 |
|---|
| Law |
| Administrative divisions |
The land area of Bermuda is divided into nine parishes. There are also two defined municipalities, located in the boundaries of two of the parishes.
 |
|---|
| Law |
| Administrative divisions |
The land area of Bermuda is divided into nine parishes. There are also two defined municipalities, located in the boundaries of two of the parishes.
Bermuda has nine "Parishes", originally called "Tribes". Each of the nine parishes with the exception of St. George's covers the same land area of 597 hectares. The Parishes are not administrative divisions, and have no relationship with Bermuda's electoral districts.
| Parish | Population (2016) [1] | Population (2010) [1] | Change (%) [1] | Land area (km2) | Population density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Devonshire | 7,087 | 7,330 | −3.3% | 5.97 | 1,187.1/km2 |
| Hamilton | 5,584 | 5,862 | −4.7% | 5.97 | 935.3/km2 |
| Paget | 5,899 | 5,702 | +3.5% | 5.97 | 988.1/km2 |
| Pembroke | 11,160 | 10,614 | +5.1% | 5.97 | 1,869.3/km2 |
| St George's | 5,659 | 6,422 | −11.9% | 6.6 | 857.4/km2 |
| Sandys | 6,983 | 7,653 | −8.8% | 5.97 | 1,169.7/km2 |
| Smith's | 5,984 | 5,406 | +10.7% | 5.97 | 1,002.3/km2 |
| Southampton | 6,421 | 6,633 | −3.2% | 5.97 | 1,075.5/km2 |
| Warwick | 9,002 | 8,615 | +4.5% | 5.97 | 1,507.9/km2 |
Note on pronunciation:
Whereas the town of St George's is surrounded by St George's Parish, Hamilton Parish and the city of Hamilton are not close to each other geographically.
Saint George's, the larger of the two municipalities, served as Bermuda's capital until 1815 until the newly established Hamilton replaced it.
Bermuda has two villages (unincorporated urban areas)

Bermuda is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about 1,035 km (643 mi) to the west-northwest.

Bermuda is the oldest British Overseas Territory, and the oldest self-governing British Overseas Territory, and has a great degree of internal autonomy through authority and roles of governance delegated to it by the national Government. Its parliament held its first session in 1620, making it the third-oldest continuous parliament in the world. As part of the British realm, King Charles III is head of state and is represented in Bermuda by a Governor, whom he appoints on the advice of the British Government. The Governor has special responsibilities in four areas: external affairs, defence, internal security, and policing.

Bermuda is an overseas territory of the United Kingdom in the North Atlantic Ocean. Located off the east coast of the United States, it is situated around 1,770 km (1,100 mi) northeast of Miami, Florida, and 1,350 km (840 mi) south of Halifax, Nova Scotia, west of Portugal, northwest of Brazil, 1,759 km (1,093 mi) north of Havana, Cuba and north-northeast of San Juan, Puerto Rico. The nearest landmass is Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, about 1,030 km (640 mi) west-northwest, followed by Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia, Canada 1,236 km northward. Although commonly referred to in the singular, the territory consists of approximately 138 islands, with a total area of 57 km2 (22 sq mi).

Bermuda consists of several islands with an area of 53.2 km2 (20.5 sq mi) with 447 km (278 mi) of paved roads — 225 km (140 mi) of which are public roads and 222 km (138 mi) are private paved roads. A former railway track has been converted into a walking trail. There are also two marine ports, and an airport, the L.F. Wade International Airport, located at the former U.S. Naval Air Station. A causeway links Hamilton Parish, Bermuda to St. George's and the airport.
In the United States, a county or county equivalent is an administrative or political subdivision of a U.S. state or other territories of the United States which consists of a geographic area with specific boundaries and usually some level of governmental authority. The term "county" is used in 48 states, while Louisiana and Alaska have functionally equivalent subdivisions called parishes and boroughs, respectively. Counties and other local governments exist as a matter of U.S. state law, so the specific governmental powers of counties may vary widely between the states, with many providing some level of services to civil townships, municipalities, and unincorporated areas. Certain municipalities are in multiple counties; New York City is uniquely partitioned into five counties, referred to at the city government level as boroughs. Some municipalities have been consolidated with their county government to form consolidated city-counties, or have been legally separated from counties altogether to form independent cities. Conversely, counties in Connecticut and Rhode Island, eight of Massachusetts's 14 counties, and Alaska's Unorganized Borough have no government power, existing only as geographic distinctions.

An unincorporated area is a region that is not governed by a local municipal corporation. There are many unincorporated communities and areas in the United States and Canada.

St. George's, located on the island and within the parish of the same names, settled in 1612, is the first permanent English settlement on the islands of Bermuda. It is often described as the third permanent British settlement in the Americas, after Jamestown, Virginia (1607), and Cupids, Newfoundland (1610), and the oldest continuously-inhabited British town in the New World, since the other two settlements were seasonal for a number of years.

Hamilton Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It was renamed for Scottish aristocrat James Hamilton, 2nd Marquess of Hamilton (1589–1625) when he purchased the shares originally held in the Virginia Company by Lucy Russell, Countess of Bedford.
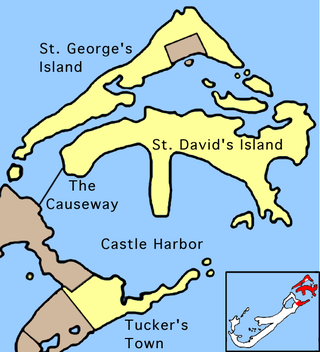
St. George's Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after the founder of the Bermuda colony, Admiral Sir George Somers.

Tucker's Town is a small community in St. George's Parish, Bermuda at the mouth of Castle Harbour. It is the only part of the parish on the Main Island, and includes the Tucker's Town Peninsula that today is the site of many homes belonging to wealthy non-Bermudians. The most densely populated part of Tucker's Town was historically situated west of Tucker's Town Bay, and was almost entirely cleared to make way for golf links.

The Bermuda Police Service is the law enforcement agency of the British Overseas Territory and former Imperial fortress of Bermuda. It is responsible for policing the entire archipelago, including incorporated municipalities, and the surrounding waters. It is part of, and entirely funded by, the Government of Bermuda. Like the Royal Bermuda Regiment, it is under the nominal control of the territory's Governor and Commander in Chief, although, for day-to-day purposes, control is delegated to a minister of the local government. It was created in 1879, as Bermuda's first professional police service. In organisation, operation, and dress, it was created and has developed in line with the patterns established by British Isles police services, such as the City of Glasgow Police, and the Metropolitan Police Service.
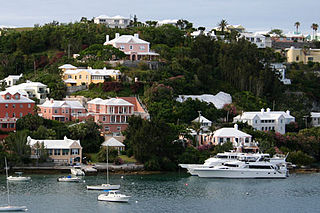
The architecture of Bermuda has developed over the past four centuries. The archipelago's isolation, environment, climate, and scarce resources have been key driving points, though inspiration from Europe, the Caribbean and the Americas is evident. Distinctive elements appeared with initial settlement in the early 17th century, and by the second half of that century features that remain common today began to appear.
Henry Jennings was an English privateer-turned-pirate. Jennings's first recorded act of piracy took place in early 1716 when, with three vessels and 150–300 men, Jennings's fleet ambushed the Spanish salvage camp from the 1715 Treasure Fleet. After the Florida raid, Jennings and his crew also linked up with Benjamin Hornigold's "three sets of pirates" from New Providence Island.
The Talbot Brothers were a musical group based in Bermuda that were among the most popular calypso performers of the 1950s. The band was composed of brothers Archie, Austin, Bryan, a.k.a. "Dick", Ross, a.k.a. "Blackie" and Roy Talbot (bass), and their cousin Cromwell "Mandy" Mandres (accordion).

Mortlach is a village in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan within the Rural Municipality of Wheatlands No. 163 and Census Division No. 7. The village is on the Trans Canada Highway about 40 km west of the City of Moose Jaw. Thunder Creek passes the community to the north where it is joined by Sandy Creek. Mortlach became a village on April 19, 1906, and is one of two towns in Saskatchewan to have been incorporated as a town to then be reverted to village status on January 1, 1949; the other is the village of Alsask.

The Anglican Church of Bermuda is a single diocese consisting of nine parishes and is part of the Anglican Communion, though not a part of an ecclesiastical province. The current Bishop of Bermuda, seated at the Cathedral of the Most Holy Trinity in the City of Hamilton, is Nicholas Dill, who was installed on 29 May 2013.