Related Research Articles

The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'.

The brainstem is the stalk-like part of the brain that connects the forebrain with the spinal cord. In the human brain, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch.
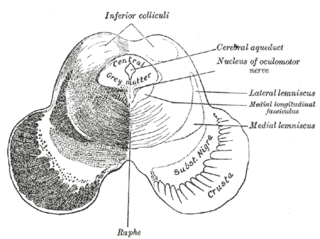
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is a prominent bundle of nerve fibres which pass within the ventral/anterior portion of periaqueductal gray of the mesencephalon (midbrain). It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement.

The abducens nucleus is the originating nucleus from which the abducens nerve (VI) emerges—a cranial nerve nucleus. This nucleus is located beneath the fourth ventricle in the caudal portion of the pons near the midline, medial to the sulcus limitans.

The paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) is a subset of neurons of the oral and caudal pontine reticular nuclei mediating horizontal gaze. It is situated in the pons adjacent to the abducens nucleus. It projects to the ipsilateral abducens nucleus, and contralateral oculomotor nucleus to mediate conjugate horizontal eye movements and saccades.

The nucleus of the trochlear nerve is a motor nucleus in the medial midbrain giving rise to the trochlear nerve.

The posterior commissure is a rounded band of white fibers crossing the middle line on the dorsal aspect of the rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct. It is important in the bilateral pupillary light reflex. It constitutes part of the epithalamus.

The lateral vestibular nucleus is the continuation upward and lateralward of the principal nucleus, and in it terminate many of the ascending branches of the vestibular nerve.
The mammillothalamic tract is an efferent pathway of the mammillary body which projects to the anterior nuclei of thalamus. It consists of heavily myelinated fibres. It is part of a brain circuit involved in spatial memory.
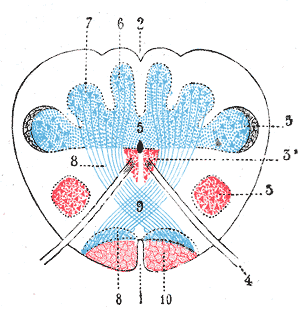
In neuroanatomy, the dorsal column nuclei are a pair of nuclei in the dorsal columns in the brainstem. The name refers collectively to the cuneate nucleus and gracile nucleus, which are situated at the lower end of the medulla oblongata. Both nuclei contain second-order neurons of the dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway, which convey fine touch and proprioceptive information from the body to the brain. The dorsal column nuclei project to the thalamus.
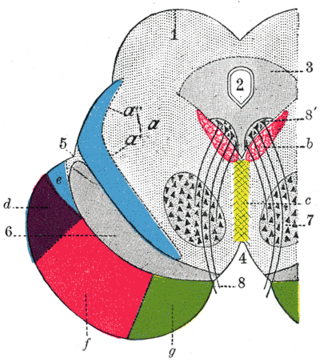
The rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF) is a collection of neurons in the mesencephalon (midbrain) responsible for mediating vertical conjugate eye movements and vertical saccades. It mostly projects efferents to the ipsilateral oculomotor and trochlear nuclei.
The term gaze is frequently used in physiology to describe coordinated motion of the eyes and neck. The lateral gaze is controlled by the paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF). The vertical gaze is controlled by the rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus and the interstitial nucleus of Cajal.

The nucleus prepositus or nucleus prepositus hypoglossi is one of the largest of the three perihypoglossal nuclei. It is situated in the caudal pons and rostral medulla oblongata. It contributes to several aspects of gaze control including the horizontal gaze holding system.
Conjugate eye movement refers to motor coordination of the eyes that allows for bilateral fixation on a single object. A conjugate eye movement is a movement of both eyes in the same direction to maintain binocular gaze. This is in contrast to vergence eye movement, where binocular gaze is maintained by moving eyes in opposite directions, such as going “cross eyed” to view an object moving towards the face. Conjugate eye movements can be in any direction, and can accompany both saccadic eye movements and smooth pursuit eye movements.
The interpeduncular nucleus (IPN) is an unpaired, ovoid cell group at the base of the midbrain tegmentum. It is located in the mesencephalon below the interpeduncular fossa. As the name suggests, the interpeduncular nucleus lies in between the cerebral peduncles.
Serotonergic cell groups refer to collections of neurons in the central nervous system that have been demonstrated by histochemical fluorescence to contain the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine). Since they are for the most part localized to classical brainstem nuclei, particularly the raphe nuclei, they are more often referred to by the names of those nuclei than by the B1-9 nomenclature. These cells appear to be common across most mammals and have two main regions in which they develop; one forms in the mesencephlon and the rostral pons and the other in the medulla oblongata and the caudal pons.
Perihypoglossal nuclei are three prominent groups of neurons in the caudal medulla oblongata near the hypoglossal nucleus: the nucleus prepositus hypoglossi, intercalated nucleus, and sublingual nucleus. They are involved in controling eye movements: they send their principal projections to the three cranial nerve nuclei controling extrinsic eye muscles via the medial longitudinal fasciculus.
The interstitial nucleus of Cajal is a collection of neurons in the mesencephalon (midbrain) which are involved in integrating eye position-velocity information in order to coordinate head-eye movements - especially those related to vertical and torsional conjugate eye movements (gaze). It also mediates vertical gaze holding.
The nucleus of Darkschewitsch is an accessory oculomotor nucleus situated in the ventrolateral portion of the periaqueductal gray of the mesencephalon (midbrain) near its junction with the diencephalon. It is involved in mediating vertical eye movements. It projects to the trochlear nucleus, receives afferents from the visual cortex, and forms a reciprocal (looping) connection with the cerebellum by way of the inferior olive.
References
- ↑ Kiernan, John A.; Rajakumar, Nagalingam (2013). Barr's The Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint (10th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 156. ISBN 978-1-4511-7327-7.
- ↑ Patestas, Maria A.; Gartner, Leslie P. (2016). A Textbook of Neuroanatomy (2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 241. ISBN 978-1-118-67746-9.