Related Research Articles

Alexander of Aphrodisias was a Peripatetic philosopher and the most celebrated of the Ancient Greek commentators on the writings of Aristotle. He was a native of Aphrodisias in Caria and lived and taught in Athens at the beginning of the 3rd century, where he held a position as head of the Peripatetic school. He wrote many commentaries on the works of Aristotle, extant are those on the Prior Analytics, Topics, Meteorology, Sense and Sensibilia, and Metaphysics. Several original treatises also survive, and include a work On Fate, in which he argues against the Stoic doctrine of necessity; and one On the Soul. His commentaries on Aristotle were considered so useful that he was styled, by way of pre-eminence, "the commentator".

Proclus Lycius, called Proclus the Successor, was a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher, one of the last major classical philosophers of late antiquity. He set forth one of the most elaborate and fully developed systems of Neoplatonism and, through later interpreters and translators, exerted an influence on Byzantine philosophy, Early Islamic philosophy, Scholastic philosophy, and German Idealism, especially G.W.F. Hegel, who called Proclus's Platonic Theology "the true turning point or transition from ancient to modern times, from ancient philosophy to Christianity."
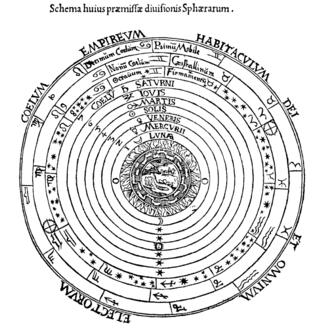
The celestial spheres, or celestial orbs, were the fundamental entities of the cosmological models developed by Plato, Eudoxus, Aristotle, Ptolemy, Copernicus, and others. In these celestial models, the apparent motions of the fixed stars and planets are accounted for by treating them as embedded in rotating spheres made of an aetherial, transparent fifth element (quintessence), like gems set in orbs. Since it was believed that the fixed stars did not change their positions relative to one another, it was argued that they must be on the surface of a single starry sphere.
Richard Henry Popkin was an American academic philosopher who specialized in the history of enlightenment philosophy and early modern anti-dogmatism. His 1960 work The History of Scepticism from Erasmus to Descartes introduced one previously unrecognized influence on Western thought in the seventeenth century, the Pyrrhonian Scepticism of Sextus Empiricus. Popkin also was an internationally acclaimed scholar on Christian millenarianism and Jewish messianism.
The Laws is Plato's last and longest dialogue. The conversation depicted in the work's twelve books begins with the question of who is given the credit for establishing a civilization's laws. Its musings on the ethics of government and law have established it as a classic of political philosophy alongside Plato's more widely read Republic.

On the Heavens is Aristotle's chief cosmological treatise: written in 350 BC, it contains his astronomical theory and his ideas on the concrete workings of the terrestrial world. It should not be confused with the spurious work On the Universe.
On the Universe is a theological and scientific treatise included in the Corpus Aristotelicum but usually regarded as spurious. It was likely published between the 3rd century BCE and the 2nd century CE. The work discusses cosmological, geological, and meteorological subjects, alongside a consideration of the role an independent god plays in maintaining the universe.
Metaphysics is one of the principal works of Aristotle, in which he develops the doctrine that he calls First Philosophy. The work is a compilation of various texts treating abstract subjects, notably substance theory, different kinds of causation, form and matter, the existence of mathematical objects and the cosmos, which together constitute much of the branch of philosophy later known as metaphysics.
Olympiodorus the Younger was a Neoplatonist philosopher, astrologer and teacher who lived in the early years of the Byzantine Empire, after Justinian's Decree of 529 AD which closed Plato's Academy in Athens and other pagan schools. Olympiodorus was the last pagan to maintain the Platonist tradition in Alexandria ; after his death the School passed into the hands of Christian Aristotelians, and was eventually moved to Constantinople. He is not to be confused with Olympiodorus the Deacon, a contemporary Alexandrian writer of Bible commentaries.
Diairesis is a form of classification used in ancient logic that serves to systematize concepts and come to definitions. When defining a concept using diairesis, one starts with a broad concept, then divides this into two or more specific sub-concepts, and this procedure is repeated until a definition of the desired concept is reached. Aristotle makes extensive use of diaresis in categorization as basis for syllogizing. He makes clear, however, that definition by diaresis does not in itself prove anything. Apart from this definition, the procedure also results in a taxonomy of other concepts, ordered according to a general–specific relation.

The Theology of Aristotle, also called Theologia Aristotelis is a paraphrase in Arabic of parts of Plotinus' Six Enneads along with Porphyry's commentary. It was traditionally attributed to Aristotle, but as this attribution is certainly untrue it is conventional to describe the author as "Pseudo-Aristotle". It had a significant effect on early Islamic philosophy, due to Islamic interest in Aristotle. Al-Kindi (Alkindus) and Avicenna, for example, were influenced by Plotinus' works as mediated through the Theology and similar works. The translator attempted to integrate Aristotle's ideas with those of Plotinus — while trying to make Plotinus compatible with Christianity and Islam, thus yielding a unique synthesis.
Lawrence Krader was an American socialist anthropologist and ethnologist.
David Neil Sedley FBA is a British philosopher and historian of philosophy. He was the seventh Laurence Professor of Ancient Philosophy at Cambridge University.
Neoplatonism is a version of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a series of thinkers. Among the common ideas it maintains is monism, the doctrine that all of reality can be derived from a single principle, "the One".
On Breath is a philosophical treatise included in the Corpus Aristotelicum but usually regarded as spurious. Its opening sentence raises the question: "What is the mode of growth, and the mode of maintenance, of the natural vital spirit (pneuma)?"
Sander Griffioen is a Dutch philosopher, and Emeritus Professor for intercultural philosophy at the Vrije Universiteit in Amsterdam.

Otto Dirk Duintjer was a Dutch philosopher.
Charles H. Kahn was a classicist and professor emeritus of philosophy at the University of Pennsylvania. His work focused on early Greek philosophy, up to the times of Plato. His 1960 monograph on Anaximander was still as of 2020 the most important reference work on the subject, and his 1979 edition of the Heraclitus fragments likewise remained the most widely cited English translation of Heraclitus, more or less representing the 'standard interpretation' for non-expert scholars.

Arie Abraham (Ary) Kampman was a Dutch scholar of Ancient Near Eastern studies, an initiator of scholarly societies and journals, and a secondary school teacher. Kampman obtained his Dutch PhD degree with professor Frans de Liagre Böhl on the 1945 thesis De historische beteekenis der Hethietische vestingbouwkunde. In 1939 he was a founder of the Nederlands Archaeologisch Instituut voor het Nabije Oosten, the predecessor of the present The Netherlands Institute for the Near East.
Jaap Mansfeld is a Dutch Emeritus Professor of philosopher and a historian of philosophy.