
Mitanni, earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, c. 1600 BC; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or Naharin in Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria and southeast Anatolia with Indo-Aryan linguistic and political influences. Since no histories, royal annals or chronicles have yet been found in its excavated sites, knowledge about Mitanni is sparse compared to the other powers in the area, and dependent on what its neighbours commented in their texts.

Immanuel Velikovsky was a Russian-American psychoanalyst, writer, and catastrophist. He is the author of several books offering pseudohistorical interpretations of ancient history, including the U.S. bestseller Worlds in Collision published in 1950. Velikovsky's work is frequently cited as a canonical example of pseudoscience and has been used as an example of the demarcation problem.
The New Chronology is an alternative chronology of the ancient Near East developed by English Egyptologist David Rohl and other researchers beginning with A Test of Time: The Bible - from Myth to History in 1995. It contradicts mainstream Egyptology by proposing a major revision of the established Egyptian chronology, in particular by re-dating Egyptian kings of the Nineteenth through Twenty-fifth Dynasties, bringing forward conventional dating by up to 350 years. Rohl asserts that the New Chronology allows him to identify some of the characters in the Hebrew Bible with people whose names appear in archaeological finds.
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to the era of the Egyptian, Hittite, and Mitanni conflict, as well as in ancient China.
The history of ancient Egypt spans the period from the early prehistoric settlements of the northern Nile valley to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 BC. The pharaonic period, the period in which Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh, is dated from the 32nd century BC, when Upper and Lower Egypt were unified, until the country fell under Macedonian rule in 332 BC.

Wahibre Psamtik I was the first pharaoh of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt, the Saite period, ruling from the city of Sais in the Nile delta between 664–610 BC. He was installed by Ashurbanipal of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, against the Kushite rulers of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty, but later gained more autonomy as the Assyrian Empire declined.

The New Kingdom, also called the Egyptian New kingdom Empire, refers to ancient Egypt between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC. This period of ancient Egyptian history covers the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties. Through radiocarbon dating, the establishment of the New Kingdom has been placed between 1570 BC and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period. It was the most prosperous time for the Egyptian people and marked the peak of Egypt's power.
Shishak, also spelled Shishaq or Susac, was, according to the Hebrew Bible, an Egyptian pharaoh who sacked Jerusalem in the 10th century BC. He is usually identified with the pharaoh Shoshenq I.

The Third Intermediate Period of ancient Egypt began with the death of Pharaoh Ramesses XI in 1077 BC, which ended the New Kingdom, and was eventually followed by the Late Period. Various points are offered as the beginning for the latter era, though it is most often regarded as dating from the foundation of the Twenty-Sixth Dynasty by Psamtik I in 664 BC, following the departure of the Nubian Kushite rulers of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty after they were driven out by the Assyrians under King Ashurbanipal. The use of the term "Third Intermediate Period", based on the analogy of the well-known First and Second Intermediate Periods, was popular by 1978, when British Egyptologist Kenneth Kitchen used the term for the title of his book on the period. While Kitchen argued that the period was 'far from being chaotic' and hoped that his work would lead to the abolishment of the term, with his own preference being the 'Post-Imperial epoch', his use of the term as a title seems only to have entrenched the use of the term.
The Glasgow Chronology is a proposed revision of the Egyptian chronology of ancient Egypt. It was first formulated between the years 1978 and 1982 by a working group following the Glasgow Conference of Society for Interdisciplinary Studies.

The majority of Egyptologists agree on the outline and many details of the chronology of Ancient Egypt. This scholarly consensus is known as the Conventional Egyptian chronology, which places the beginning of the Old Kingdom in the 27th century BC, the beginning of the Middle Kingdom in the 21st century BC and the beginning of the New Kingdom in the mid-16th century BC.

Pi-Ramesses was the new capital built by the Nineteenth Dynasty Pharaoh Ramesses II at Qantir, near the old site of Avaris. The city had served as a summer palace under Seti I, and may have been founded by Ramesses I while he served under Horemheb.

Tuya was the wife of Pharaoh Seti I of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt and mother of Tia, Ramesses II, and possibly Henutmire.

Ramesses II, commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was an Egyptian pharaoh. He was the third ruler of the Nineteenth Dynasty. Along with Thutmose III of the Eighteenth Dynasty, he is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the New Kingdom, which itself was the most powerful period of ancient Egypt. He is also widely considered one of ancient Egypt's most successful warrior pharaohs, conducting no fewer than 15 military campaigns, all resulting in victories, excluding the Battle of Kadesh, generally considered a stalemate.
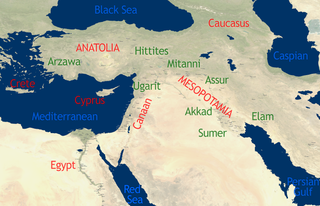
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Comparing many records pieces together a relative chronology relating dates in cities over a wide area.
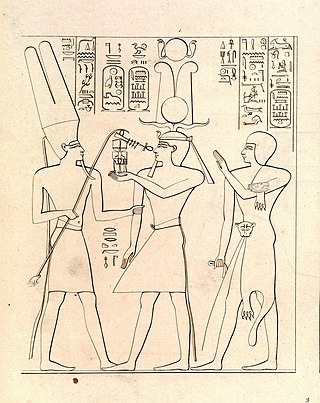
The Bible makes reference to various pharaohs of Egypt. These include unnamed pharaohs in events described in the Torah, as well as several later named pharaohs, some of whom were historical or can be identified with historical pharaohs.

The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties together constitute an era known as the Ramesside period owing to the predominance of rulers with the given name "Ramesses". This dynasty is generally considered to mark the beginning of the decline of Ancient Egypt at the transition from the Late Bronze to Iron Age. During the period of the Twentieth Dynasty, Ancient Egypt faced the crisis of invasions by Sea Peoples. The dynasty successfully defended Egypt, while sustaining heavy damage.

Djedneferre Dedumose II was a native ancient Egyptian pharaoh during the Second Intermediate Period. According to egyptologists Kim Ryholt and Darrell Baker, he was a ruler of the Theban 16th Dynasty. Alternatively, Jürgen von Beckerath, Thomas Schneider and Detlef Franke see him as a king of the 13th Dynasty.

2 Chronicles 12 is the twelfth chapter of the Second Book of Chronicles the Old Testament in the Christian Bible or of the second part of the Books of Chronicles in the Hebrew Bible. The book is compiled from older sources by an unknown person or group, designated by modern scholars as "the Chronicler", and had the final shape established in late fifth or fourth century BCE. This chapter belongs to the section focusing on the kingdom of Judah until its destruction by the Babylonians under Nebuchadnezzar and the beginning of restoration under Cyrus the Great of Persia. The focus of this chapter is the kingdom of Israel's division in the beginning of Rehoboam's reign.

1 Kings 14 is the fourteenth chapter of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the First Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BCE, with a supplement added in the sixth century BCE. 1 Kings 12:1 to 16:14 documents the consolidation of the kingdoms of northern Israel and Judah: this chapter focusses on the reigns of Jeroboam and Nadab in the northern kingdom and Rehoboam in the southern kingdom.

















