
While the defence of Bermuda remains the responsibility of the government of the United Kingdom, rather than of the local Bermudian Government, the island still maintains a militia for the purpose of defence.

The Royal Gibraltar Regiment is part of British Forces Gibraltar for the British overseas territory of Gibraltar, which historically, along with Bermuda, Halifax, Nova Scotia, and Malta, had been designated an Imperial fortress rather than a colony. It was formed in 1958 from the Gibraltar Defence Force as an infantry unit, with an integrated artillery troop. The regiment is included in the British Army as a defence engagement force.

Kindley Air Force Base was a United States Air Force base in Bermuda from 1948–1970, having been operated from 1943 to 1948 by the United States Army Air Forces as Kindley Field.

The governor of Bermuda is the representative of the British monarch in the British overseas territory of Bermuda.

HMD Bermuda was the principal base of the Royal Navy in the Western Atlantic between American independence and the Cold War. The Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda had occupied a useful position astride the homeward leg taken by many European vessels from the New World since before its settlement by England in 1609. French privateers may have used the islands as a staging place for operations against Spanish galleons in the 16th century. Bermudian privateers certainly played a role in many English and British wars following settlement, with its utility as a base for his privateers leading to the Earl of Warwick, the namesake of Warwick Parish, becoming the most important investor of the Somers Isles Company. Despite this, it was not until the loss of bases on most of the North American Atlantic seaboard threatened Britain's supremacy in the Western Atlantic that the island assumed great importance as a naval base. In 1818 the Royal Naval Dockyard, Bermuda officially replaced the Royal Naval Dockyard, Halifax, as the British headquarters for the North America Station (which would become the North America and West Indies Station after absorbing the Jamaica Station in 1830.

The Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps (BVRC) was created in 1894 as a reserve for the Regular Army infantry component of the Bermuda Garrison. Renamed the Bermuda Rifles in 1951, it was amalgamated into the Bermuda Regiment in 1965.

The Bermuda Militia Artillery was a unit of part-time soldiers organised in 1895 as a reserve for the Royal Garrison Artillery detachment of the Regular Army garrison in the Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda. Militia Artillery units of the United Kingdom and Colonies were intended to man coastal batteries in times of war, which were manned by under-strength numbers of regular army gunners in peace time. The unit was embodied during both world wars, fulfilling its role within the garrison, and also sending contingents overseas to more active theatres of the wars.

The Bermuda Garrison was the military establishment maintained on the British Overseas Territory and Imperial fortress of Bermuda by the regular British Army and its local militia and voluntary reserves from 1701 to 1957. The garrison evolved from an independent company, to a company of Royal Garrison Battalion during the American War of Independence, and a steadily growing and diversifying force of artillery and infantry with various supporting corps from the French Revolution onwards. During the American War of Independence, the garrison in Bermuda fell under the military Commander-in-Chief of America. Subsequently, it was part of the Nova Scotia Command until 1868, and was an independent Bermuda Command from then until its closure in 1957.

Prospect Camp, also referred to as Prospect Garrison, was the main infantry camp of the Bermuda Garrison, the military force stationed in the Imperial fortress of Bermuda. It also contained Fort Prospect, Fort Langton, and Fort Hamilton, as well as being the base for mobile artillery batteries, manned by the Royal Artillery. Outlying parts of the camp were disposed of in the early decades of the Twentieth Century as the garrison in Bermuda was reduced. The core area, including the barracks, passed to the local government when the garrison was withdrawn in 1957.

The Historic Town of St George and Related Fortifications is the name used by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization's (UNESCO) World Heritage Committee to identify collectively as a World Heritage Site St. George's Town, founded in 1612, and a range of fortifications, batteries, and magazines built between 1612 and 1939, the last of which was removed from use in 1953.

Lieutenant General Sir George Mackworth Bullock, was an officer of the British Army. He served during World War I, rising to the rank of lieutenant general, and was also the one-hundred and eighth civil Governor and military Commander-in-Chief of Bermuda.

St. David's Battery is a disused fixed battery on St. David's Island, Bermuda maintained until 1953 by the Bermuda Garrison of the British Army. It was built and manned by the Royal Garrison Artillery and the Royal Engineers, and their part-time reserves, the Bermuda Militia Artillery and the Bermuda Volunteer Engineers. Its rifled breech-loader (RBL) artillery guns guarded the eastern approach to St. George's Harbour. In wartime it served as an examination battery.
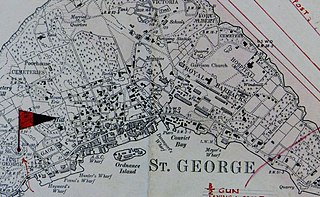
The Western Redoubt, or Fort William, is a square fort built on a crest on the eastern side of Government Hill, and within the boundaries of the original main British Army camp in the Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda, St. George's Garrison.

The United States Naval Station Whites Island was a United States Navy (USN) facility located on White's Island in Hamilton Harbour, in the British Colony of Bermuda, 640 miles off the coast of North Carolina.

The Bermuda Base Command was a command of the United States Army, established to defend the British Colony of Bermuda, located 640 miles off Cape Hatteras, North Carolina. It was created in April 1941 when United States Army troops were sent to the island.

The Bermuda Militia Infantry was raised in 1939 as a part-time reserve of the British Army's Bermuda Garrison.

St. George's Garrison was the first permanent military camp of the Bermuda Garrison established in the British colony and Imperial fortress of Bermuda, with construction of Old Military Road and the original Royal Barracks commencing during the war between Britain and France that followed the French Revolution. It would remain in use until 1957, when it was transferred to the civil (colonial) government with most of the other Admiralty and War Office properties in Bermuda.

Lord Salisbury described Malta, Gibraltar, Bermuda, and Halifax as Imperial fortresses at the 1887 Colonial Conference, though by that point they had been so designated for decades. Later historians have also given the title "imperial fortress" to St. Helena and Mauritius.

Scaur Hill Fort, also called Scaur Hill Lines and Somerset Lines, is a fortified position erected in the 1870s at Scaur Hill, on Somerset Island, in Sandys Parish, the westernmost parish of the Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda.

Fort George is a square fort built on the crest of Mount Hill to the west of St. George's Town, near to, but outside of the boundaries of the original main British Army camp in the Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda, St. George's Garrison.



















