and over 17,000 vertebrate fossil specimens to date ranging from 200,000 to 6,000,000 years in age. Researchers have discovered the remains of four hominin species, the earliest subspecies of homo sapiens as well as stone tools. All specimens are permanently held at the National Museum of Ethiopia, where the project's laboratory work is conducted year round.














