Related Research Articles
NetApp, Inc. is an American data infrastructure company that provides unified data storage, integrated data services, and cloud operations (CloudOps) solutions to enterprise customers. The company is based in San Jose, California. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 from 2012 to 2021. Founded in 1992 with an initial public offering in 1995, NetApp offers cloud data services for management of applications and data both online and physically.

A content delivery network or content distribution network (CDN) is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers. The goal is to provide high availability and performance ("speed") by distributing the service spatially relative to end users. CDNs came into existence in the late 1990s as a means for alleviating the performance bottlenecks of the Internet as the Internet was starting to become a mission-critical medium for people and enterprises. Since then, CDNs have grown to serve a large portion of the Internet content today, including web objects, downloadable objects, applications, live streaming media, on-demand streaming media, and social media sites.

lighttpd is an open-source web server optimized for speed-critical environments while remaining standards-compliant, secure and flexible. It was originally written by Jan Kneschke as a proof-of-concept of the c10k problem – how to handle 10,000 connections in parallel on one server, but has gained worldwide popularity. Its name is a portmanteau of "light" and "httpd".
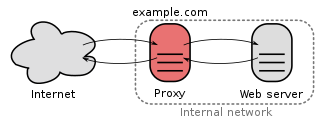
In computer networks, a reverse proxy or surrogate server is a proxy server that appears to any client to be an ordinary web server, but in reality merely acts as an intermediary that forwards the client's requests to one or more ordinary web servers. Reverse proxies help increase scalability, performance, resilience, and security, but they also carry a number of risks.
WebSphere Application Server (WAS) is a software product that performs the role of a web application server. More specifically, it is a software framework and middleware that hosts Java-based web applications. It is the flagship product within IBM's WebSphere software suite. It was initially created by Donald F. Ferguson, who later became CTO of Software for Dell. The first version was launched in 1998. This project was an offshoot from IBM HTTP Server team starting with the Domino Go web server.
A web accelerator is a proxy server that reduces website access time. They can be a self-contained hardware appliance or installable software.
In computing, a solution stack or software stack is a set of software subsystems or components needed to create a complete platform such that no additional software is needed to support applications. Applications are said to "run on" or "run on top of" the resulting platform.

F5, Inc. is an American technology company specializing in application security, multi-cloud management, online fraud prevention, application delivery networking (ADN), application availability & performance, network security, and access & authorization.

Zeus Technology, Ltd. was a software company founded in 1995 and based in Cambridge, England, known for its web server. In July 2011, Zeus Technology was acquired by Riverbed Technology. In March 2015, Riverbed Technology sold the SteelApp business unit to Brocade Communications Systems. In June 2017, Brocade Communications Systems sold the vADC business unit to Pulse Secure. In December 2020 Pulse Secure, including the vADC business unit, was acquired by Ivanti.

The IBM Storage product portfolio includes disk, flash, tape, NAS storage products, storage software and services. IBM's approach is to focus on data management.
An application delivery network (ADN) is a suite of technologies that, when deployed together, provide availability, security, visibility, and acceleration for Internet applications such as websites. ADN components provide supporting functionality that enables website content to be delivered to visitors and other users of that website, in a fast, secure, and reliable way.
Coyote Point Systems was a manufacturer of computer networking equipment for application traffic management, also known as server load balancing. In March 2013, the company was acquired by Fortinet.

The Rackspace Cloud is a set of cloud computing products and services billed on a utility computing basis from the US-based company Rackspace. Offerings include Cloud Storage, virtual private server, load balancers, databases, backup, and monitoring.
Resin is a web server and Java application server developed by Caucho Technology. There are currently only two versions available: Resin (GPL), which is free for production use, and Resin Pro, designed for enterprise and production environments with a licensing fee. Resin supports the Java EE standard and features a mod_php/PHP-like engine known as Quercus.
Eucalyptus is a paid and open-source computer software for building Amazon Web Services (AWS)-compatible private and hybrid cloud computing environments, originally developed by the company Eucalyptus Systems. Eucalyptus is an acronym for Elastic Utility Computing Architecture for Linking Your Programs To Useful Systems. Eucalyptus enables pooling compute, storage, and network resources that can be dynamically scaled up or down as application workloads change. Mårten Mickos was the CEO of Eucalyptus. In September 2014, Eucalyptus was acquired by Hewlett-Packard and then maintained by DXC Technology. After DXC stopped developing the product in late 2017, AppScale Systems forked the code and started supporting Eucalyptus customers.
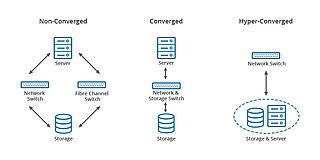
Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with virtualization, where converged storage increases the supply of resources along with new VM demands in parallel.
Kemp, Inc. is an American technology company that was founded in 2000 in Bethpage, New York and operates in the application delivery controller industry. The company builds load balancing products which balances user traffic between multiple application servers in a physical, virtual or cloud environment.

Dell Technologies PowerFlex, is a commercial software-defined storage product from Dell Technologies that creates a server-based storage area network (SAN) from local server storage using x86 servers. It converts this direct-attached storage into shared block storage that runs over an IP-based network.
A software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) is a wide area network that uses software-defined networking technology, such as communicating over the Internet using overlay tunnels which are encrypted when destined for internal organization locations.
NetScaler is a line of networking products owned by Cloud Software Group. The products consist of NetScaler, an application delivery controller (ADC), NetScaler AppFirewall, an application firewall, NetScaler Unified Gateway, NetScaler Application Delivery Management (ADM), and NetScaler SD-WAN, which provides software-defined wide-area networking management. NetScaler was initially developed in 1997 by Michel K Susai and acquired by Citrix Systems in 2005. Citrix consolidated all of its networking products under the NetScaler brand in 2016. On September 30, 2022, when Citrix was taken private as part of the merger with TIBCO Software, NetScaler was formed as a business unit under the Cloud Software Group.
References
- ↑ "AICACHE AND WOOT.COM". Foetron: IT Product & Security reseller. Retrieved 24 April 2023.
- ↑ "AWS Marketplace: AiScaler Dynamic Site Acceleration & Traffic Manager".
- ↑ "About Us".
- ↑ "Performance reports". aiscaler.com. Retrieved 24 April 2023.
- ↑ "aiScaler website". Archived from the original on 8 February 2014. Retrieved 12 January 2014.
- ↑ "Dell Hardware Application Delivery Controller".
- ↑ ""aiScaler Admin Guide", Jan. 14, 2011" (PDF). Retrieved 24 April 2023.