

Acridone alkaloids are natural products derived from acridone. [1]


Acridone alkaloids are natural products derived from acridone. [1]
Acridone alkaloids are found in bark, wood, leaves and roots of rue plants, [1] especially in roots and suspension cultures of rue. [2]
This group is named after the acridone. Further members are acronycin, melicopicine and rutacridone, among others: [1] [3]
Many acridone alkaloids are methylated on the nitrogen atom and also have two oxygen functional groups, which can be free, alkylated or incorporated into rings. Acridone alkaloids show a blue-green fluorescence so that they can be detected with UV light. Some alkaloids of this group are effective against malaria pathogens. Furthermore, acronycin inhibits cell division. [2]

Ayahuasca is a South American psychoactive and entheogenic brewed drink traditionally used both socially and as a ceremonial or shamanic spiritual medicine among the indigenous peoples of the Amazon basin, especially in the areas of Peru, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Panama, Venezuela and more recently in North America and Europe. The infusion causes altered states of consciousness often known as "psychedelic experiences" which include visual hallucinations and altered perceptions of reality.

Herbal teas, also known as herbal infusions and less commonly called tisanes, are beverages made from the infusion or decoction of herbs, spices, or other plant material in hot water. Oftentimes herb tea, or the plain term tea, is used as a reference to all sorts of herbal teas. Many herbs are used in herbal medicine. Some herbal blends contain actual tea.

Several alkaloids that function as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are found in the seeds of Peganum harmala, as well as tobacco leaves including harmine, harmaline, and harmalol, which are members of a group of substances with a similar chemical structure collectively known as harmala alkaloids. These alkaloids are of interest for their use in Amazonian shamanism, where they are derived from other plants. The harmala alkaloid harmine, once known as telepathine and banisterine, is a naturally occurring beta-carboline alkaloid that is structurally related to harmaline, and also found in the vine Banisteriopsis caapi. Tetrahydroharmine is also found in B. caapi and P. harmala. Dr. Alexander Shulgin has suggested that harmine may be a breakdown product of harmaline. Harmine and harmaline are both a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs). They can stimulate the central nervous system by inhibiting the metabolism of monoamine compounds such as serotonin and norepinephrine.

Peganum harmala, commonly called wild rue, Syrian rue, African rue, esfand or espand, or harmel, is a perennial, herbaceous plant, with a woody underground rootstock, of the family Nitrariaceae, usually growing in saline soils in temperate desert and Mediterranean regions. Its common English-language name came about because of a resemblance to rue. Because eating it can cause livestock to sicken or die, it is considered a noxious weed in a number of countries. It has become an invasive species in some regions of the western United States. The plant is popular in Middle Eastern and north African folk medicine. The alkaloids contained in the plant, including the seeds, are monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
Harmine is a beta-carboline and a harmala alkaloid. It occurs in a number of different plants, most notably the Syrian rue and Banisteriopsis caapi. Harmine reversibly inhibits monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), an enzyme which breaks down monoamines, making it a Reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA). Harmine does not inhibit MAO-B. Harmine is also known as banisterin, banisterine, telopathin, telepathine, leucoharmine and yagin, yageine.

Harmaline is a fluorescent indole alkaloid from the group of harmala alkaloids and beta-carbolines. It is the partly hydrogenated form of harmine.

Ruta graveolens, commonly known as rue, common rue or herb-of-grace, is a species of Ruta grown as an ornamental plant and herb. It is native to the Balkan Peninsula. It is grown throughout the world in gardens, especially for its bluish leaves, and sometimes for its tolerance of hot and dry soil conditions. It is also cultivated as a culinary herb, and to a lesser extent as an insect repellent and incense.

Choisya is a small genus of aromatic evergreen shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Members of the genus are commonly known as Mexican orange due to the similarity of their flowers to those of the closely related orange, both in shape and scent. They are native to southern North America, from Arizona, New Mexico, Texas and south through most of Mexico. In its generic name Humboldt and Bonpland honoured Swiss botanist Jacques Denis Choisy (1799–1859).

Catharanthus roseus, commonly known as bright eyes, Cape periwinkle, graveyard plant, Madagascar periwinkle, old maid, pink periwinkle, rose periwinkle, is a perennial species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native and endemic to Madagascar, but grown elsewhere as an ornamental and medicinal plant. It is a source of the drugs vincristine and vinblastine, used to treat cancer. It was formerly included in the genus Vinca as Vinca rosea.
The Lehmstedt–Tanasescu reaction is a method in organic chemistry for the organic synthesis of acridone derivatives (3) from a 2-nitrobenzaldehyde (1) and an arene compound (2):
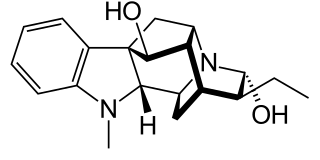
Ajmaline is an alkaloid that is classified as a 1-A antiarrhythmic agent. It is often used to induce arrhythmic contraction in patients suspected of having Brugada syndrome. Individuals suffering from Brugada syndrome will be more susceptible to the arrhythmogenic effects of the drug, and this can be observed on an electrocardiogram as an ST elevation.

Fenamic acid is an organic compound, which, especially in its ester form, is called fenamate. serves as a parent structure for several nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including mefenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, flufenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid. These drugs are commonly referred to as "anthranilic acid derivatives" or "fenamates" because fenamic acid is a derivative of anthranilic acid.
In enzymology, an anthranilate N-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acridone synthase (EC 2.3.1.159) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
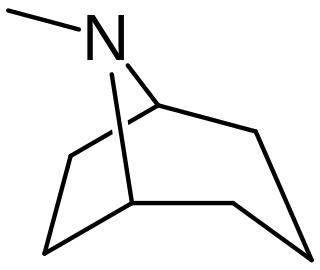
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic [3.2.1] alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkaloids such as cocaine and scopolamine are notorious for their psychoactive effects, related usage and cultural associations. Particular tropane alkaloids such as these have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants.

Alchornea cordifolia is a shrub or small tree distributed throughout tropical Africa, it can grow up to 8 metres tall. The plant is used in traditional African medicine. Common name is the Christmas bush.

Toxiferine is a curare toxin. It is a bisindole alkaloid derived from Strychnos toxifera and a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. This alkaloid is the main toxic component of Calabash curare, and one of the most toxic plant alkaloids known. The lethal dose (LD50) for mice has been determined as 10 - 60 µg/kg by intravenous administration. It is a muscle relaxant that causes paralysis of skeletal muscle, which takes approximately 2 hours to recovery for a moderate dose, and 8 hours of total paralysis with a 20-fold paralytic dose. The paralysis can be antagonized by neostigmine

Acridone is an organic compound based on the acridine skeleton, with a carbonyl group at the 9 position.

Furoquinoline alkaloids are a group of alkaloids with simple structure. Distribution of this group of alkaloids is essentially limited to plant family Rutaceae. The simplest member of this group is dictamnine and most widespread member is skimmianine.

Isoquinoline alkaloids are natural products of the group of alkaloids, which are chemically derived from isoquinoline. They form the largest group among the alkaloids.