
The Acido-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. It is found only in acidobacteriota, and appears to be a non-coding RNA as it does not have a consistent association with protein-coding genes.

The Bacillaceae-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics within bacteria in the family bacillaceae. The RNA is presumed to operate as a non-coding RNA, and is sometimes adjacent to operons containing ribosomal RNAs. The most characteristic feature is two terminal loops that have the nucleotide consensus RUCCU, where R is either A or G. The motif might be related to the Desulfotalea-1 RNA motif, as the motifs share some similarity in conserved features, and the Desulfotalea-1 RNA motif is also sometimes adjacent to ribosomal RNA operons.

The Bacteroidales-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. It has been identified only in bacteria within the order (biology) Bacteroidales. Its presumed length is marked by a promoter on one end that conforms to an alternate consensus sequence that is common in the phylum Bacteroidota, and its 3′ end is indicated by predicted transcription terminators. It is often located downstream of a gene that encodes the L20 ribosomal subunit, although it is unclear whether there is a functional reason underlying this apparent association.

The Bacteroides-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified in bacteria within the genus Bacteroides. The RNAs are typically found downstream of of genes that participate in the synthesis of exopolysaccharides of unknown types. It is possible that Bacteroides-1 RNAs regulate the upstream genes, but since this mode of regulation is unusual in bacteria, it is more likely that the structure functions as a non-coding RNA.
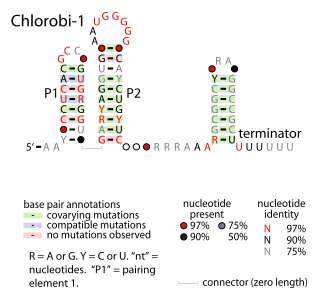
The Chlorobi-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA secondary structure identified by bioinformatics. It is predicted to be used only by Chlorobiota, a phylum of bacteria. The motif consists of two stem-loops that are followed by an apparent rho-independent transcription terminator. The motif is presumed to function as an independently transcribed non-coding RNA.

The Chloroflexi-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure detected by bioinformatics within the species Chloroflexus aggregans. C. aggregans has three predicted Chloroflexi-1 RNAs, which are located nearby to one another. This arrangement might suggest a repetitive element. C. aggregans is classified as belonging to the bacterial phylum Chloroflexota.
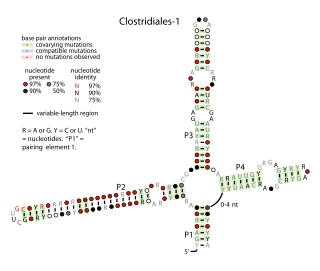
The Clostridiales-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. It is a four-stem structure common in bacteria that inhabit the human gut and is also found in a variety of bacteria classified within the order Clostridiales. Its function is unknown.

The Collinsella-1 RNA motif denotes a particular conserved RNA structure discovered by bioinformatics. Of the six sequences belonging to this motif that were originally identified, five are from uncultivated bacteria residing in the human gut, while only the sixth is in a cultivated species, Collinsella aerofaciens. The evidence supporting the stem-loops designated as "P1" and "P2" is ambiguous.
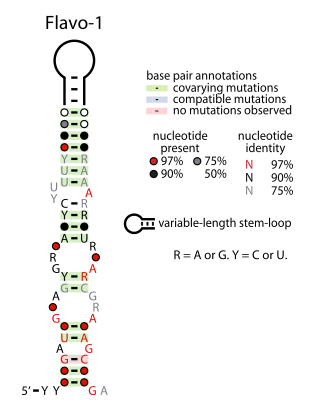
The Flavo-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was identified by bioinformatics. The vast majority of Flavo-1 RNAs are found in Flavobacteria, but some were detected in the phylum Bacteroidota, which contains Flavobacteria, or the phylum Spirochaetota, which is evolutionarily related to Bacteroidota. It was presumed that Flavo-1 RNAs function as non-coding RNAs.

The Gut-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. These RNAs are present in environmental sequences, and as of 2010 are not known to be present in any species that has been grown under laboratory conditions. Gut-1 RNA is exclusively found in DNA from uncultivated bacteria present in samples from the human gut.
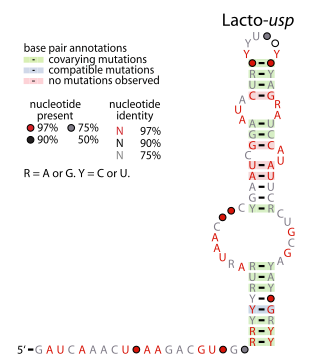
The Lacto-usp RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified in bacteria by bioinformatics. Lacto-usp RNAs are found exclusively in lactic acid bacteria, and exclusively in the possible 5′ untranslated regions of operons that contain a hypothetical gene and a usp gene. The usp gene encodes the universal stress protein. It was proposed that the Lacto-usp might correspond to the 6S RNA of the relevant species, because four of five of these species lack a predicted 6S RNA, and 6S RNAs commonly occur in 5′ UTRs of usp genes. However, given that the Lacto-usp RNA motif is much shorter than the standard 6S RNA structure, the function of Lacto-usp RNAs remains unclear.
The Lnt RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure found in certain bacteria. Specifically, Lnt RNAs are known only in species within the phylum Chlorobiota, and are located in the possible 5' untranslated regions of genes that are annotated as encoding apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase enzymes. There is some doubt as to whether the indicated motif is transcribed as RNA, or whether its reverse complement is transcribed. If the reverse complement is transcribed it would potentially in 5' UTRs of genes encoding bacteriochlorophyll A, and would be close to the start codon of those genes.

The Methylobacterium-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure discovered using bioinformatics. Almost all known examples of this RNA are found in DNA extracted from marine bacteria. However, one instance is predicted in Methylobacterium sp. 4-46, a species of alphaproteobacteria. The motif is presumed to function as a non-coding RNA.
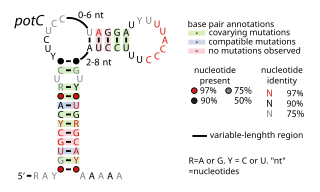
The potC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure discovered using bioinformatics. The RNA is detected only in genome sequences derived from DNA that was extracted from uncultivated marine bacteria. Thus, this RNA is present in environmental samples, but not yet found in any cultivated organism. potC RNAs are located in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of genes predicted to encode either membrane transport proteins or peroxiredoxins. Therefore, it was hypothesized that potC RNAs are cis-regulatory elements, but their detailed function is unknown.

The Pseudomon-Rho RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure that was discovered using bioinformatics. The RNAs that conform to this motif are found in species within the genus Pseudomonas, as well as the related Azotobacter vinelandii. They are consistently located in what could be the 5' untranslated regions of genes that encode the Rho factor protein, and this arrangement in bacteria suggested that Pseudomon-Rho RNAs might be cis-regulatory elements that regulate concentrations of the Rho protein.

The Rhizobiales-2 RNA motif is a set of RNAs found in certain bacteria that are presumed to be homologous because they conserve a common primary and secondary structure. The motif was discovered using bioinformatics, and is found only within bacteria that belong to the order Hyphomicrobiales, in turn a kind of alphaproteobacteria. Because Rhizobiales-2 RNAs are not consistently located in proximity to genes of a consistent class or function, these RNAs are presumed to function as non-coding RNAs.
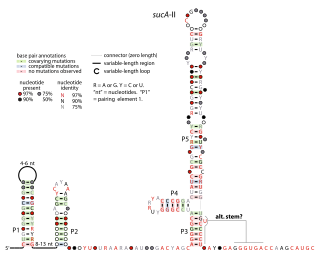
The sucA-II RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. It is consistently found in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of sucA genes, which encode Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase enzymes that participate in the citric acid cycle. Given this arrangement, sucA-II RNAs might regulate the downstream sucA gene. This genetic arrangement is similar to the previously reported sucA RNA motif. However, sucA-II RNAs are found only in bacteria classified within the genus Pseudomonas, whereas the previously reported motif is found only in betaproteobacteria.

The sucC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure discovered using bioinformatics. sucC RNAs are found in the genus Pseudomonas, and are consistently found in possible 5' untranslated regions of sucC genes. These genes encode Succinyl coenzyme A synthetase, and are hypothesised to be regulated by the sucC RNAs. sucC genes participate in the citric acid cycle, and another gene involved in the citric acid cycle, sucA, is also predicted to be regulated by a conserved RNA structure.
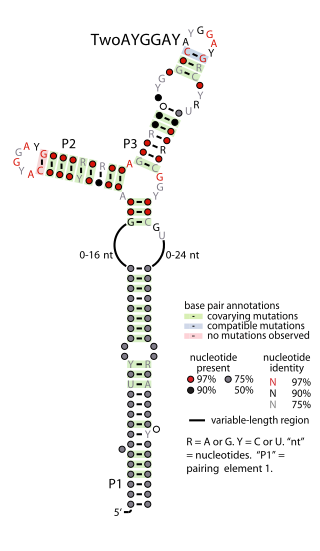
The TwoAYGGAY RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. Its name refers to the conserved AYGGAY nucleotide sequence found in the motif's two terminal loops. The RNAs are found in sequences derived from DNA extracted from uncultivated bacteria present in the human gut, as well as some bacteria in the classes Clostridia and Gammaproteobacteria.

The Whalefall-1 RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure that was discovered using bioinformatics. Structurally, the motif consists of two stem-loops, the second of which is often terminated by a CUUG tetraloop, which is an energetically favorable RNA sequence. Whalefall-1 RNAs are found only in DNA extracted from uncultivated bacteria found on whale fall, i.e., a whale carcass. As of 2010, Whalefall-1 RNAs have not been detected in any known, cultivated species of bacteria, and are thus one of several RNAs present in environmental samples.



















