Related Research Articles

A backplane or backplane system is a group of electrical connectors in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors, forming a computer bus. It is used to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete computer system. Backplanes commonly use a printed circuit board, but wire-wrapped backplanes have also been used in minicomputers and high-reliability applications.

Eurocard is an IEEE standard format for printed circuit board (PCB) cards that can be plugged together into a standard chassis which, in turn, can be mounted in a 19-inch rack. The chassis consists of a series of slotted card guides on the top and bottom, into which the cards are slid so they stand on end, like books on a shelf. At the spine of each card is one or more connectors which plug into mating connectors on a backplane that closes the rear of the chassis.

In computing, an expansion card is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot on a computer's motherboard to add functionality to a computer system. Sometimes the design of the computer's case and motherboard involves placing most of these slots onto a separate, removable card. Typically such cards are referred to as a riser card in part because they project upward from the board and allow expansion cards to be placed above and parallel to the motherboard.

VMEbus is a computer bus standard physically based on Eurocard sizes.

A single-board computer (SBC) is a complete computer built on a single circuit board, with microprocessor(s), memory, input/output (I/O) and other features required of a functional computer. Single-board computers are commonly made as demonstration or development systems, for educational systems, or for use as embedded computer controllers. Many types of home computers or portable computers integrate all their functions onto a single printed circuit board.
A PCI Mezzanine Card or PMC is a printed circuit board assembly manufactured to the IEEE P1386.1 standard. This standard combines the electrical characteristics of the PCI bus with the mechanical dimensions of the Common Mezzanine Card or CMC format.

CompactPCI is a computer bus interconnect for industrial computers, combining a Eurocard-type connector and PCI signaling and protocols. Boards are standardized to 3U or 6U sizes, and are typically interconnected via a passive backplane. The connector pin assignments are standardized by the PICMG US and PICMG Europe organizations. The connectors and the electrical rules allow for eight boards in a PCI segment. Multiple bus segments are allowed with bridges.

A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, while still having all the functional components to be considered a computer. Unlike a rack-mount server, a blade server fits inside a blade enclosure, which can hold multiple blade servers, providing services such as power, cooling, networking, various interconnects and management. Together, blades and the blade enclosure form a blade system, which may itself be rack-mounted. Different blade providers have differing principles regarding what to include in the blade itself, and in the blade system as a whole.

PICMG, or PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group, is a consortium of over 140 companies in the fields of computer science and engineering. Founded in 1994, the group was originally formed to adapt PCI technology for use in high-performance telecommunications, military, and industrial computing applications, but its work has grown to include newer technologies. PICMG currently focuses on developing and implementing specifications and guidelines for open standards–based computer architectures from a wide variety of interconnects.
Advanced Telecommunications Computing Architecture is the largest specification effort in the history of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group (PICMG), with more than 100 companies participating. Known as AdvancedTCA, the official specification designation PICMG 3.x was ratified by the PICMG organization in December 2002. AdvancedTCA is targeted primarily to requirements for "carrier grade" communications equipment, but has recently expanded its reach into more ruggedized applications geared toward the military/aerospace industries as well. This series of specifications incorporates the latest trends in high speed interconnect technologies, next-generation processors, and improved Reliability, Availability and Serviceability (RAS).
Communications servers are open, standards-based computing systems that operate as a carrier-grade common platform for a wide range of communications applications and allow equipment providers to add value at many levels of the system architecture.

COM Express is a form factor for computer-on-modules (COMs), which are highly integrated and compact computers that can be used in design applications much like integrated circuit components. Each module integrates core CPU and memory functionality, the common I/O of a PC/AT, USB, audio, graphics (PEG), and Ethernet. All I/O signals are mapped to two high density, low profile connectors on the bottom side of the module. COM Express employs a mezzanine-based approach. The COM modules plug into a baseboard that is typically customized to the application. Over time, the COM Express mezzanine modules can be upgraded to newer, backwards-compatible versions. COM Express is commonly used in Industrial, military, aerospace, gaming, medical, transportation, Internet of things, and general computing embedded applications.

VPX, also known as VITA 46, is a set of standards for connecting components of a computer, commonly used by defense contractors. Some are ANSI standards such as ANSI/VITA 46.0–2019. VPX provides VMEbus-based systems with support for switched fabrics over a new high speed connector. Defined by the VMEbus International Trade Association (VITA) working group starting in 2003, it was first demonstrated in 2004, and became an ANSI standard in 2007.
M-Modules are a mezzanine standard mainly used in industrial computers. Being mezzanines, they are always plugged on a carrier printed circuit board (PCB) that supports this format. The modules communicate with their carrier over a dedicated bus, and can have all kinds of special functions.
CompactPCI Serial is an industrial standard for modular computer systems. It is based on the established PICMG 2.0 CompactPCI standard, which uses the parallel PCI bus for communication among a system's card components. In contrast to this, CompactPCI Serial uses only serial point-to-point connections. CompactPCI Serial was officially adopted by the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group PICMG as PICMG CPCI-S.0 CompactPCI Serial in March 2011. Its mechanical concept is based on the proven standards of IEEE 1101-1-1998 and IEEE 1101-10-1996. CompactPCI Serial includes different connectors that permit very high data rates. The new technology standard succeeding parallel CompactPCI comprises another specification called PICMG 2.30 CompactPCI PlusIO. This is why CompactPCI Serial and CompactPCI PlusIO as a whole were also called CompactPCI Plus. PICMG's first working title of CompactPCI Serial was CPLUS.0. CompactPCI Serial backplanes and chassis are developed by Schroff, Elmа, and Pixus Technologies companies, as for the CompactPCI Serial board level electronics – they are developed by MEN Mikro Elektronik, Fastwel, EKF, Emerson Embedded Computing, ADLINK, and Kontron.
PICMG 1.0 is a PICMG specification that defines a CPU form factor and corresponding backplane connectors for PCI-ISA passive backplanes. This standard moves components typically located on the motherboard to a single plug-in card. PICMG 1.0 CPU Cards look much like standard ISA cards with extra gold finger connections for the ISA bus and the root PCI bus. The "motherboard" is replaced with a simple "passive backplane" that has only PCI and ISA connectors attached to it. These backplane connections include a dedicated system slot of the PICMG 1.0 CPU and various connections for standard ISA and PCI peripheral cards. This backplane is simple and robust, with a very low likelihood of failure, given its passive nature. This allows a much lower Mean Time to Repair than classic computer motherboard approaches, as electronics associated with CPUs can be replaced without having to remove peripheral devices.
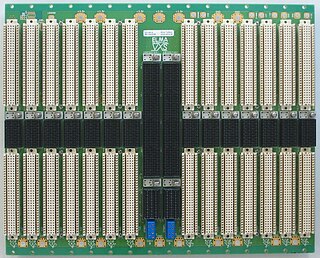
Elma Electronic is a publicly traded Swiss electronics company founded in 1960 and based in Wetzikon, Switzerland. The company has 5 product divisions: Systems Platforms, Backplanes, Enclosures & Components, Rotary Switches, and Cabinet Enclosures. The largest segment is systems packaging serving the military, aerospace, homeland security, medical and industrial markets. The Elma Bustronic division develops backplanes, including VME320, which was the world's fastest VME backplane in 1997. Elma Bustronic also develops backplanes in OpenVPX, VMEbus, VME64X, CompactPCI, MicroTCA, and custom bus structures. Elma is an executive member of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group (PICMG), VME International Trade Association, and member of the OpenVPX Industry Working Standards Group.

Modular crate electronics are a general type of electronics and support infrastructure commonly used for trigger electronics and data acquisition in particle detectors. These types of electronics are common in such detectors because all the electronic pathways are made by discrete physical cables connecting together logic blocks on the fronts of modules. This allows circuits to be designed, built, tested, and deployed very quickly as an experiment is being put together. Then the modules can all be removed and used again when the experiment is done.
MicroTCA is a modular, open standard, created and maintained by the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group (PICMG). It provides the electrical, mechanical, thermal and management specifications to create a switched fabric computer system, using Advanced Mezzanine Cards (AMC), connected directly to a backplane. MicroTCA is a descendant of the AdvancedTCA standard.

COM-HPC is a computer-on-module form factor standard that targets high performance compute and high I/O levels. Each COM-HPC module integrates core CPU and memory functionality and input and output including USB up to Gen 4, audio, graphics, up to Gen. 5, and Ethernet up to 25 Gbit/s per lane. All I/O signals are mapped to two high density, high speed and low profile connectors on the bottom side of the module. COM-HPC employs a mezzanine-based approach. The COM modules plug into a carrier or base board that is typically customized to the application. Over time, the COM-HPC mezzanine modules can be upgraded to newer, backwards-compatible versions. COM-HPC targets Industrial, Military/Aerospace, Gaming, Medical, Transportation, IoT, and General Computing embedded applications and even scales up to RAM and performance hungry server or edge server applications.
References
- ↑ "Advanced Mezzanine Card Base Specification AMC.0 R2.0". PICMG.
- ↑ PICMG Advanced Mezzanine Card AMC.0 R2.0, Table 2-1