An impact crater is a depression in the surface of a solid astronomical body formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Impact craters are typically circular, though they can be elliptical in shape or even irregular due to events such as landslides. Impact craters range in size from microscopic craters seen on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program to simple bowl-shaped depressions and vast, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth.

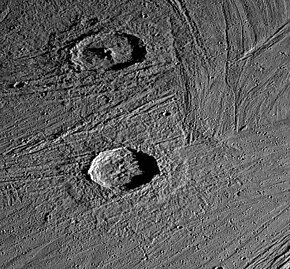
Neith crater is a crater on Jupiter's moon Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system.
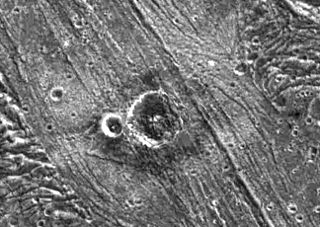
Nergal crater is a crater on Jupiter's moon Ganymede. It has a distinctive ejecta blanket surrounding it that's darker nearer the craters and brighter further away. The inner region of the ejecta is characterized by a lobate appearance indicative of the flow of a liquid substance over the surface. The flow was probably icy surface material melted by the energy released during the impact that formed the crater.

Ejecta are particles ejected from an area. In volcanology, in particular, the term refers to particles including pyroclastic materials (tephra) that came out of a volcanic explosion and magma eruption volcanic vent, or crater, has traveled through the air or under water, and fell back on the ground surface or on the ocean floor.

An ejecta blanket is a generally symmetrical apron of ejecta that surrounds an impact crater; it is layered thickly at the crater's rim and thin to discontinuous at the blanket's outer edge. The impact cratering is one of the basic surface formation mechanisms of the solar system bodies and the formation and emplacement of ejecta blankets are the fundamental characteristics associated with impact cratering event. The ejecta materials are considered as the transported materials beyond the transient cavity formed during impact cratering regardless of the state of the target materials.

The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term geology is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, areology, from the Greek word Arēs (Mars), sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction. The term areology is also used by the Areological Society.

The geology of solar terrestrial planets mainly deals with the geological aspects of the four terrestrial planets of the Solar System – Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars – and one terrestrial dwarf planet: Ceres. Earth is the only terrestrial planet known to have an active hydrosphere.

The Beethoven quadrangle is located in the equatorial region of Mercury, in the center of the area imaged by Mariner 10. Most pictures of the quadrangle were obtained at high sun angles as the Mariner 10 spacecraft receded from the planet. Geologic map units are described and classified on the basis of morphology, texture, and albedo, and they are assigned relative ages based on stratigraphic relations and on visual comparisons of the density of superposed craters. Crater ages are established by relative freshness of appearance, as indicated by topographic sharpness of their rim crests and degree of preservation of interior and exterior features such as crater floors, walls, and ejecta aprons. Generally, topography appears highly subdued because of the sun angle, and boundaries between map units are not clearly defined.

Enki Catena is a crater chain on Ganymede measuring 161.3 kilometres (100.2 mi) long.

Gula is a crater on Ganymede. It is a fresh crater with a distinctive central peak. It is about 40 km in diameter.

Jeanne is an impact crater on Venus.

The Casius quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars' eastern hemisphere and covers 60° to 120° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Casius quadrangle is also referred to as MC-6. Casius quadrangle contains part of Utopia Planitia and a small part of Terra Sabaea. The southern and northern borders of the Casius quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km and 1,500 km wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km. The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars' surface area.

The Arabia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Arabia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-12.

The Amazonis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Amazonis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-8.
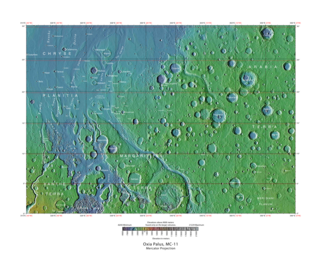
The Oxia Palus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Oxia Palus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-11.

Arandas is a crater in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle of Mars, located 42.77° North and 15.17° West. It is 24.76 km (15.39 mi) in diameter and is named after the town of Arandas in Mexico.
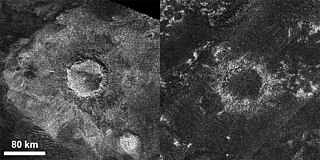
Sinlap is a shallow impact crater on Titan, a natural satellite of Saturn. Located in the Fensal region, Sinlap is one of the most pristine craters on Titan, surrounded by a bright ejecta blanket.

Denning Crater is a large Noachian-age impact crater in the southwestern Terra Sabaea region of the southern Martian highlands, within the Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle. It is located to the northwest of the Hellas impact basin within the furthest outskirts of the Hellas debris apron. The crater is 165 km in diameter and likely formed during the Late Heavy Bombardment, a period of intense bolide impacts affecting the entirety of the Solar System; during the Hesperian period, aeolian processes caused significant degradation of the crater's rim features and infilled the crater's floor. Similar to other large craters in this region of Mars, wind-eroded features are sporadically found on the basin floor. The presence of wrinkle ridges of varying orientations within and around the Denning basin has been correlated to regional tectonic events, including the formation of the Hellas basin itself. The crater was named for British astronomer William Frederick Denning.

Inktomi, informally nicknamed the Splat, is a prominent rayed impact crater 47.2 kilometres (29.3 mi) in diameter located in the southern hemisphere of Saturn's moon Rhea. The crater is named for the Lakota spider-god Iktomi and is located at 14.1 S, 112.1 W. Inktomi is thought to be the youngest major surface feature on Rhea, with estimates ranging from 8 to 280 million years.