Related Research Articles
Phosgene is the organic chemical compound with the formula COCl2. It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. Phosgene is a valued and important industrial building block, especially for the production of precursors of polyurethanes and polycarbonate plastics.

Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell (cytotoxicity) or an organ such as the liver (hepatotoxicity). By extension, the word may be metaphorically used to describe toxic effects on larger and more complex groups, such as the family unit or society at large. Sometimes the word is more or less synonymous with poisoning in everyday usage.

Ethion (C9H22O4P2S4) is an organophosphate insecticide. Ethion is known to affect a neural enzyme called acetylcholinesterase and prevent it from working.

Aquatic toxicology is the study of the effects of manufactured chemicals and other anthropogenic and natural materials and activities on aquatic organisms at various levels of organization, from subcellular through individual organisms to communities and ecosystems. Aquatic toxicology is a multidisciplinary field which integrates toxicology, aquatic ecology and aquatic chemistry.
Acute toxicity describes the adverse effects of a substance that result either from a single exposure or from multiple exposures in a short period of time. To be described as acute toxicity, the adverse effects should occur within 14 days of the administration of the substance.

A chemical hazard is a (non-biological) substance that has the potential to cause harm to life or health. Chemicals are widely used in the home and in many other places. Exposure to chemicals can cause acute or long-term detrimental health effects. There are many types of hazardous chemicals, including neurotoxins, immune agents, dermatologic agents, carcinogens, reproductive toxins, systemic toxins, asthmagens, pneumoconiotic agents, and sensitizers. In the workplace, exposure to chemical hazards is a type of occupational hazard. The use of protective personal equipment (PPE) may substantially reduce the risk of damage from contact with hazardous materials.
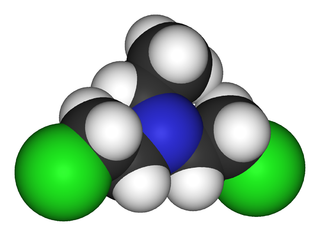
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ethylamine is the organic compound with the formula C2H5N(CH2CH2Cl)2. Often abbreviated HN1, it is a powerful vesicant and a nitrogen mustard gas used for chemical warfare. HN1 was developed in the 1920s and 1930s to remove warts and later as a military agent. Because of the latter use, it is a Schedule 1 chemical within the Chemical Weapons Convention and therefore use and production is strongly restricted. It has never been used in warfare.

Phosmet is a phthalimide-derived, non-systemic, organophosphate insecticide used on plants and animals. It is mainly used on apple trees for control of codling moth, though it is also used on a wide range of fruit crops, ornamentals, and vines for the control of aphids, suckers, mites, and fruit flies.

Benzotrichloride (BTC), also known as α,α,α-trichlorotoluene, phenyl chloroform or (trichloromethyl)benzene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CCl3. Benzotrichloride is an unstable, colorless (to yellowish), viscous, chlorinated hydrocarbon with a penetrating odor. Benzotrichloride is used extensively as a chemical intermediate for products of various classes, i.e. dyes and antimicrobial agents.

1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane (TeCA), also known as bonoform, cellon, or westron is a toxic, synthetic halogen rich alkane. It is colorless liquid and has a sweet odor. It is used as an industrial solvent or as a separation agent. TeCA can be inhaled, consumed or absorbed through the skin. After exposure, nausea, dizziness or even liver damage may occur.

Hexachlorocyclopentadiene (HCCPD), also known as C-56, Graphlox, and HRS 1655, is an organochlorine compound with the formula C5Cl6. It is a precursor to pesticides, flame retardants, and dyes. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples appear lemon-yellow liquid sometimes with a bluish vapour. Many of its derivatives proved to be highly controversial, as studies showed them to be persistent organic pollutants. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced until 1976, and smaller amounts continue to be produced today. Two prominent manufacturers are Velsicol Chemical Corporation in the US and by Jiangsu Anpon Electrochemicals Co. in China.
In analytical chemistry, biomonitoring is the measurement of the body burden of toxic chemical compounds, elements, or their metabolites, in biological substances. Often, these measurements are done in blood and urine. Biomonitoring is performed in both environmental health, and in occupational safety and health as a means of exposure assessment and workplace health surveillance.

Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) is a toxin produced by cyanobacteria. It is the most toxic of the microcystins.
Toxic equivalency factor (TEF) expresses the toxicity of dioxins, furans and PCBs in terms of the most toxic form of dioxin, 2,3,7,8-TCDD. The toxicity of the individual congeners may vary by orders of magnitude.
Throughout history, chemical weapons have been used as strategic weaponry to devastate the enemy in times of war. After the mass destruction created by WWI and WWII, chemical weapons have been considered to be inhumane by most nations, and governments and organizations have undertaken to locate and destroy existing chemical weapons. However, not all nations have been willing to cooperate with disclosing or demilitarizing their inventory of chemical weapons. Since the start of the worldwide efforts to destroy all existing chemical weapons, some nations and terrorist organizations have used and threatened the use of chemical weapons to leverage their position in conflict. A notable example includes the use of such weapons by the US government that sprayed more than 20 million gallons of various herbicides over Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos from 1961 to 1971. Agent Orange, which contained the deadly chemical dioxin, was the most commonly used herbicide. Other examples of the use of chemical weapons are Iraq’s Saddam Hussein on the Kurdish village Halabja in 1988 and their employment against civilian passengers of the Tokyo subway by Aum Shinrikyo in 1995. The efforts made by the United States and other chemical weapon destruction agencies intend to prevent such use, but this is a difficult and ongoing effort. Aside from the difficulties of cooperation and locating chemical weapons, the methods to destroy the weapons and to do this safely are also a challenge.
In the United States, the Emergency Management Issues Special Interest Group state that "Protective Action Criteria (PACs) are essential components for planning and response to uncontrolled releases of hazardous chemicals. These criteria, combined with estimates of exposure, provide the information necessary to evaluate chemical release events for the purpose of taking appropriate protective actions. During an emergency response, these criteria may be used to evaluate the severity of the event, to identify potential outcomes, and to decide what protective actions should be taken".
Methacrylonitrile, MeAN in short, is a chemical compound that is an unsaturated aliphatic nitrile, widely used in the preparation of homopolymers, copolymers, elastomers, and plastics and as a chemical intermediate in the preparation of acids, amides, amines, esters, and other nitriles. MeAN is also used as a replacement for acrylonitrile in the manufacture of an acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene-like polymer. It is a clear and colorless liquid, that has a bitter almond smell.

EPN is an insecticide of the phosphonothioate class. It is used against pests such as European corn borer, rice stem borer, bollworm, tobacco budworm, and boll weevil.

Nitrogen dioxide poisoning is the illness resulting from the toxic effect of nitrogen dioxide. It usually occurs after the inhalation of the gas beyond the threshold limit value. Nitrogen dioxide is reddish-brown with a very harsh smell at high concentrations, at lower concentrations it is colorless but may still have a harsh odour. Nitrogen dioxide poisoning depends on the duration, frequency, and intensity of exposure.
References
- ↑ "Acute Exposure Guideline Levels for Airborne Chemicals". Environmental Protection Agency. 14 November 2013.
- 1 2 "Acute Exposure Guideline Levels Program". dels.nas.edu. Retrieved 2019-04-28.
- 1 2 3 "Acute Exposure Guideline Levels (AEGLs)". Office of Response and Restoration. Retrieved 2019-04-28.