Related Research Articles

Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).

Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a hydrocarbon side chain with a branch (a central carbon atom bound to three other carbon atoms). It is classified as a non-polar, uncharged (at physiological pH), branched-chain, aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it. Essential amino acids are necessary in the human diet. In plants isoleucine can be synthesized from threonine and methionine. In plants and bacteria, isoleucine is synthesized from a pyruvate employing leucine biosynthesis enzymes. It is encoded by the codons AUU, AUC, and AUA.
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excreted by cells to create non-cellular structures such as hair, scales, feathers, or exoskeletons. Some nutrients can be metabolically converted into smaller molecules in the process of releasing energy such as for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and fermentation products leading to end-products of water and carbon dioxide. All organisms require water. Essential nutrients for animals are the energy sources, some of the amino acids that are combined to create proteins, a subset of fatty acids, vitamins and certain minerals. Plants require more diverse minerals absorbed through roots, plus carbon dioxide and oxygen absorbed through leaves. Fungi live on dead or living organic matter and meet nutrient needs from their host.
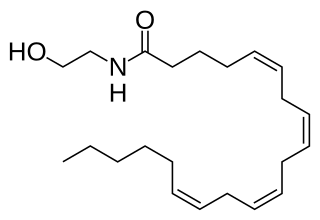
Anandamide (ANA), also referred to as N-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA) is a fatty acid neurotransmitter belonging to the fatty acid derivative group known as N-Acylethanolamine (NAE). Anandamide takes its name from the Sanskrit word ananda, meaning "joy, bliss, delight," plus amide. Anandamide, the first discovered endocannabinoid, engages with the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to the same cannabinoid receptors that THC found in cannabis acts on. Anandamide can be found within tissues in a wide range of animals. It has also been found in plants, such as the cacao tree.

N-acetylcysteine, also known as Acetylcysteine and NAC, is a medication that is used to treat paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose and to loosen thick mucus in individuals with chronic bronchopulmonary disorders, such as pneumonia and bronchitis. It has been used to treat lactobezoar in infants. It can be taken intravenously, orally, or inhaled as a mist. It is also sometimes used as a dietary supplement.

Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis and steatotic liver disease (SLD), is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complications may include cirrhosis, liver cancer, and esophageal varices.

Cysteamine is an organosulfur compound with the formula HSCH2CH2NH2. A white, water-soluble solid, it contains both an amine and a thiol functional groups. It is often used as salts of the ammonium derivative [HSCH2CH2NH3]+ including the hydrochloride, phosphocysteamine, and the bitartrate.The intermediate pantetheine is broken down into cysteamine and pantothenic acid.

Steatohepatitis is a type of fatty liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver. Mere deposition of fat in the liver is termed steatosis, and together these constitute fatty liver changes.
In chemistry, de novo synthesis is the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules such as sugars or amino acids, as opposed to recycling after partial degradation. For example, nucleotides are not needed in the diet as they can be constructed from small precursor molecules such as formate and aspartate. Methionine, on the other hand, is needed in the diet because while it can be degraded to and then regenerated from homocysteine, it cannot be synthesized de novo.

Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a type of chronic liver disease. This condition is diagnosed when there is excessive fat build-up in the liver, and at least one metabolic risk factor. When there is also increased alcohol intake, the term MetALD, or metabolic dysfunction and alcohol associated/related liver disease is used, and differentiated from alcohol-related liver disease (ALD) where alcohol is the predominant cause of the steatotic liver disease. The terms non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis have been used to describe different severities, the latter indicating the presence of further liver inflammation. NAFL is less dangerous than NASH and usually does not progress to it, but this progression may eventually lead to complications, such as cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure, and cardiovascular disease.
Starvation response in animals is a set of adaptive biochemical and physiological changes, triggered by lack of food or extreme weight loss, in which the body seeks to conserve energy by reducing metabolic rate and/or non-resting energy expenditure to prolong survival and preserve body fat and lean mass.

Interleukin 19 (IL-19) is an immunosuppressive protein that belongs to the IL-10 cytokine subfamily.

A ketogenic amino acid is an amino acid that can be degraded directly into acetyl-CoA, which is the precursor of ketone bodies and myelin, particularly during early childhood, when the developing brain requires high rates of myelin synthesis. This is in contrast to the glucogenic amino acids, which are converted into glucose. Ketogenic amino acids are unable to be converted to glucose as both carbon atoms in the ketone body are ultimately degraded to carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle.

The fatty-acid-binding proteins (FABPs) are a family of transport proteins for fatty acids and other lipophilic substances such as eicosanoids and retinoids. These proteins are thought to facilitate the transfer of fatty acids between extra- and intracellular membranes. Some family members are also believed to transport lipophilic molecules from outer cell membrane to certain intracellular receptors such as PPAR. The FABPs are intracellular carriers that “solubilize” the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA), transporting AEA to the breakdown by FAAH, and compounds that bind to FABPs block AEA breakdown, raising its level. The cannabinoids are also discovered to bind human FABPs that function as intracellular carriers, as THC and CBD inhibit the cellular uptake and catabolism of AEA by targeting FABPs. Competition for FABPs may in part or wholly explain the increased circulating levels of endocannabinoids reported after consumption of cannabinoids. Levels of fatty-acid-binding protein have been shown to decline with ageing in the mouse brain, possibly contributing to age-associated decline in synaptic activity.

Succinate receptor 1 (SUCNR1), previously named G protein-coupled receptor 91 (GPR91), is a receptor that is activated by succinate, i.e., the anionic form of the dicarboxylic acid, succinic acid. Succinate and succinic acid readily convert into each other by gaining (succinate) or losing (succinic acid) protons, i.e., H+ (see Ions). Succinate is by far the predominant form of this interconversion in living organisms. Succinate is one of the intermediate metabolites in the citric acid cycle (also termed the TCA cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle). This cycle is a metabolic pathway that operates in the mitochondria of virtually all eucaryotic cells. It consists of a series of biochemical reactions that serve the vital function of releasing the energy stored in nutrient carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Recent studies have found that some of the metabolites in this cycle are able to regulate various physiological and pathological functions in a wide range of cell types. The succinyl CoA in this cycle may release its bound succinate; succinate is one of these mitochondrial-formed bioactive metabolites.

S-Nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) is an endogenous S-nitrosothiol (SNO) that plays a critical role in nitric oxide (NO) signaling and is a source of bioavailable NO. NO coexists in cells with SNOs that serve as endogenous NO carriers and donors. SNOs spontaneously release NO at different rates and can be powerful terminators of free radical chain propagation reactions, by reacting directly with ROO• radicals, yielding nitro derivatives as end products. NO is generated intracellularly by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) family of enzymes: nNOS, eNOS and iNOS while the in vivo source of many of the SNOs is unknown. In oxygenated buffers, however, formation of SNOs is due to oxidation of NO to dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3). Some evidence suggests that both exogenous NO and endogenously derived NO from nitric oxide synthases can react with glutathione to form GSNO.
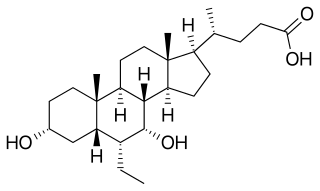
Obeticholic acid (OCA), sold under the brand name Ocaliva, is a semi-synthetic bile acid analogue which has the chemical structure 6α-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid. It is used as a medication used to treat primary biliary cholangitis. Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. hold the worldwide rights to develop OCA outside Japan and China, where it is licensed to Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma.
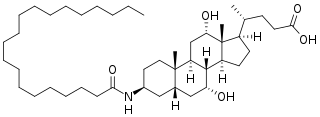
Aramchol is an investigational drug being developed by Galmed Pharmaceuticals as a first-in-class, potentially disease modifying treatment for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH, a more advanced condition of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.

Tropifexor is an investigational drug that acts as an agonist of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR). It was discovered by researchers from Novartis and Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation. Its synthesis and pharmacological properties were published in 2017. It was developed for the treatment of cholestatic liver diseases and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). In combination with cenicriviroc, a CCR2 and CCR5 receptor inhibitor, it is undergoing a phase II clinical trial for NASH and liver fibrosis.

Rubicon is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RUBCN gene. Rubicon is one of the few known negative regulators of autophagy, a cellular process that degrades unnecessary or damaged cellular components. Rubicon is recruited to its sites of action through interaction with the small GTPase Rab7, and impairs the autophagosome-lysosome fusion step of autophagy through inhibition of PI3KC3-C2.
References
- ↑ Harrison, Stephen A.; Baum, Seth J.; Gunn, Nadege T.; Younes, Ziad H.; Kohli, Anita; Patil, Rashmee; Koziel, Margaret J.; Chera, Harinder; Zhao, Jeff; Chakravarthy, Manu V. (December 2021). "Safety, Tolerability, and Biologic Activity of AXA1125 and AXA1957 in Subjects With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 116 (12): 2399–2409. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001375 . ISSN 0002-9270. PMC 8631161 . PMID 34382947.
- ↑ Finnigan, Lucy E.M.; Cassar, Mark Philip; Koziel, Margaret James; Pradines, Joel; Lamlum, Hanan; Azer, Karim; Kirby, Dan; Montgomery, Hugh; Neubauer, Stefan; Valkovič, Ladislav; Raman, Betty (May 2023). "Efficacy and tolerability of an endogenous metabolic modulator (AXA1125) in fatigue-predominant long COVID: a single-centre, double-blind, randomised controlled phase 2a pilot study". eClinicalMedicine. 59: 101946. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101946 . PMC 10102537 . PMID 37223439.
- ↑ Park, Brian. "Orally Active Amino Acid Mixture Fast Tracked for NASH With Liver Fibrosis." Medical Bag, 16 Feb. 2022, p. NA. Gale OneFile: Health and Medicine, link.gale.com/apps/doc/A693790920/HRCA?u=anon~8aede0d3&sid=googleScholar&xid=1e146086. Accessed 3 Dec. 2023.
- ↑ "Axcella antes up in key liver diseases with EMM (endogenous metabolic modulator) compositions" . Retrieved 3 December 2023.
- ↑ Daou, Nadine; Viader, Andreu; Cokol, Murat; Nitzel, Arianna; Chakravarthy, Manu V.; Afeyan, Raffi; Tramontin, Tony; Marukian, Svetlana; Hamill, Michael J. (2021). "A novel, multitargeted endogenous metabolic modulator composition impacts metabolism, inflammation, and fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-relevant primary human cell models". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 11861. Bibcode:2021NatSR..1111861D. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-88913-1. PMC 8178416 . PMID 34088912.