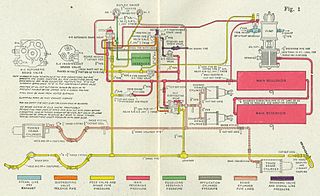
A railway air brake is a railway brake power braking system with compressed air as the operating medium. Modern trains rely upon a fail-safe air brake system that is based upon a design patented by George Westinghouse on April 13, 1869. The Westinghouse Air Brake Company was subsequently organized to manufacture and sell Westinghouse's invention. In various forms, it has been nearly universally adopted.

Pneumatics use of gas or pressurized air in mechanical systems.

The vacuum brake is a braking system employed on trains and introduced in the mid-1860s. A variant, the automatic vacuum brake system, became almost universal in British train equipment and in countries influenced by British practice. Vacuum brakes also enjoyed a brief period of adoption in the United States, primarily on narrow-gauge railroads. Their limitations caused them to be progressively superseded by compressed air systems starting in the United Kingdom from the 1970s onward. The vacuum brake system is now obsolete; it is not in large-scale usage anywhere in the world, other than in South Africa, largely supplanted by air brakes.
Compressed air is air kept under a pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure. Compressed air in vehicle tyres and shock absorbers is commonly used for improved traction and reduced vibration. Compressed air is an important medium for transfer of energy in industrial processes, and is used for power tools such as air hammers, drills, wrenches, and others, as well as to atomize paint, to operate air cylinders for automation, and can also be used to propel vehicles. Brakes applied by compressed air made large railway trains safer and more efficient to operate. Compressed air brakes are also found on large highway vehicles.

A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.

A diving air compressor is a breathing air compressor that can provide breathing air directly to a surface-supplied diver, or fill diving cylinders with high-pressure air pure enough to be used as a hyperbaric breathing gas. A low pressure diving air compressor usually has a delivery pressure of up to 30 bar, which is regulated to suit the depth of the dive. A high pressure diving compressor has a delivery pressure which is usually over 150 bar, and is commonly between 200 and 300 bar. The pressure is limited by an overpressure valve which may be adjustable.

A hose is a flexible hollow tube designed to carry fluids from one location to another. Hoses are also sometimes called pipes, or more generally tubing. The shape of a hose is usually cylindrical.
This is a glossary of firefighting equipment.
Air suspension is a type of vehicle suspension powered by an electric or engine-driven air pump or compressor. This compressor pumps the air into a flexible bellows, usually made from textile-reinforced rubber. Unlike hydropneumatic suspension, which offers many similar features, air suspension does not use pressurized liquid, but pressurized air. The air pressure inflates the bellows, and raises the chassis from the axle.

An air pump is a pump for pushing air. Examples include a bicycle pump, pumps that are used to aerate an aquarium or a pond via an airstone; a gas compressor used to power a pneumatic tool, air horn or pipe organ; a bellows used to encourage a fire; a vacuum cleaner and a vacuum pump. All air pumps contain a part that moves which drives the flow of air. When the air gets moved, an area of low pressure gets created which fills up with more air.

A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.
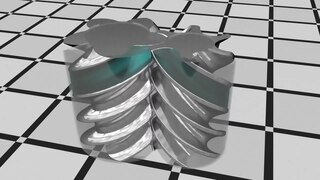
A rotary-screw compressor is a type of gas compressor, such as an air compressor, that uses a rotary-type positive-displacement mechanism. These compressors are common in industrial applications and replace more traditional piston compressors where larger volumes of compressed gas are needed, e.g. for large refrigeration cycles such as chillers, or for compressed air systems to operate air-driven tools such as jackhammers and impact wrenches. For smaller rotor sizes the inherent leakage in the rotors becomes much more significant, leading to this type of mechanism being less suitable for smaller compressors than piston compressors.

A expansion joint, or movement joint, is an assembly designed to hold parts together while safely absorbing temperature-induced expansion and contraction of building materials. They are commonly found between sections of buildings, bridges, sidewalks, railway tracks, piping systems, ships, and other structures.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of fluids such as water for potatory, irrigational, sanitary, and refrigerative purposes, gas, petroleum, liquid waste, or any other liquid or gaseous substances required in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes, connected by various methods, as dictated by the material of which these are made, the material being conveyed, and the particular environmental context in which they will be used, such as soldering, mortaring, caulking, plastic welding, welding, friction fittings, threaded fittings, and compression fittings.

An air brake or, more formally, a compressed-air-brake system, is a type of friction brake for vehicles in which compressed air pressing on a piston is used to both release the parking/emergency brakes in order to move the vehicle, and also to apply pressure to the brake pads or brake shoes to slow and stop the vehicle. Air brakes are used in large heavy vehicles, particularly those having multiple trailers which must be linked into the brake system, such as trucks, buses, trailers, and semi-trailers, in addition to their use in railroad trains. George Westinghouse first developed air brakes for use in railway service. He patented a safer air brake on March 5, 1872. Westinghouse made numerous alterations to improve his air pressured brake invention, which led to various forms of the automatic brake. In the early 20th century, after its advantages were proven in railway use, it was adopted by manufacturers of trucks and heavy road vehicles.

The Meillerwagen was a German World War II trailer used to transport a V-2 rocket from the 'transloading point' of the Technical Troop Area to the launching point, to erect the missile on the Brennstand, and to act as the service gantry for fuelling and launch preparation.

Pipe Insulation is thermal or acoustic insulation used on pipework.

Copper tubing is available in two basic types of tube—plumbing tube and air conditioning/refrigeration (ACR) tube, and in both drawn (hard) and annealed (soft) tempers. Because of its high level of corrosion resistance, it is used for water distribution systems, oil fuel transfer lines, non-flammable medical-gas systems, and as a refrigerant line in HVAC systems. Copper tubing is joined using flare connection, compression connection, pressed connection, or solder.

A gas cabinet is a metallic enclosure which is used to provide local exhaust ventilation system for virtually all of the gases used or generated in the semiconductor, solar, MEMS, NANO, solar PV, manufacturing and other advanced technologies.
Compressed air dryers are special types of filter systems that are specifically designed to remove the water that is inherent in compressed air. The compression of air raises its temperature and concentrates atmospheric contaminants, primarily water vapor, as resulting in air with elevated temperature and 100% relative humidity. As the compressed air cools down, water vapor condenses into the tank(s), pipes, hoses and tools connected downstream from the compressor which may be damaging. Therefore water vapor is removed from compressed air to prevent condensation from occurring and to prevent moisture from interfering in sensitive industrial processes.















