
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting gametes, as well as facilitating fertilization and supporting the development and birth of offspring. Sex organs are found in many species of animals and plants, with their features varying depending on the species.

Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida.

In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite-sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. Fertilization is the fusion of two gametes. Copulation is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reproducing animals for insemination and subsequent internal fertilization. Mating may also lead to external fertilization, as seen in amphibians, fishes and plants. For most species, mating is between two individuals of opposite sexes. However, for some hermaphroditic species, copulation is not required because the parent organism is capable of self-fertilization (autogamy); for example, banana slugs.

Sperm competition is the competitive process between spermatozoa of two or more different males to fertilize the same egg during sexual reproduction. Competition can occur when females have multiple potential mating partners. Greater choice and variety of mates increases a female's chance to produce more viable offspring. However, multiple mates for a female means each individual male has decreased chances of producing offspring. Sperm competition is an evolutionary pressure on males, and has led to the development of adaptations to increase male's chance of reproductive success. Sperm competition results in a sexual conflict between males and females. Males have evolved several defensive tactics including: mate-guarding, mating plugs, and releasing toxic seminal substances to reduce female re-mating tendencies to cope with sperm competition. Offensive tactics of sperm competition involve direct interference by one male on the reproductive success of another male, for instance by physically removing another male's sperm prior to mating with a female. For an example, see Gryllus bimaculatus.

A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophores may additionally contain nourishment for the female, in which case it is called a nuptial gift, as in the instance of bush crickets. In the case of the toxic moth Utetheisa ornatrix, the spermatophore includes sperm, nutrients, and pyrrolizidine alkaloids which prevent predation because it is poisonous to most organisms. However, in some species such as the Edith's checkerspot butterfly, the "gift" provides little nutrient value. The weight of the spermatophore transferred at mating has little effect on female reproductive output.
An ovipore is a pore-like sexual organ of a female insect that is inseminated by the spermatophores ejected by the aedeagus of a male insect during copulation. The spermatophores that pass through the ovipore are stored in most insect species in another organ called spermatheca.
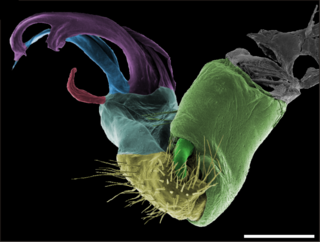
Gonopods are specialized appendages of various arthropods used in reproduction or egg-laying. In males, they facilitate the transfer of sperm from male to female during mating, and thus are a type of intromittent organ. In crustaceans and millipedes, gonopods are modified walking or swimming legs. Gonopods may be highly decorated with elaborate structures which may play roles in sperm competition, and can be used to differentiate and identify closely related species. Gonopods generally occur in one or more pairs, as opposed to the single (un-paired) reproductive organs such as the aedeagus of insects or the penis of harvestmen.

Traumatic insemination, also known as hypodermic insemination, is the mating practice in some species of invertebrates in which the male pierces the female's abdomen with his aedeagus and injects his sperm through the wound into her abdominal cavity (hemocoel). The sperm diffuses through the female's hemolymph, reaching the ovaries and resulting in fertilization.

Unicorn ("one horn", in Latin) is a genus of goblin spiders from South America, containing seven species that occur predominantly in high elevation, semi-desert regions of Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Individuals are relatively large for goblin spiders, measuring up to 3.0 mm (0.12 in) in body length. The genus name refers to a characteristic pointed projection between the eyes and jaws of males. In at least one species, broken-off tips of the male pedipalps have been found within the genitalia of females, postulated as a means of sperm competition. Unicorn possesses several traits that suggest it is a relatively "primitive" member of the Oonopidae, and is classified with other similar, soft-bodied goblin spiders in the subfamily Sulsulinae.
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring.

Pholcus phalangioides, commonly known as the cosmopolitan cellar spider, long-bodied cellar spider or one of various types called a daddy long-legs spider, is a spider of the family Pholcidae. It is also known as the skull spider, since its cephalothorax is said to resemble a human skull. This is the only spider species described by the Swiss entomologist Johann Kaspar Füssli, who first recorded it in 1775. Its common name of "daddy long-legs" should not be confused with a different arachnid group with the same common name, the harvestman (Opiliones), or the crane flies of the superfamily Tipuloidea.
An intromittent organ is any external organ of a male organism that is specialized to deliver sperm during copulation. Intromittent organs are found most often in terrestrial species, as most non-mammalian aquatic species fertilize their eggs externally, although there are exceptions. For many species in the animal kingdom, the male intromittent organ is a hallmark characteristic of internal fertilization.
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids.

The study of the genitalia of Lepidoptera is important for Lepidoptera taxonomy in addition to development, anatomy and natural history. The genitalia are complex and provide the basis for species discrimination in most families and also in family identification. The genitalia are attached onto the tenth or most distal segment of the abdomen. Lepidoptera have some of the most complex genital structures in the insect groups with a wide variety of complex spines, setae, scales and tufts in males, claspers of different shapes and different modifications of the ductus bursae in females.
A nuptial gift is a nutritional gift given by one partner in some animals' sexual reproduction practices.
Spermozoros impolitus is a species of insect in the order Zoraptera.
Most insects reproduce oviparously, i.e. by laying eggs. The eggs are produced by the female in a pair of ovaries. Sperm, produced by the male in one testicle or more commonly two, is transmitted to the female during mating by means of external genitalia. The sperm is stored within the female in one or more spermathecae. At the time of fertilization, the eggs travel along oviducts to be fertilized by the sperm and are then expelled from the body ("laid"), in most cases via an ovipositor.

The two palpal bulbs – also known as palpal organs and genital bulbs – are the copulatory organs of a male spider. They are borne on the last segment of the pedipalps, giving the spider an appearance often described as like wearing boxing gloves. The palpal bulb does not actually produce sperm, being used only to transfer it to the female. Palpal bulbs are only fully developed in adult male spiders and are not completely visible until after the final moult. In the majority of species of spider, the bulbs have complex shapes and are important in identification.

In zoology, copulation is animal sexual behavior in which a male introduces sperm into the female's body, especially directly into her reproductive tract. This is an aspect of mating. Many animals that live in water use external fertilization, whereas internal fertilization may have developed from a need to maintain gametes in a liquid medium in the Late Ordovician epoch. Internal fertilization with many vertebrates occurs via cloacal copulation, known as cloacal kiss, while mammals copulate vaginally, and many basal vertebrates reproduce sexually with external fertilization.

Philodromus cespitum is a species of running crab spider in the family Philodromidae. It is found in North America, Europe, North Africa, and parts of the Middle East and Asia. P. cespitum is a foliage-dweller, and is the most abundant species found in European fruit orchards. It acts as a biological control by preying on orchard pests. P. cespitum is a diurnal ambush hunter and preys on aphids, insects, and occasionally competitor spider species. Males court females by tapping on the females’ bodies with their forelegs. They then insert a genital plug into the female during copulation. Unlike in many other spider species, subsequent males can mate with plugged females by removing part of the plug prior to copulation. Males discriminate among females based on virginity and plug size, and can determine these factors using the females’ draglines and plug samples.














