
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a telecommunications standard defined by the American National Standards Institute and ITU-T for digital transmission of multiple types of traffic. ATM was developed to meet the needs of the Broadband Integrated Services Digital Network as defined in the late 1980s, and designed to integrate telecommunication networks. It can handle both traditional high-throughput data traffic and real-time, low-latency content such as telephony (voice) and video. ATM provides functionality that uses features of circuit switching and packet switching networks by using asynchronous time-division multiplexing.
In telecommunications, asynchronous communication is transmission of data, generally without the use of an external clock signal, where data can be transmitted intermittently rather than in a steady stream. Any timing required to recover data from the communication symbols is encoded within the symbols.
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that directs data from one node to the next based on labels rather than network addresses. Whereas network addresses identify endpoints the labels identify established paths between endpoints. MPLS can encapsulate packets of various network protocols, hence the multiprotocol component of the name. MPLS supports a range of access technologies, including T1/E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL.
In computer networking, the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is one of the core communication protocols of the Internet protocol suite used to send messages to other hosts on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Within an IP network, UDP does not require prior communication to set up communication channels or data paths.

Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without the problems of synchronization.
In computer networking, cell relay refers to a method of statistically multiplexing small fixed-length packets, called "cells", to transport data between computers or kinds of network equipment. It is a reliable, connection-oriented packet switched data communications protocol.
Connectionless communication, often referred to as CL-mode communication, is a data transmission method used in packet switching networks in which each data unit is individually addressed and routed based on information carried in each unit, rather than in the setup information of a prearranged, fixed data channel as in connection-oriented communication.
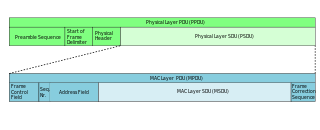
In telecommunications, a protocol data unit (PDU) is a single unit of information transmitted among peer entities of a computer network. It is composed of protocol-specific control information and user data. In the layered architectures of communication protocol stacks, each layer implements protocols tailored to the specific type or mode of data exchange.
A virtual circuit (VC) is a means of transporting data over a data network, based on packet switching and in which a connection is first established across the network between two endpoints. The network, rather than having a fixed data rate reservation per connection as in circuit switching, takes advantage of the statistical multiplexing on its transmission links, an intrinsic feature of packet switching.

In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide end-to-end communication services for applications. It provides services such as connection-oriented communication, reliability, flow control, and multiplexing.
Throughput of a network can be measured using various tools available on different platforms. This page explains the theory behind what these tools set out to measure and the issues regarding these measurements.

Segmentation and reassembly (SAR) is the process used to fragment and reassemble variable length packets into fixed length cells so as to allow them to be transported across Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks or other cell based infrastructures. Since ATM's payload is only 48 bytes, nearly every packet from any other protocol has to be processed in this way. Thus, it is an essential process for any ATM node. It is usually handled by a dedicated chip, called the SAR.
In computer networking and telecommunications, TDM over IP (TDMoIP) is the emulation of time-division multiplexing (TDM) over a packet-switched network (PSN). TDM refers to a T1, E1, T3 or E3 signal, while the PSN is based either on IP or MPLS or on raw Ethernet. A related technology is circuit emulation, which enables transport of TDM traffic over cell-based (ATM) networks.
If a network service wishes to use a broadband network to transport a particular kind of traffic, it must first inform the network about what kind of traffic is to be transported, and the performance requirements of that traffic. The application presents this information to the network in the form of a traffic contract.
ATM Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL5) is an ATM adaptation layer used to send variable-length packets up to 65,535 octets in size across an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) network.
In telecommunications and computer networking, connection-oriented communication is a communication protocol where a communication session or a semi-permanent connection is established before any useful data can be transferred. The established connection ensures that data is delivered in the correct order to the upper communication layer. The alternative is called connectionless communication, such as the datagram mode communication used by Internet Protocol (IP) and User Datagram Protocol, where data may be delivered out of order, since different network packets are routed independently and may be delivered over different paths.
In computer networking, a reliable protocol is a communication protocol that notifies the sender whether or not the delivery of data to intended recipients was successful. Reliability is a synonym for assurance, which is the term used by the ITU and ATM Forum.
ATM Adaptation Layer 2 (AAL2) is an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) adaptation layer, used primarily in telecommunications; for example, it is used for the Iu interfaces in the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, and is also used for transporting digital voice. The standard specifications related to AAL2 are ITU standards I.363.2 and I366.1.

CANaerospace is a higher layer protocol based on Controller Area Network (CAN) which has been developed by Stock Flight Systems in 1998 for aeronautical applications.
Voice over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (VoATM) is a data protocol used to transport packetized voice signals over an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) network. In ATM, the voice traffic is encapsulated using AAL1/AAL2 ATM packets. VoATM over DSL is a similar service, which is used to carry packetized voice signals over a DSL connection.





