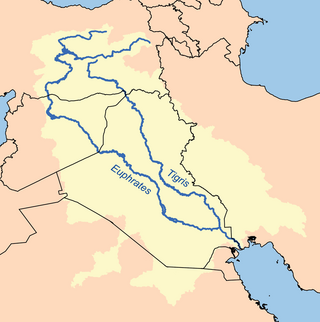
The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia that flows into the Persian Gulf. Its primary rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates, along with smaller tributaries.

The Marsh Arabs, also referred to as Ahwaris, the Maʻdān or Shroog —the latter two often considered derogatory in the present day—are Arab inhabitants of the Mesopotamian marshlands in the modern-day south Iraq, as well as in the Hawizeh Marshes straddling the Iraq-Iran border.
Umm al Binni lake is a mostly dry lake within the Central Marshes in Maysan Governorate in southern Iraq. The 3.4 km (2.1 mi) wide lake is approximately 45 km (28 mi) northwest of the Tigris–Euphrates confluence. Because of its shape, location, and other details, it was first conjectured by Sharad Master, a geoarchaeologist, to represent an impact crater. However, these claims have been disputed, with other studies finding subsidence of the underlying rock a more plausible explanation.

The Mesopotamian Marshes, also known as the Iraqi Marshes, are a wetland area located in Southern Iraq and southwestern Iran. The marshes are primarily located on the floodplains of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers bound by the cities of Basra, Nasiriyah, Amarah and a portion of southwestern Iran. Historically the marshlands, mainly composed of the separate but adjacent Central, Hawizeh and Hammar Marshes, used to be the largest wetland ecosystem of Western Eurasia. The unique wetland landscape is home to the Marsh people, who have developed a unique culture tightly coupled to the landscape – harvesting reeds and rice, fishing, and herding water buffalo.

The Mesopotamian Marshes were drained in Iraq and to a smaller degree in Iran between the 1950s and 1990s to clear large areas of the marshes in the Tigris-Euphrates river system. The marshes formerly covered an area of around 20,000 km2 (7,700 sq mi). The main sub-marshes, the Hawizeh, Central, and Hammar marshes, were drained at different times for different reasons.

The Hammar Marshes are a large wetland complex in southeastern Iraq that are part of the Mesopotamian Marshes in the Tigris–Euphrates river system. Historically, the Hammar Marshes extended up to 4,500 km2 (1,700 sq mi) during seasonal floods. They were destroyed during the 1990s by large-scale drainage, dam and dike construction projects. Since 2003, they are recovering following reflooding and destruction of dams.
The archaeological site of Abu Salabikh, around 20 km (12 mi) northwest of the site of ancient Nippur and about 150 kilometers southeast of the modern city of Baghdad in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq marks the site of a small Sumerian city that existed from the Neolithic through the late 3rd millennium, with cultural connections to the cities of Kish, Mari and Ebla. Its ancient name is unknown though Eresh and Kesh have been suggested as well as Gišgi. Kesh was suggested by Thorkild Jacobsen before excavations began. The Euphrates was the city's highway and lifeline; when it shifted its old bed, in the late third millennium BC, the city dwindled away. Only eroded traces remain on the site's surface of habitation after the Early Dynastic Period. There is another small archaeological site named Abu-Salabikh in the Hammar Lake region of Southern Iraq, which has been suggested as the possible capital of the Sealand dynasty.

The Hawizeh Marshes are a complex of marshes that straddle the Iran–Iraq border. The marshes are fed by two branches of the Tigris River in Iraq and the Karkheh River in Iran. The Hawizeh marsh is critical to the survival of the Central and Hammar marshes also make up the Mesopotamian Marshes, because they are a refuge for species that may recolonize or reproduce in other marshlands. Hawizeh Marshes are drained by the Al-Kassarah. This river plays a critical role in maintaining the marshes as a flow-through system and preventing it from becoming a closed saline basin.

The Central or Qurna Marshes are a large complex of wetlands in Iraq that, along with the Hawizeh and Hammar marshes, make up the Mesopotamian Marshes of the Tigris–Euphrates river system. Formerly covering an area of around 3000 square kilometres, they were almost completely drained following the 1991 uprisings in Iraq and have in recent years been reflooded.

Al-Chibayish District is a district of the Dhi Qar Governorate, Iraq, located to the east of Nasiriyah and northwest of Basra Governorate. The district capital is Al-Chibayish. The district's geography is dominated by the Hammar Marshes, a subset of the Mesopotamian Marshes, and by the Euphrates River that feeds the marshes.

Tourism in Iraq refers to tourism in the Western Asian country of Iraq. Iraq was one of the main destinations for many years, however this changed dramatically due to conflicts. Tourism in Iraq has faced many challenges, however, in recent years there have been improvements. The capital city Baghdad is the second largest city in the Arab world and the 4th largest in the Middle East. Iraq has several World Heritage Sites, dating back to ancient Mesopotamia, most notably Babylon Iraq. Iraq is considered to be a potential location for ecotourism. Erbil was chosen as "Arab Tourism Capital" in 2014 by the Arab Tourism Committee. Then, Baghdad was chosen as Arab Tourism Capital in 2024-2025

Al-Bubsairy is a village on the Shatt El Arab in Iraq, inhabited by Marsh Arabs. It is located at 30°53'48.5"N 47°32'16.9"E, south of Al Qurnah, and in Al-Qurna District.

Ash Shabaziyah, Iraq is a village of Basrah Governorate in southern Iraq located on the west bank of the Shatt Al-Arab River between the Shatt al Arab and Hamma marshes. The town has a primary school and at least 3 mosques. The area is close to the Mesopotamian Marshes(Hammar Marshes), and has traditionally been home to many Marsh Arabs.

Shafi is a town of Basrah Governorate in southern Iraq, on the west bank of the Shatt Al-Arab River.

Ad Dayr is a town of Basrah Governorate in southern Iraq, on the west bank of the Shatt Al-Arab River. The town has one of the few bridges over the Shatt Al-Arab.

Madaniyah, Iraq is a small village of Basrah Governorate, on the west bank of the Shatt Al-Arab River in southern Iraq. It is adjacent to the town of Ad Dayr and is located at 30.802088, 47.574837.
Qaryat Nasr is a town of Basrah Governorate in southern Iraq, on the west bank of the Shatt Al-Arab River. Qaryat Nasr, Iraq is located at 30.78n and 47.55e.
The mid-24th century BCE climate anomaly is the period, between 2354 and 2345 BCE, of consistently reduced annual temperatures that are reconstructed from consecutive abnormally narrow, Irish oak tree rings. These tree rings are indicative of a period of catastrophically reduced growth in Irish trees during that period. This range of dates also matches the transition from the Neolithic to the Bronze Age in the British Isles and a period of widespread societal collapse in the Near East. It has been proposed that this anomalous downturn in the climate might have been the result of comet debris suspended in the atmosphere.
The town of Qal'at Saleh is the district centre of Qal'at Saleh District, Maysan Governorate, southern Iraq. It is located along the road that links Basra to Amarah, a mere 40 km away. Qalat Saleh’s nearest towns are the district centres of Al-Majar Al Kabeer, Al Kahlaa, and Al Azeer. The town is surrounded by agricultural villages and rural communities: Sulaymaniyah village, Abu Samih village, and Beit Khaled village.
Tell Khaiber is a tell, or archaeological settlement mound, in southern Mesopotamia. It is located thirteen kilometers west of the modern city of Nasiriyah, about 19 kilometers northwest of the ancient city of Ur in Dhiq Qar Province and 25 kilometers south of the ancient city of Larsa. In 2012, the site was visited by members of the Ur Region Archaeology Project (URAP), a cooperation between the British Institute for the Study of Iraq, the University of Manchester and the Iraqi State Board for Antiquities and Heritage. They found that the site had escaped looting, and applied for an excavation permit.