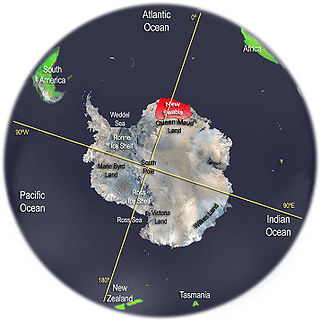
New Swabia was a disputed Antarctic claim by Nazi Germany within the Norwegian territorial claim of Queen Maud Land and is now a cartographic name sometimes given to an area of Antarctica between 20°E and 10°W in Queen Maud Land. New Swabia was explored by Germany in early 1939 and named after that expedition's ship, Schwabenland, itself named after the German region of Swabia.

Booth Island is a rugged, Y-shaped island, 8 kilometres (5 mi) long and rising to 980 m (3,215 ft) off the northwest coast of Kyiv Peninsula in Graham Land, Antarctica in the northeastern part of the Wilhelm Archipelago. The narrow passage between the island and the mainland is the Lemaire Channel.

Adelaide Island is a large, mainly ice-covered island, 139 kilometres (75 nmi) long and 37 kilometres (20 nmi) wide, lying at the north side of Marguerite Bay off the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. The Ginger Islands lie off the southern end. Mount Bodys is the easternmost mountain on Adelaide Island, rising to over 1,220 m. The island lies within the Argentine, British and Chilean Antarctic claims.
Renaud Island is an ice-covered island in the Biscoe Islands of Antarctica, 40 km (25 mi) long and from 6.4 to 16.1 km wide, lying between the Pitt Islands and Rabot Island. It is separated from the Pitt Islands to the northeast by Mraka Sound, and from Lavoisier Island to the southwest by Pendleton Strait.
Trinity Island or Île de la Trinité or Isla Trinidad is an island 24 km (15 mi) long and 10 km (6 mi) wide in the northern part of the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It lies 37 km (23 mi) east of Hoseason Island, 72.6 km (45 mi) south of Deception Island in the South Shetland Islands, and 10.3 km (6 mi) north-northwest of Cape Andreas on the Antarctic Peninsula. The island was named by Otto Nordenskiöld, leader of the 1901-1904 Swedish Antarctic Expedition (SAE) in commemoration of Edward Bransfield's "Trinity Land" of 1820.
Mill Inlet is an ice-filled inlet which recedes 8 nautical miles (15 km) in a northwesterly direction and is some 20 nautical miles (37 km) wide at its entrance between Cape Robinson and Monnier Point, along the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1947 and named for Hugh Robert Mill. It was photographed from the air during 1947 by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne.

Lars Christensen was a Norwegian shipowner and whaling magnate. He was also a philanthropist with a keen interest in the exploration of Antarctica.

Snow Hill Island is an almost completely snowcapped island, 33 km (21 mi) long and 12 km (7.5 mi) wide, lying off the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from James Ross Island to the north-east by Admiralty Sound and from Seymour Island to the north by Picnic Passage. It is one of several islands around the peninsula known as Graham Land, which is closer to Argentina and South America than any other part of the Antarctic continent.

The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria.

Aagaard Glacier, also known as Glaciar Alderete, is an 8-mile (13 km) long Antarctic glacier which lies close to the east of Gould Glacier and flows in a southerly direction into Mill Inlet, on the east coast of Graham Land. It was charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition during December 1947; it was named by the FIDS for Bjarne Aagaard, a Norwegian authority on Antarctic whaling and exploration.

Shambles Glacier is a steep glacier 4 miles (6 km) long and 6 miles (10 km) wide, with very prominent hummocks and crevasses, flowing east between Mount Bouvier and Mount Mangin into Stonehouse Bay on the east side of Adelaide Island. It is the island's largest glacier, and provides an eastern outlet from the giant Fuchs Ice Piedmont which covers the entire western two-thirds of the island. In doing so, Shambles Glacier provides the largest 'gap' in Adelaide Island's north–south running mountain chain.
Aagaard or Ågård is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
Emperor Island is a small island in Marguerite Bay, lying close north-east of the Courtier Islands in the Dion Islands. The islands in this group were discovered and roughly charted in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition. This island was surveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey and so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee because a low rock and shingle isthmus at the south-eastern end of the island was the winter breeding site of emperor penguins.

Proclamation Island is a small rocky island 2.5 nautical miles west of Cape Batterbee and close east of the Aagaard Islands of Antarctica.

Cape Batterbee is a small, rocky point on the coast, the most northerly cape of Enderby Land. It is located 92 km north of Mount Elkins.

The Curzon Islands are a small group of rocky islands lying close off Cape Découverte, Adélie Coast. They were probably sighted in January 1840 by a French expedition under Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville, though not identified as islands on d'Urville's maps. The islands were roughly charted in 1912 by Captain J.K. Davis of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition ship Aurora and named by Mawson for Lord Curzon, the President of the Royal Geographical Society, 1911–14. The islands were mapped in detail by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1950–52.
Bjarne Aagaard Strøm was a Norwegian newspaper editor and politician for the Liberal Party.

Brunvoll Glacier is a broad glacier flowing north to the coast between Murray Monolith and Torlyn Mountain on the east and Scullin Monolith and Mikkelsen Peak on the west. The name was suggested by Bjarne Aagaard for the brothers Arnold and Saebjorn Brunvoll, Norwegian whaling captains who explored along this coast in the Seksern in January 1931.
The Henkes Islands are a group of small islands and rocks 4 kilometres (2 nmi) in extent, lying 2 kilometres (1 nmi) southwest of Avian Island, close off the southern extremity of Adelaide Island, Antarctica. The islands were discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, and named by him for one of the Dutch directors of the Magellan Whaling Company at Punta Arenas. Charcot applied the name to the scattered rocks and islands between Cape Adriasola and Cape Alexandra, and the name was restricted to the group described by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UKAPC) following definitive mapping by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) in 1961 and the British Royal Navy Hydrographic Survey (BRNHS) in 1963. All of the islands in the group were named by UKAPC.

Roscoe Promontory is a massive ice-capped promontory between Aagaard Glacier and Mitterling Glacier on the north side of Mill Inlet, Foyn Coast, Graham Land. The feature was photographed by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) and surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1947. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in 1987 after John H. Roscoe, photogrammetrist on U.S. Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47, and Operation Windmill, 1947–48; author of Antarctic Bibliography, U.S. Naval Photographic Interpretation Center, Department of the Navy, 1951, and Antarctica, Regional Photo Interpretation Series, Department of the Air Force, 1953. The promontory is in proximity to several features named after Antarctic bibliographers.













