Keynesian economics are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand strongly influences economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the productive capacity of the economy. Instead, it is influenced by a host of factors – sometimes behaving erratically – affecting production, employment, and inflation.

Microeconomics is a branch of mainstream economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the national economy as whole, which is studied in macroeconomics.

In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of the euro.
Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. It states that the reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of water, for example, owes to the greater additional satisfaction of the diamonds over the water. Thus, while the water has greater total utility, the diamond has greater marginal utility.
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. But the concept of equilibrium in economics also applies to imperfectly competitive markets, where it takes the form of a Nash equilibrium.

In economics, a country's current account records the value of exports and imports of both goods and services and international transfers of capital. It is one of the three components of its balance of payments, the others being the capital account and the financial account. Current account measures the nation's earnings and spendings abroad and it consists of the balance of trade, net primary income or factor income and net unilateral transfers, that have taken place over a given period of time. The current account balance is one of two major measures of a country's foreign trade. A current account surplus indicates that the value of a country's net foreign assets grew over the period in question, and a current account deficit indicates that it shrank. Both government and private payments are included in the calculation. It is called the current account because goods and services are generally consumed in the current period.
In classical economics, Say's law, or the law of markets, is the claim that the production of a product creates demand for another product by providing something of value which can be exchanged for that other product. So, production is the source of demand. In his principal work, A Treatise on Political Economy, Jean-Baptiste Say wrote: "A product is no sooner created, than it, from that instant, affords a market for other products to the full extent of its own value." And also, "As each of us can only purchase the productions of others with his own productions – as the value we can buy is equal to the value we can produce, the more men can produce, the more they will purchase."

In microeconomics, the law of demand is a fundamental principle which states that there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. In other words, "conditional on all else being equal, as the price of a good increases (↑), quantity demanded will decrease (↓); conversely, as the price of a good decreases (↓), quantity demanded will increase (↑)". Alfred Marshall worded this as: "When then we say that a person's demand for anything increases, we mean that he will buy more of it than he would before at the same price, and that he will buy as much of it as before at a higher price". The law of demand, however, only makes a qualitative statement in the sense that it describes the direction of change in the amount of quantity demanded but not the magnitude of change.
Output in economics is the "quantity of goods or services produced in a given time period, by a firm, industry, or country", whether consumed or used for further production. The concept of national output is essential in the field of macroeconomics. It is national output that makes a country rich, not large amounts of money.

In economics, a country's national saving is the sum of private and public saving. It equals a nation's income minus consumption and the government spending.

A balanced budget is a budget in which revenues are equal to expenditures. Thus, neither a budget deficit nor a budget surplus exists. More generally, it is a budget that has no budget deficit, but could possibly have a budget surplus. A cyclically balanced budget is a budget that is not necessarily balanced year-to-year, but is balanced over the economic cycle, running a surplus in boom years and running a deficit in lean years, with these offsetting over time.
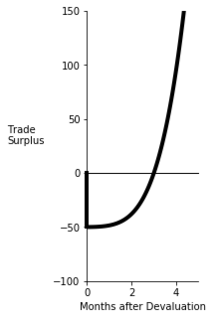
The Marshall–Lerner condition is satisfied if the absolute sum of a country's export and import demand elasticities is greater than one. If it is satisfied, then if a country begins with a zero trade deficit then when the country's currency depreciates, its balance of trade will improve. The country's imports become more expensive and exports become cheaper due to the change in relative prices, and the Marshall-Lerner condition implies that the indirect effect on the quantity of trade will exceed the direct effect of the country having to pay a higher price for its imports and receive a lower price for its exports.
In economics, a price mechanism is the manner in which the profits of goods or services affects the supply and demand of goods and services, principally by the price elasticity of demand. A price mechanism affects both buyer and seller who negotiate prices. A price mechanism, part of a market system, comprises various ways to match up buyers and sellers.
Walras's law is a principle in general equilibrium theory asserting that budget constraints imply that the values of excess demand must sum to zero regardless of whether the prices are general equilibrium prices. That is:

A market is a composition of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations or infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services to buyers in exchange for money. It can be said that a market is the process by which the prices of goods and services are established. Markets facilitate trade and enable the distribution and resource allocation in a society. Markets allow any trade-able item to be evaluated and priced. A market emerges more or less spontaneously or may be constructed deliberately by human interaction in order to enable the exchange of rights of services and goods. Markets generally supplant gift economies and are often held in place through rules and customs, such as a booth fee, competitive pricing, and source of goods for sale.

In economics, competition is a scenario where different economic firms are in contention to obtain goods that are limited by varying the elements of the marketing mix: price, product, promotion and place. In classical economic thought, competition causes commercial firms to develop new products, services and technologies, which would give consumers greater selection and better products. The greater the selection of a good is in the market, prices are typically lower for the products, compared to what the price would be if there was no competition (monopoly) or little competition (oligopoly). This is because there is now no rivalry between firms to obtain the product as there is enough for everyone. The level of competition that exists within the market is dependant on a variety of factors both on the firm/ seller side; the number of firms, barriers to entry, information availability, availability/ accessibility of resources. The number of buyers within the market also factors into competition with each buyer having a willingness to pay, influencing overall demand for the product in the market.
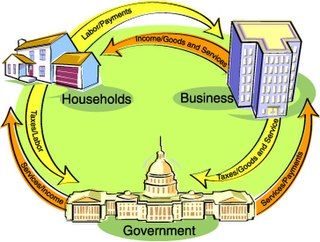
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services by different agents. In general, it is defined 'as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of scarce resources'. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure and legal systems, as well as its geography, natural resource endowment, and ecology, as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone.

An import is the receiving country in an export from the sending country. Importation and exportation are the defining financial transactions of international trade.

Scarcity as an economic concept "refers to the basic fact of life that there exists only a finite amount of human and nonhuman resources which the best technical knowledge is capable of using to produce only limited maximum amounts of each economic good." If the conditions of scarcity didn't exist and an "infinite amount of every good could be produced or human wants fully satisfied ... there would be no economic goods, i.e. goods that are relatively scarce..." Scarcity is the limited availability of a commodity, which may be in demand in the market or by the commons. Scarcity also includes an individual's lack of resources to buy commodities. The opposite of scarcity is abundance.
This glossary of economics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in economics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.










