Related Research Articles
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. It is essential because, apart from relatively recent results concerning the hydrogen molecular ion, the quantum many-body problem cannot be solved analytically, much less in closed form. While computational results normally complement the information obtained by chemical experiments, it can in some cases predict hitherto unobserved chemical phenomena. It is widely used in the design of new drugs and materials.

Theoretical chemistry is the branch of chemistry which develops theoretical generalizations that are part of the theoretical arsenal of modern chemistry: for example, the concepts of chemical bonding, chemical reaction, valence, the surface of potential energy, molecular orbitals, orbital interactions, and molecule activation.
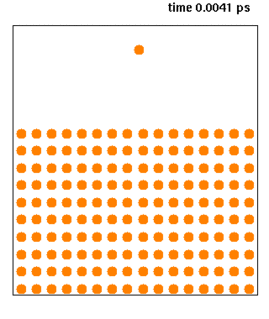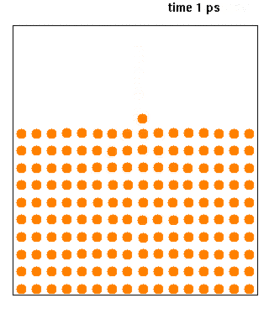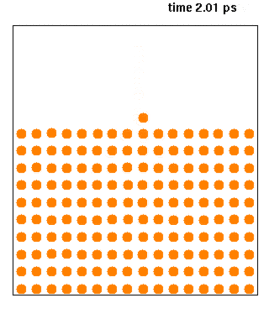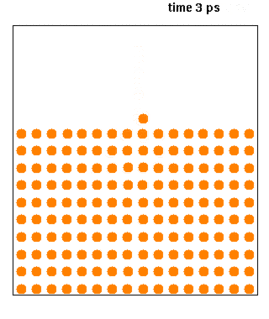
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by numerically solving Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where forces between the particles and their potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanics force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics.
In quantum chemistry, electronic structure is the state of motion of electrons in an electrostatic field created by stationary nuclei. The term encompasses both the wave functions of the electrons and the energies associated with them. Electronic structure is obtained by solving quantum mechanical equations for the aforementioned clamped-nuclei problem.
Vibronic coupling in a molecule involves the interaction between electronic and nuclear vibrational motion. The term "vibronic" originates from the combination of the terms "vibrational" and "electronic", denoting the idea that in a molecule, vibrational and electronic interactions are interrelated and influence each other. The magnitude of vibronic coupling reflects the degree of such interrelation.
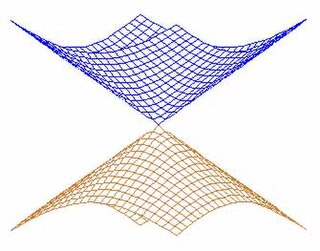
In quantum chemistry, a conical intersection of two or more potential energy surfaces is the set of molecular geometry points where the potential energy surfaces are degenerate (intersect) and the non-adiabatic couplings between these states are non-vanishing. In the vicinity of conical intersections, the Born–Oppenheimer approximation breaks down and the coupling between electronic and nuclear motion becomes important, allowing non-adiabatic processes to take place. The location and characterization of conical intersections are therefore essential to the understanding of a wide range of important phenomena governed by non-adiabatic events, such as photoisomerization, photosynthesis, vision and the photostability of DNA. The conical intersection involving the ground electronic state potential energy surface of the C6H3F3+ molecular ion is discussed in connection with the Jahn–Teller effect in Section 13.4.2 on pages 380-388 of the textbook by Bunker and Jensen.
The COLUMBUS PROGRAMS are a computational chemistry software suite for calculating ab initio molecular electronic structures, designed as a collection of individual programs communicating through files. The programs focus on extended multi-reference calculations of atomic and molecular ground and excited states. In addition to standard classes of reference wave functions such as CAS and RAS, calculations can be performed with selected configurations. Some features employ the atomic orbital integrals and gradient routines from the Dalton program suite. COLUMBUS is available free of charge under license.
Semi-empirical quantum chemistry methods are based on the Hartree–Fock formalism, but make many approximations and obtain some parameters from empirical data. They are very important in computational chemistry for treating large molecules where the full Hartree–Fock method without the approximations is too expensive. The use of empirical parameters appears to allow some inclusion of electron correlation effects into the methods.
Ab initio quantum chemistry methods are computational chemistry methods based on quantum chemistry. The term ab initio was first used in quantum chemistry by Robert Parr and coworkers, including David Craig in a semiempirical study on the excited states of benzene. The background is described by Parr. Ab initio means "from first principles" or "from the beginning", implying that the only inputs into an ab initio calculation are physical constants. Ab initio quantum chemistry methods attempt to solve the electronic Schrödinger equation given the positions of the nuclei and the number of electrons in order to yield useful information such as electron densities, energies and other properties of the system. The ability to run these calculations has enabled theoretical chemists to solve a range of problems and their importance is highlighted by the awarding of the Nobel prize to John Pople and Walter Kohn.
The Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research was founded in 1969 and is one of the 82 Max Planck Institutes of the Max Planck Society. It is located on a campus in Stuttgart, together with the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems.
Car–Parrinello molecular dynamics or CPMD refers to either a method used in molecular dynamics or the computational chemistry software package used to implement this method.
Todd J. Martínez is a David Mulvane Ehrsam and Edward Curtis Franklin Professor of Chemistry at Stanford University and a Professor of Photon Science at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
Molecular modeling on GPU is the technique of using a graphics processing unit (GPU) for molecular simulations.

CP2K is a freely available (GPL) quantum chemistry and solid state physics program package, written in Fortran 2008, to perform atomistic simulations of solid state, liquid, molecular, periodic, material, crystal, and biological systems. It provides a general framework for different methods: density functional theory (DFT) using a mixed Gaussian and plane waves approach (GPW) via LDA, GGA, MP2, or RPA levels of theory, classical pair and many-body potentials, semi-empirical and tight-binding Hamiltonians, as well as Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) hybrid schemes relying on the Gaussian Expansion of the Electrostatic Potential (GEEP). The Gaussian and Augmented Plane Waves method (GAPW) as an extension of the GPW method allows for all-electron calculations. CP2K can do simulations of molecular dynamics, metadynamics, Monte Carlo, Ehrenfest dynamics, vibrational analysis, core level spectroscopy, energy minimization, and transition state optimization using NEB or dimer method.
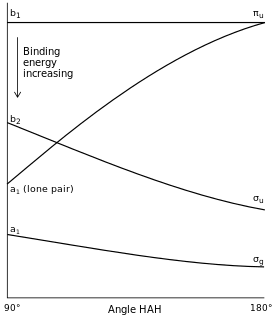
Walsh diagrams, often called angular coordinate diagrams or correlation diagrams, are representations of calculated orbital binding energies of a molecule versus a distortion coordinate, used for making quick predictions about the geometries of small molecules. By plotting the change in molecular orbital levels of a molecule as a function of geometrical change, Walsh diagrams explain why molecules are more stable in certain spatial configurations.
TeraChem is a computational chemistry software program designed for CUDA-enabled Nvidia GPUs. The initial development started at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and was subsequently commercialized. It is currently distributed by PetaChem, LLC, located in Silicon Valley. As of 2020, the software package is still under active development.

Newton-X is a general program for molecular dynamics simulations beyond the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. It has been primarily used for simulations of ultrafast processes in photoexcited molecules. It has also been used for simulation of band envelops of absorption and emission spectra.

Oleg V. Prezhdo is a Ukrainian–American physical chemist whose research focuses on non-adiabatic molecular dynamics and time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT). His research interests range from fundamental aspects of semi-classical and quantum-classical physics to excitation dynamics in condensed matter and biological systems. His research group focuses on the development of new theoretical models and computational tools aimed at understanding chemical reactivity and energy transfer at a molecular level in complex condensed phase environment. Since 2014, he is a professor of chemistry and of physics & astronomy at the University of Southern California.
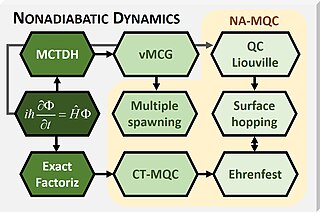
Mixed quantum-classical (MQC) dynamics is a class of computational theoretical chemistry methods tailored to simulate nonadiabatic (NA) processes in molecular and supramolecular chemistry. Such methods are characterized by:
- Propagation of nuclear dynamics through classical trajectories;
- Propagation of the electrons through quantum methods;
- A feedback algorithm between the electronic and nuclear subsystems to recover nonadiabatic information.
Anastassia N. Alexandrova is an American chemist who is a Professor at the University of California, Los Angeles. Her research considers the computational design of functional materials.
References
- Ab Initio Multiple Spawning: Photochemistry from First Principles Quantum Molecular Dynamics, M. Ben-Nun, Jason Quenneville, and Todd J. Martínez, J. Phys. Chem. A104 (2000), #22, pp. 5161–5175. DOI 10.1021/jp994174i.
- Nonadiabatic molecular dynamics: Validation of the multiple spawning method for a multidimensional problem, M. Ben-Nun and Todd J. Martínez, Journal of Chemical Physics108, #17 (May 1, 1998), pp. 7244–7257. DOI 10.1063/1.476142.