
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country largely located in Central Asia with the most western parts of it being located in Eastern Europe. It is the world's largest landlocked country, and the ninth-largest country in the world, with an area of 2,724,900 square kilometres (1,052,100 sq mi). Kazakhstan is the most dominant nation of Central Asia economically, generating 60% of the region's GDP, primarily through its oil and gas industry. It also has vast mineral resources.

Kazakhstan, the largest country fully within the Eurasian Steppe, has been a historical "crossroads" and home to numerous different peoples, states and empires throughout history.
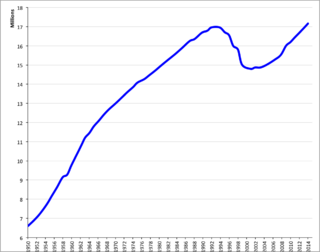
The demographics of Kazakhstan enumerate the demographic features of the population of Kazakhstan, including population growth, population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population. Some use the word Kazakh to refer to the Kazakh ethnic group and language and Kazakhstani to refer to Kazakhstan and its citizens regardless of ethnicity, but it is common to use Kazakh in both senses.

The Armed Forces of the Republic of Kazakhstan is the unified armed forces of Kazakhstan. It consists of the Ground Forces, Air and Air Defence Forces, Naval Forces, and National Guard. The national defence policy aims are based on the Constitution of Kazakhstan. They guarantee the preservation of the independence and sovereignty of the state and the integrity of its land area, territorial waters and airspace and its constitutional order. The armed forces of Kazakhstan act under the authority of the Kazakhstan Ministry of Defence.

Nur-Sultan, known, between 1998 and 2019, as Astana, is the capital city of Kazakhstan. In March 2019, it was renamed Nur-Sultan in honour of the departing Kazakh president, Nursultan Nazarbayev. It stands on the banks of the Ishim River in the northern part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmola Region, though administered as a city with special status separately from the rest of the region. A 2017 official estimate reported a population of 1,029,556 within the city limits, making it the second-largest city in the country, after Almaty, the previous capital, between 1991 and 1997.

The Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan oversees a presidential republic. The President of Kazakhstan, currently Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, is head of state and nominates the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of parliament.

Almaty, formerly known as Alma-Ata and Verniy, is the largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2,000,000 people, about 11% of the country's total population, and more than 2.7 million in its built-up area that encompasses Talgar, Boraldai, Otegen Batyr and many other suburbs. It served as capital of the Soviet and later independent Kazakhstan from 1929 to 1997. In 1997, the government relocated the capital to Astana in the north of the country and about 12 hours away by train.

The Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic was one of the transcontinental constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1936 to 1991 in northern Central Asia. It was created on 5 December 1936 from the Kazakh ASSR, an autonomous republic of the Russian SFSR.

East Kazakhstan Region is a region of Kazakhstan. It occupies the easternmost part of Kazakhstan, along both sides of the Irtysh River and Lake Zaysan. Its administrative center is Oskemen. The region borders Russia in the north and northeast and the People's Republic of China in the south and southeast. The easternmost point of the Oblast is within about 50 kilometres of the westernmost tip of Mongolia; however, Kazakhstan and Mongolia do not share a common border, the two countries being separated by a small part of Russia and China. East Kazakhstan Region borders the Kazakh regions of Pavlodar Region to the north west, Karaganda Region to the west, Almaty Region to the south, Russia's Altai Krai and Altai Republic to the north and China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region to the east. Population: 1,396,593 ; 1,531,024. 318,800 live in the capital. The area has many Russians and Ukrainians; the capital itself has more of those two groups than Kazakhs themselves. The area is 283,300 square kilometers.

Pavlodar Region is a region of Kazakhstan. The population of the region was 742,475 ; and 806,983 .; the latest official estimate was 754,739. Its capital is the city of Pavlodar, which had a population of 360,014 at the start of 2018.

The Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic, abbreviated as Kazak ASSR and simply Kazakhstan, was an autonomous republic of the Soviet Union within the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR) existing from 1925 until 1936.

The Football Federation of Kazakhstan is the governing body of football in Kazakhstan. It organizes the football league, the Kazakhstan Premier League, and the Kazakhstan national football team. It is based in Almaty.

Satbayev University is a technical university Almaty, Kazakhstan. The university is the oldest technical university in Kazakhstan, comprising 10 institutions and 27 departments.

The Kazakh is a horse breed of the Kazakh people, who live mainly in Kazakhstan, but also in parts of China, Mongolia, Russia and Uzbekistan. It is used mainly as a riding horse, and is known for its hardiness and stamina.

Kazakhstani passports are issued to citizens of the Republic of Kazakhstan to facilitate international travel. Within the Republic of Kazakhstan citizens are required to use internal identification card which can also be used for travel to Russian Federation, Kyrgyzstan, Azerbaijan and Albania. The Kazakhstani Ministry of Justice started issuing biometric passports on January 5, 2009.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Kazakhstan:

Akkuli, until 2018 Lebyazhye is a district of Pavlodar Region in northern Kazakhstan. The administrative center of the district is the selo of Akkuli (Kazakh: Аққулы, Aqqýly; formerly Akku, Kazakh: Аққу, Aqqý ; Lebyazhye. Population: 12444 ; 13,798 ; 14,593 ; 19,653.
The 78th Tank Division was a division of the Soviet Ground Forces, active from 1965 to the 1990s. It was originally established in 1949 as the 15th Tank Division, from the 78th Heavy Tank Self-Propelled Regiment. It gained the 78th designation in 1965. It was part of the 1st Army Corps from 1960, and was based at Ayaguz from 1970. Anatoly Kvashnin commanded the division from 1982 to 1987. In 1991, on the fall of the Soviet Union, the 78th Tank Division was serving at Ayaguz, Kazakh SSR, in the Turkestan Military District. In March 1992 it became part of the Kazakh Ground Forces, and soon after became the 78th Mechanized Division.

Akmola Region is a centrally located region of Kazakhstan. Its capital is Kokshetau. The national capital, Nur-Sultan, is enclosed by the region, but is politically separate from Akmola Region. The region's population is 715,000; Kokshetau's is 157,000. The area is 146,200 square kilometers. It and Karaganda Region are Kazakhstan's only two regions which don't touch the country's outer borders. Akmola Region borders North Kazakhstan Region in the north, Pavlodar Region in the east, Karagandy Region in the south, and Kostanay Region in the west. Some gold and coal mining occur in the area.

The Ministry of National Economy is central executive body of the Government of Kazakhstan, which administers in the areas of strategic planning, tax and budgetary policies, as well as customs policy, state and state-guaranteed borrowing and debt, public-private partnerships, state investment projects, protection of competition and restriction of monopolistic activities, natural monopolies and regulated markets, international economic and financial relations.

















