Related Research Articles

Marcus Licinius Crassus was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome".
Year 53 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Calvinus. The denomination 53 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Gaius Cassius Longinus was a Roman senator and general best known as a leading instigator of the plot to assassinate Julius Caesar on 15 March 44 BC. He was the brother-in-law of Brutus, another leader of the conspiracy. He commanded troops with Brutus during the Battle of Philippi against the combined forces of Mark Antony and Octavian, Caesar's former supporters, and committed suicide after being defeated by Mark Antony.
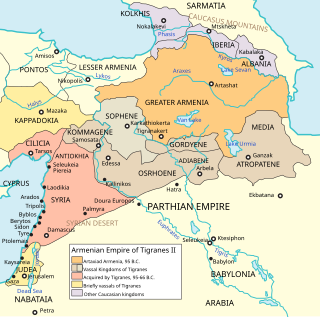
Osroene or Osrhoene was an ancient region and state in Upper Mesopotamia. The Kingdom of Osroene, also known as the "Kingdom of Edessa", according to the name of its capital city, existed from the 2nd century BC, up to the 3rd century AD, and was ruled by the Abgarid dynasty. Generally allied with the Parthians, the Kingdom of Osroene enjoyed semi-autonomy to complete independence from the years of 132 BC to AD 214. The kingdom's population was of mixed culture, being Syriac-speaking from the earliest times. The city's cultural setting was fundamentally Syriac, alongside strong Greek and Parthian influences, though some Arab cults were also attested at Edessa.

The Battle of Carrhae was fought in 53 BC between the Roman Republic and the Parthian Empire near the ancient town of Carrhae. An invading force of seven legions of Roman heavy infantry under Marcus Licinius Crassus was lured into the desert and decisively defeated by a mixed cavalry army of heavy cataphracts and light horse archers led by the Parthian general Surena. On such flat terrain, the Legion proved to have no viable tactics against the highly-mobile Parthian horsemen, and the slow and vulnerable Roman formations were surrounded, exhausted by constant attacks, and eventually crushed. Crassus was killed along with the majority of his army. It is commonly seen as one of the earliest and most important battles between the Roman and Parthian Empires and one of the most crushing defeats in Roman history. According to the poet Ovid in Book 6 of his poem Fasti, the battle occurred on 9 June.

Phraates IV was King of Kings of the Parthian Empire from 37 to 2 BC. He was the son and successor of Orodes II, and was given the throne after the death of his brother Pacorus I. Phraates IV soon murdered all his brothers, and also possibly his father. His actions alienated the Armenians and also some of his nobles, including the distinguished Monaeses, who fled to the Roman triumvir Mark Antony, but shortly returned and reconciled with Phraates IV.

Orodes II, was King of Kings of the Parthian Empire from 57 BC to 37 BC. He was a son of Phraates III, whom he murdered in 57 BC, assisted by his elder brother Mithridates IV. The two brothers quickly fell out and entered into a dynastic struggle, in which Orodes was triumphant.

Artavasdes II, also known as Artavazd II, was king of Armenia from 55 BC to 34 BC. A member of the Artaxiad dynasty, he was the son and successor of Tigranes the Great, who ascended the throne of a still powerful and independent state. His mother was Cleopatra of Pontus, thus making his maternal grandfather the prominent King of Pontus Mithridates VI Eupator. Like his father, Artavasdes continued using the title of King of Kings, as seen from his coins.

Pacorus I was a Parthian prince, who was the son and heir of Orodes II. The numismatist David Sellwood deduced that Pacorus ruled in c. 39 BC. It is uncertain whether Pacorus ruled alongside his father, or ruled independently. His wife was an unnamed Armenian princess, who was a sister of the Artaxiad king of Armenia, Artavasdes II.

Vologases IV was King of Kings of the Parthian Empire from 147 to 191. He was the son of Mithridates V. Vologases spent the early years of his reign re-asserting Parthian control over the Kingdom of Characene. From 161 to 166, he waged war against the Roman Empire; although initially successful, conquering Armenia and Syria, he was eventually pushed back, briefly losing control of the Parthian capitals of Seleucia and Ctesiphon to the Romans. The Romans suffered heavy losses from a plague erupting from Seleucia in 166, forcing them to withdraw. The war ended soon afterward, with Vologases losing most of northern Mesopotamia to the Romans. He died in 191 and was succeeded by his son Vologases V.

The Parthian Empire, also known as the Arsacid Empire, was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquering the region of Parthia in Iran's northeast, then a satrapy (province) under Andragoras, who was rebelling against the Seleucid Empire. Mithridates I greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce.
House of Suren or Surenas is one of two[c] Parthian noble families explicitly mentioned by name in sources dateable to the Arsacid period.
Surena or Suren, also known as Rustaham Suren, was a Parthian spahbed during the first century BC. He was the leader of the House of Suren and was best known for defeating the Romans in the Battle of Carrhae. Under his command, the Parthians decisively defeated a numerically superior Roman invasion force under the command of Marcus Licinius Crassus. It is commonly seen as one of the earliest and most important battles between the Roman and Parthian empires and one of the most crushing defeats in Roman history.
The Roman–Parthian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Parthian Empire and the Roman Republic and Roman Empire. It was the first series of conflicts in what would be 682 years of Roman–Persian Wars.

Antony's Atropatene campaign, also known as Antony's Parthian campaign, was a military campaign by Mark Antony, the eastern triumvir of the Roman Republic, against the Parthian Empire under Phraates IV.

Julius Caesar's planned invasion of the Parthian Empire was a planned war of the Roman Republic against the Parthian Empire. The assassination of Julius Caesar in 44 BC prevented the invasion from taking place.
The Abgarid dynasty was a dynasty of Nabataean Arab origin. Members of the dynasty, the Abgarids, reigned between 134 BC and 242 AD over Edessa and Osroene in Upper Mesopotamia. Some members of the dynasty bore Iranian names, while others had Arabic names, including Abgar itself. J.B. Segal notes that the names ending in "-u" are "undoubtedly Nabatean". The Abgarid dynasts spoke "a form of Aramaic".
The siege of Edessa took place in 165 when the Roman Empire, under Emperor Lucius Verus, besieged the city of Edessa, held by the Parthian Empire.
The siege of Edessa took place in 163 when the Parthian Empire, under Vologases IV, besieged the city of Edessa, held by the Roman Empire.
Silaces was a Parthian commander who fought against the Roman general and triumvir Marcus Licinius Crassus. Initially the satrap of Ichnae, a fortress in Mesopotamia, he was defeated and wounded by Crassus' forces, and fled to the Parthian court, where he informed king Orodes II of the Roman invasion. Silaces later commanded the Parthian contingent alongside Surena at the Battle of Carrhae in 53 BC, where Crassus was defeated and killed. Crassus' defeat at Carrhae was one of the worst military defeats of Roman history. Parthia's victory cemented its reputation as a formidable if not equal power with Rome. While Orodes and Artavasdes II of Armenia were observing a play of The Bacchae of Euripides at the Armenian court in honor of the wedding of Orodes' son Pacorus I and Artavasdes' sister, Silaces announced the news of the victory at Carrhae, and put the head of Crassus at Orodes' feet. The head was given to the producer of the play, who decided to use Crassus' actual severed head in place of the stage-prop head of Pentheus.
References
- ↑ Segal 1982, pp. 210–213.
- ↑ Plutarch. Life of Crassus, 21.1: φύλαρχος Ἀράβων Ἄβγαρος ὄνομα