
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the progenitor, either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months.

SN 1987A was a type II supernova in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It occurred approximately 51.4 kiloparsecs from Earth and was the closest observed supernova since Kepler's Supernova in 1604. Light and neutrinos from the explosion reached Earth on February 23, 1987 and was designated "SN 1987A" as the first supernova discovered that year. Its brightness peaked in May of that year, with an apparent magnitude of about 3.

A magnetar is a type of neutron star with an extremely powerful magnetic field (~109 to 1011 T, ~1013 to 1015 G). The magnetic-field decay powers the emission of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, particularly X-rays and gamma rays.

Messier 82 (also known as NGC 3034, Cigar Galaxy or M82) is a starburst galaxy approximately 12 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. It is the second-largest member of the M81 Group, with the D25 isophotal diameter of 12.52 kiloparsecs (40,800 light-years). It is about five times more luminous than the Milky Way and its central region is about one hundred times more luminous. The starburst activity is thought to have been triggered by interaction with neighboring galaxy M81. As one of the closest starburst galaxies to Earth, M82 is the prototypical example of this galaxy type. SN 2014J, a type Ia supernova, was discovered in the galaxy on 21 January 2014. In 2014, in studying M82, scientists discovered the brightest pulsar yet known, designated M82 X-2.

Messier 66 or M66, also known as NGC 3627, is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the southern, equatorial half of Leo. It was discovered by French astronomer Charles Messier on 1 March 1780, who described it as "very long and very faint". This galaxy is a member of a small group of galaxies that includes M65 and NGC 3628, known as the Leo Triplet or the M66 Group. M65 and M66 are a common object for amateur astronomic observation, being separated by only 20′.

Messier 74 is a large spiral galaxy in the equatorial constellation Pisces. It is about 32 million light-years away from Earth. The galaxy contains two clearly defined spiral arms and is therefore used as an archetypal example of a grand design spiral galaxy. The galaxy's low surface brightness makes it the most difficult Messier object for amateur astronomers to observe. Its relatively large angular size and the galaxy's face-on orientation make it an ideal object for professional astronomers who want to study spiral arm structure and spiral density waves. It is estimated that M74 hosts about 100 billion stars.

The known history of supernova observation goes back to 1006 AD. All earlier proposals for supernova observations are speculations with many alternatives.

Type Ib and Type Ic supernovae are categories of supernovae that are caused by the stellar core collapse of massive stars. These stars have shed or been stripped of their outer envelope of hydrogen, and, when compared to the spectrum of Type Ia supernovae, they lack the absorption line of silicon. Compared to Type Ib, Type Ic supernovae are hypothesized to have lost more of their initial envelope, including most of their helium. The two types are usually referred to as stripped core-collapse supernovae.

SN 2006gy was an extremely energetic supernova, also referred to as a hypernova, that was discovered on September 18, 2006. It was first observed by Robert Quimby and P. Mondol, and then studied by several teams of astronomers using facilities that included the Chandra, Lick, and Keck Observatories. In May 2007, NASA and several of the astronomers announced the first detailed analyses of the supernova, describing it as the "brightest stellar explosion ever recorded". In October 2007, Quimby announced that SN 2005ap had broken SN 2006gy's record as the brightest-ever recorded supernova, and several subsequent discoveries are brighter still. Time magazine listed the discovery of SN 2006gy as third in its Top 10 Scientific Discoveries for 2007.

NGC 1260 is a spiral or lenticular galaxy located 250 million light years away from earth in the constellation Perseus. It was discovered by astronomer Guillaume Bigourdan on 19 October 1884. NGC 1260 is a member of the Perseus Cluster and forms a tight pair with the galaxy PGC 12230. This galaxy is dominated by a population of many old stars.

Gamma-ray burst progenitors are the types of celestial objects that can emit gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). GRBs show an extraordinary degree of diversity. They can last anywhere from a fraction of a second to many minutes. Bursts could have a single profile or oscillate wildly up and down in intensity, and their spectra are highly variable unlike other objects in space. The near complete lack of observational constraint led to a profusion of theories, including evaporating black holes, magnetic flares on white dwarfs, accretion of matter onto neutron stars, antimatter accretion, supernovae, hypernovae, and rapid extraction of rotational energy from supermassive black holes, among others.
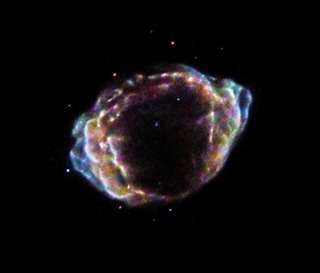
G1.9+0.3 is a supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation of Sagittarius. It is the youngest-known SNR in the Milky Way, resulting from an explosion the light from which would have reached Earth some time between 1890 and 1908. The explosion was not seen from Earth as it was obscured by the dense gas and dust of the Galactic Center, where it occurred. The remnant's young age was established by combining data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and the VLA radio observatory. It was a type Ia supernova. The remnant has a radius of over 1.3 light-years.

NGC 7424 is a barred spiral galaxy located 37.5 million light-years away in the southern constellation Grus. Its size makes it similar to our own galaxy, the Milky Way. It is called a "grand design" galaxy because of its well defined spiral arms. Two supernovae and two ultraluminous X-ray sources have been discovered in NGC 7424.
GRB 980425 was a gamma-ray burst (GRB) that was detected on 25 April 1998 at 21:49 UTC. GRB 980425 occurred at approximately the same time as SN 1998bw, providing the first evidence that gamma-ray bursts and supernovae are related, and at a distance of 40 megaparsecs (130,000,000 ly), remains the closest GRB yet observed.

Swift J164449.3+573451, initially referred to as GRB 110328A, and sometimes abbreviated to Sw J1644+57, was a tidal disruption event (TDE), the destruction of a star by a supermassive black hole. It was first detected by the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission on March 28, 2011. The event occurred in the center of a small galaxy in the Draco constellation, about 3.8 billion light-years away. It was the first confirmed jetted tidal disruption event and is the most luminous and energetic TDE recorded.
SN 2013ej is a Type II-P supernova in the nearby spiral galaxy Messier 74. It was discovered by the Lick Observatory Supernova Search on July 25, 2013, with the 0.76 m Katzman Automatic Imaging Telescope, with pre-discovery images having been taken the day before.
SN 2009ip was a supernova discovered in 2009 in the spiral galaxy NGC 7259 in the constellation of Piscis Austrinus. Since the brightness waned after days post-discovery, it was redesignated as Luminous blue variable (LBV) Supernova impostor.

In astronomy, a fast blue optical transient (FBOT), or more specifically, luminous fast blue optical transient (LFBOT), is an explosive transient event similar to supernovae and gamma-ray bursts with high optical luminosity, rapid evolution, and predominantly blue emission. The origins of such explosions are currently unclear, with events occurring at not more than 0.1% of the typical core-collapse supernova rate. This class of transients initially emerged from large sky surveys at cosmological distances, yet in recent years a small number have been discovered in the local Universe, most notably AT 2018cow.

SN 2004et is a bright type IIP supernova that occurred in the spiral galaxy NGC 6946, about 22 million light years away from Earth. The star that made the supernova was falsely identified to be a yellow supergiant but was then identified to be a type red supergiant of 13.8 solar masses. It was discovered alongside SN 2017eaw. SN 2004et showed some rebrightening about 1,000 days after the initial supernova probably due to ejecta of circumstellar material or thermal echo. SN 2004et was one of the most luminous type IIP supernovae ever recorded and characterized.
















