
Interplanetary spaceflight or interplanetary travel is the crewed or uncrewed travel between stars and planets, usually within a single planetary system. In practice, spaceflights of this type are confined to travel between the planets of the Solar System. Uncrewed space probes have flown to all the observed planets in the Solar System as well as to dwarf planets Pluto and Ceres, and several asteroids. Orbiters and landers return more information than fly-by missions. Crewed flights have landed on the Moon and have been planned, from time to time, for Mars, Venus and Mercury. While many scientists appreciate the knowledge value that uncrewed flights provide, the value of crewed missions is more controversial. Science fiction writers propose a number of benefits, including the mining of asteroids, access to solar power, and room for colonization in the event of an Earth catastrophe.
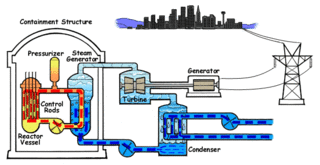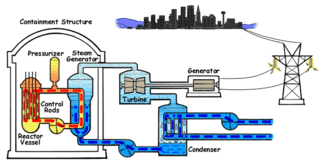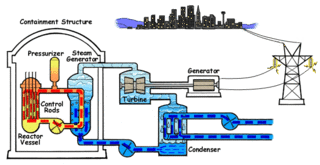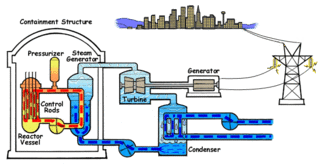
Nuclear engineering is the engineering discipline concerned with designing and applying systems that utilize the energy released by nuclear processes. The most prominent application of nuclear engineering is the generation of electricity. Worldwide, some 440 nuclear reactors in 32 countries generate 10 percent of the world's energy through nuclear fission. In the future, it is expected that nuclear fusion will add another nuclear means of generating energy. Both reactions make use of the nuclear binding energy released when atomic nucleons are either separated (fission) or brought together (fusion). The energy available is given by the binding energy curve, and the amount generated is much greater than that generated through chemical reactions. Fission of 1 gram of uranium yields as much energy as burning 3 tons of coal or 600 gallons of fuel oil, without adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.

Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federally funded research and development center in California, United States. Originally established in 1952, the laboratory now is sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administered privately by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC.

Nuclear pulse propulsion or external pulsed plasma propulsion is a hypothetical method of spacecraft propulsion that uses nuclear explosions for thrust. It originated as Project Orion with support from DARPA, after a suggestion by Stanislaw Ulam in 1947. Newer designs using inertial confinement fusion have been the baseline for most later designs, including Project Daedalus and Project Longshot.
TRW Inc. was an American corporation involved in a variety of businesses, mainly aerospace, electronics, automotive, and credit reporting. It was a pioneer in multiple fields including electronic components, integrated circuits, computers, software and systems engineering. TRW built many spacecraft, including Pioneer 1, Pioneer 10, and several space-based observatories. It was #57 on the 1986 Fortune 500 list, and had 122,258 employees. The company was called Thompson Ramo Wooldridge Inc., after the 1958 merger of the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation and Thompson Products. This was later shortened to TRW.
Nuclear propulsion includes a wide variety of propulsion methods that use some form of nuclear reaction as their primary power source. The idea of using nuclear material for propulsion dates back to the beginning of the 20th century. In 1903 it was hypothesized that radioactive material, radium, might be a suitable fuel for engines to propel cars, planes, and boats. H. G. Wells picked up this idea in his 1914 fiction work The World Set Free. Many aircraft carriers and submarines currently use uranium fueled nuclear reactors that can provide propulsion for long periods without refueling. There are also applications in the space sector with nuclear thermal and nuclear electric engines which could be more efficient than conventional rocket engines.
NASTRAN is a finite element analysis (FEA) program that was originally developed for NASA in the late 1960s under United States government funding for the aerospace industry. The MacNeal-Schwendler Corporation (MSC) was one of the principal and original developers of the publicly available NASTRAN code. NASTRAN source code is integrated in a number of different software packages, which are distributed by a range of companies.
The Aerospace Corporation is an American nonprofit corporation that operates a federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in El Segundo, California. The corporation provides technical guidance and advice on all aspects of space missions to military, civil, and commercial customers. As the FFRDC for national-security space, Aerospace works closely with organizations such as the United States Space Force (USSF) and the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) to provide "objective technical analyses and assessments for space programs that serve the national interest". Although the USSF and NRO are the primary customers, Aerospace also performs work for civil agencies such as NASA and NOAA as well as international organizations and governments in the national interest.
ams OSRAM AG is an Austrian semiconductor manufacturer headquartered in Premstätten, Austria with a co-headquarters in Munich, Germany. The company develops and produces intelligent sensors and emitter components
The Westinghouse Astronuclear Laboratory (WANL) was a division of Westinghouse Electric Corporation. Established in 1959 to develop nuclear space propulsion technologies for the government, the lab was located, for most of its history, in the paradoxically small town of "Large" along Pa. Rte 51, about 13 miles (21 km) south of Pittsburgh in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, USA. The site is not far from the Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory in West Mifflin, which Westinghouse operated during the same time and later.
Instituto Pedro Nunes (IPN) is a non-profit private organization for innovation and technology transfer based in Coimbra, Portugal. It is named after the Portuguese 16th century mathematician and professor Pedro Nunes, who lived in the city of Coimbra and worked for the local university.

Arctic Slope Regional Corporation, or ASRC, is one of 13 Alaska Native Regional Corporations created under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of 1971 (ANCSA) in settlement of aboriginal land claims. ASRC was incorporated in Alaska on June 22, 1972. Headquartered in Utqiaġvik, Alaska, with administrative offices in Anchorage, ASRC was as of 2017, a for-profit corporation with nearly 11,000 Alaska Native shareholders primarily of Inupiat Eskimo descent.

Ibercivis was a volunteer computing platform which allows internet users to participate in scientific research by donating unused computer cycles to run scientific simulations and other tasks. The original project, which became operational in 2008, was a scientific collaboration between the Portuguese and Spanish governments, but it is open to the general public and scientific community, both within and beyond the Iberian Peninsula. The project's name is a portmanteau of Iberia and the Latin word civis, meaning 'citizen'.

Critical Software is a Portuguese international information systems and software company, headquartered in Coimbra. The company was established in 1998, from the University of Coimbra's business incubator and technology transfer centre, Instituto Pedro Nunes (IPN). The company has other offices in Porto,Lisbon (Portugal), Southampton, Munich (Germany) and California.

The John and Marcia Price College of Engineering at the University of Utah is an academic college of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, Utah. The college offers undergraduate and graduate degrees in engineering and computer science.

Swales Aerospace was an employee-owned, small business aerospace engineering firm. The company offered a full range of aerospace engineering services. It was the global leader in the development and manufacture of two-phase thermal solutions for spaceflight applications, and it was a small satellite mission provider. In 2007, it was acquired by Alliant Techsystems.
SpaceWorks Enterprises, Inc. (SEI) is an aerospace engineering company based in Atlanta, Georgia, United States that specializes in the design, assessment, hardware prototyping and flight demonstration of advanced space concepts for both government and commercial customers.
The Louisiana Business & Technology Center (LBTC) at Louisiana State University plays an important role to the state's flagship university, Louisiana State University as a part of LSU's Office of Research and Economic Development. LBTC's primary goal is to increase the economic growth of Louisiana by enhancing the development of small businesses and assisting in the development of new businesses. The center is ranked among the top ten entrepreneur programs in the nation. In 1988 it was jointly funded through LSU and the Greater Baton Rouge Chamber of Commerce to foster economic growth in Louisiana by providing businesses with applications and tools necessary for growth and survival in the real world. It comprises the Louisiana Technology Transfer Office (LTTO), the LBTC Business Incubator, and the LSU Student Incubator.
The Lockheed Martin Compact Fusion Reactor (CFR) was a fusion power project at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works. Its high-beta configuration, which implies that the ratio of plasma pressure to magnetic pressure is greater than or equal to 1, allows a compact design and expedited development. The project was active between 2010 and 2019, after that date there have been no updates and it appears the division has shut down.

Direct Fusion Drive (DFD) is a conceptual, low radioactivity, nuclear-fusion rocket engine, designed to produce both thrust and electric power, suitable for interplanetary spacecraft. The concept is based on the Princeton field-reversed configuration reactor, invented in 2002 by Samuel A. Cohen. It is being modeled and experimentally tested at Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, a U.S. Department of Energy facility, as well as modeled and evaluated by Princeton Satellite Systems (PSS). As of 2018, a direct fusion drive project driven by NASA is said to have entered its simulation phase, presented as the second phase of the concept's evolution.










