Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants are frequently added to industrial products, such as polymers, fuels, and lubricants, to extend their usable lifetimes. Foods are also treated with antioxidants to forestall spoilage, in particular the rancidification of oils and fats. In cells, antioxidants such as glutathione, mycothiol, or bacillithiol, and enzyme systems like superoxide dismutase, can prevent damage from oxidative stress.

Oxidative phosphorylation or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis.
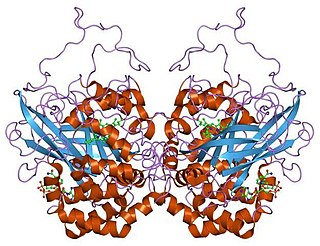
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting the cell from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all enzymes; one catalase molecule can convert millions of hydrogen peroxide molecules to water and oxygen each second.

Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing no mutation event occurs, the resulting daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell. Hence, bacterial growth occurs. Both daughter cells from the division do not necessarily survive. However, if the surviving number exceeds unity on average, the bacterial population undergoes exponential growth. The measurement of an exponential bacterial growth curve in batch culture was traditionally a part of the training of all microbiologists; the basic means requires bacterial enumeration by direct and individual, direct and bulk (biomass), indirect and individual, or indirect and bulk methods. Models reconcile theory with the measurements.

An obligate aerobe is an organism that requires oxygen to grow. Through cellular respiration, these organisms use oxygen to metabolise substances, like sugars or fats, to obtain energy. In this type of respiration, oxygen serves as the terminal electron acceptor for the electron transport chain. Aerobic respiration has the advantage of yielding more energy than fermentation or anaerobic respiration, but obligate aerobes are subject to high levels of oxidative stress.
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are embedded within the membrane.

An aerobic organism or aerobe is an organism that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment. The ability to exhibit aerobic respiration may yield benefits to the aerobic organism, as aerobic respiration yields more energy than anaerobic respiration. Energy production of the cell involves the synthesis of ATP by an enzyme called ATP synthase. In aerobic respiration, ATP synthase is coupled with an electron transport chain in which oxygen acts as a terminal electron acceptor. In July 2020, marine biologists reported that aerobic microorganisms (mainly), in "quasi-suspended animation", were found in organically poor sediments, up to 101.5 million years old, 250 feet below the seafloor in the South Pacific Gyre (SPG), and could be the longest-living life forms ever found.
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. The sea floor is possibly one of the largest accumulation of anaerobic organisms on Earth, where microbes are primarily concentrated around hydrothermal vents. These microbes produce energy in absence of sunlight or oxygen through a process called chemosynthesis, whereby inorganic compounds such as hydrogen gas, hydrogen sulfide or ferrous ions are converted into organic matter.

Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which contains energy. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into ATP, and then release waste products.
A mesophile is an organism that grows best in moderate temperature, neither too hot nor too cold, with an optimum growth range from 20 to 45 °C. The optimum growth temperature for these organisms is 37 °C. The term is mainly applied to microorganisms. Organisms that prefer extreme environments are known as extremophiles. Mesophiles have diverse classifications, belonging to two domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and to kingdom Fungi of domain Eucarya. Mesophiles belonging to the domain Bacteria can either be gram-positive or gram-negative. Oxygen requirements for mesophiles can be aerobic or anaerobic. There are three basic shapes of mesophiles: coccus, bacillus, and spiral.
Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen (O2). Although oxygen is not the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain.

A facultative anaerobic organism is an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but is capable of switching to fermentation if oxygen is absent.

In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (O2), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (O2H), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl radical (OH.), and singlet oxygen. ROS are pervasive because they are readily produced from O2, which is abundant. ROS are important in many ways, both beneficial and otherwise. ROS function as signals, that turn on and off biological functions. They are intermediates in the redox behavior of O2, which is central to fuel cells. ROS are central to the photodegradation of organic pollutants in the atmosphere. Most often however, ROS are discussed in a biological context, ranging from their effects on aging and their role in causing dangerous genetic mutations.

Obligate anaerobes are microorganisms killed by normal atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (20.95% O2). Oxygen tolerance varies between species, with some species capable of surviving in up to 8% oxygen, while others lose viability in environments with an oxygen concentration greater than 0.5%.
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum is a widespread member of the genus Lactiplantibacillus and commonly found in many fermented food products as well as anaerobic plant matter. L. plantarum was first isolated from saliva. Based on its ability to temporarily persist in plants, the insect intestine and in the intestinal tract of vertebrate animals, it was designated as a nomadic organism. L. plantarum is Gram positive, bacilli shaped bacterium. L. plantarum cells are rods with rounded ends, straight, generally 0.9–1.2 μm wide and 3–8 μm long, occurring singly, in pairs or in short chains. L. plantarum has one of the largest genomes known among the lactic acid bacteria and is a very flexible and versatile species. It is estimated to grow between pH 3.4 and 8.8. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum can grow in the temperature range 12 °C to 40 °C. The viable counts of the "L. plantarum" stored at refrigerated condition (4 °C) remained high, while a considerable reduction in the counts was observed stored at room temperature.

Staphylococcus epidermidis is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. It is part of the normal human microbiota, typically the skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although S. epidermidis is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. S. epidermidis is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, S. epidermidis is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory.

Bacteroides fragilis is an anaerobic, Gram-negative, pleomorphic to rod-shaped bacterium. It is part of the normal microbiota of the human colon and is generally commensal, but can cause infection if displaced into the bloodstream or surrounding tissue following surgery, disease, or trauma.
Microbial metabolism is the means by which a microbe obtains the energy and nutrients it needs to live and reproduce. Microbes use many different types of metabolic strategies and species can often be differentiated from each other based on metabolic characteristics. The specific metabolic properties of a microbe are the major factors in determining that microbe's ecological niche, and often allow for that microbe to be useful in industrial processes or responsible for biogeochemical cycles.

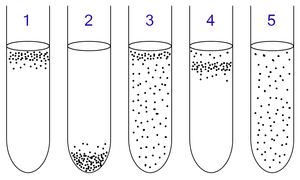
Thioglycolate broth is a multipurpose, enrichment, differential medium used primarily to determine the oxygen requirements of microorganisms. Sodium thioglycolate in the medium consumes oxygen and permits the growth of obligate anaerobes. This, combined with the diffusion of oxygen from the top of the broth, produces a range of oxygen concentrations in the medium along its depth. The oxygen concentration at a given level is indicated by a redox-sensitive dye such as resazurine that turns pink in the presence of oxygen.

Clostridium tertium is an anaerobic, motile, gram-positive bacterium. Although it can be considered an uncommon pathogen in humans, there has been substantial evidence of septic episodes in human beings. C. tertium is easily decolorized in Gram-stained smears and can be mistaken for a Gram-negative organism. However, C.tertium does not grow on selective media for Gram-negative organisms.